2023-06-26 Hits(522)
Mouse monoclonal antibody is a mouse-derived monoclonal antibody which is produced by hybridoma cells fused with activated B lymphocytes and myeloma cells, and can secrete antibodies and proliferate indefinitely.
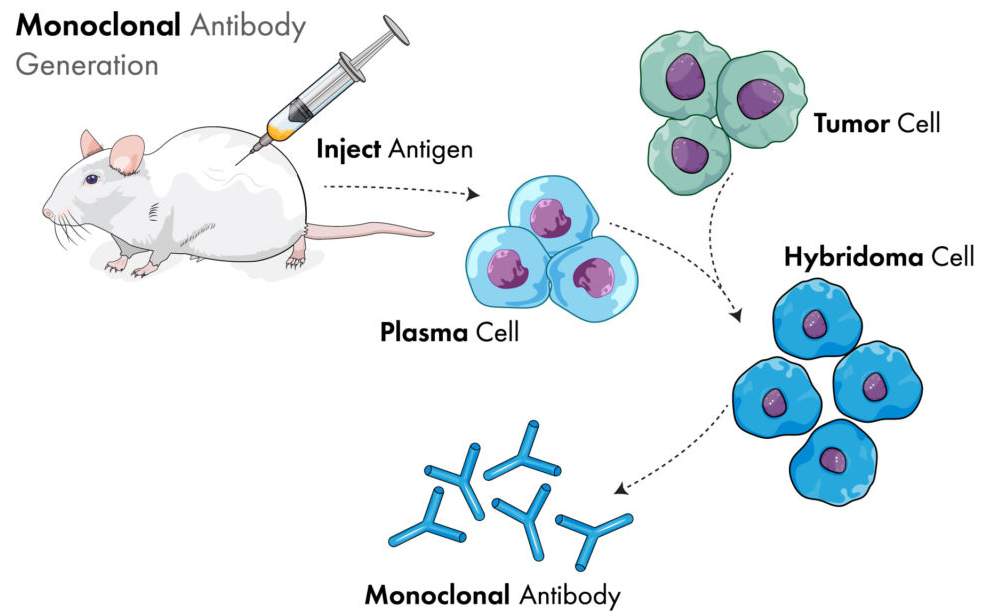
KMD Bioscience can provide customers with two ways to prepare mouse monoclonal antibodies, one is to prepare recombinant monoclonal antibodies by phage antibody display technology; The other is to prepare hybridoma cell lines by cell fusion technology.
Traditional monoclonal antibody technology refers to the fusion of myeloma cells and antibody-secreting B lymphocytes (except the generation technology of fully human monoclonal antibodies) to form hybridoma cells and secrete monoclonal antibodies. Because it only acts on an antigenic determinant on antigen complex molecules, it has the characteristics of strong specificity and high titer.
Mouse is one of the common model animal in the fields of biology and medicine, and mouse monoclonal antibody is also a commonly used monoclonal antibody, which has the advantages of strong specificity and rapid, large-scale and continuous production.
Based on the construction of mature antibody platform system, KMD Bioscience currently produce many types of mouse monoclonal antibody products. Among them, tag antibody such as HRP labeled mouse anti-human IgG (FC) (CAT: SA2265), animal epidemic antibody such as mouse anti-pseudorabies monoclonal antibody (Cat:ANAB1024) and small molecular antibody such as penicillin mouse monoclonal antibody (Cat:PA042) are used for WB, Elisa detection and other projects.
The generation service of mouse monoclonal antibody provided by KMD Bioscience mainly includes: antigen generation, mouse immunity, cell fusion, cell screening, cell subcloning, ascites generation and ascites purification.
Customers provide antigens, acceptable proteins, peptides and various small molecular antigens, and mix them with Freund's adjuvant for immunization.
Table 1: Time schedule of mouse monoclonal antibody generation planning
|
Procedure |
Time |
Description |
Date |
|
Negative serum collection |
Day1 |
Pre-immunization serum collection 20ul/per |
*** |
|
First immunization |
Day1 |
0.1mg immunogen(CFA), subcutaneous multi-point injection(5 points) |
*** |
|
Second immunization |
Day14 |
0.05mg immunogen(CFA), subcutaneous multi-point injection(4 points) |
*** |
|
Third immunization |
Day28 |
0.05mg immunogen(CFA), subcutaneous multi-point injection(4 points) |
*** |
|
Fourth immunization |
Day42 |
0.05mg immunogen(CFA), subcutaneous multi-point injection(4 points) |
*** |
|
ELISA detection |
Day49 |
According to the results of ELISA test, decide whether to continue immunization |
*** |
|
Shock immunity |
Day62 |
0.05mg immunogen (saline), abdominal cavity |
*** |
|
ELISA detection |
Day69 |
According to the results of ELISA test, decide whether to continue immunization |
*** |
|
Fusion and subclone screening |
Day76 |
The titer was qualified, myeloma cells and spleen cells were fused, and clone screening was carried out |
*** |
|
Cell colonization and expansion |
Day194 |
Clonal screening |
*** |
|
Generation and purification of ascites |
Day208 |
Protein A/G affinity purified antibody |
*** |
Five Balb/c mice were prepared, injected with immunogen every 14 days, and their blood samples were collected for titer detection.
The selected serum titer meets the requirements (protein/virus > 105; Polypeptide/small molecule > 104) mouse spleen cells were fused with mouse myeloma cells, the fused cells were cloned in a 96-well plate, HAT screened hybridoma cells, 1-10 positive clones were selected through immunogen detection, subcloned and expanded to a 96-well plate, positive subclones were screened by ELISA, and expanded culture was carried out. After fusion, one-time cloning in a limited dilution method and supernatant detection, a number of cell strains meeting the requirements of the project were obtained.
Ascites were prepared from hybridoma cells selected by customers and purified by Protein A/G method.
1) Select a suitable chromatographic column, clean it, and fix it vertically on the iron frame.
2) Take an appropriate amount of ethanol suspension of protein G-Sepharose, let it stand for gel precipitation, and then suck off the upper ethanol, and then suspend it with binding buffer for several times to completely wash off the ethanol.
3) Mix the binding buffer and protein A/G into 50-70% slurry, and pour the slurry into the column.
4) Connect a peristaltic pump, load the column at a speed of 50cm/h (equivalent to 0.7ml/min for a column with a diameter of 1cm), and after the column is completely settled, continue to clean the column with 5-10 times the volume of binding buffer.
1) 12,000×g ascites samples were centrifuged for 10min, and then the supernatant was filtered with 0.45μm pore size.
2) Loading: Add the filtered sample solution into the affinity column at a flow rate of 0.4ml/min.
3) After the sample enters the medium, reduce the flow rate to 0.7ml/min, and continue to wash with 10 times of binding buffer until the A280 value returns to the background level (< 0.02).
1) Keep the rate constant, change the elution buffer to elute the antibody bound to the column, and collect the eluent in 2ml portions (2ml/ tube). 0.1ml neutralization buffer should be added to the collection tube to neutralize the PH value of the antibody solution obtained by elution in time.
2) Detecting A280 of each tube, stopping elution when A280 is less than 0.05, and collecting peak components with A280 greater than or equal to 0.2.
3) If it is necessary to remove salt or change the buffer, dialysis can be performed in phosphate buffer (PBS) or in other specific solutions.
Electrophoresis: Add 5Xloading buffer to the purified protein according to the ratio of 4:1, then cook the sample at 100℃ for 10min, and take 10ul of the sample for SDS-PAGE electrophoresis: 120v, after 90 minutes, stain with Coomassie Brilliant Blue for 30min, and then decolorize it.
KMD Bioscience delivers 3-5 positive clones, mouse monoclonal purified antibodies with high specificity and high affinity, experimental reports and identification reports: including SDS-PAGE, ELISA detection results, and provide antibody identification results such as Western Blot, IHC, IP, IF, etc. according to customer requirements.
Mouse monoclonal antibody is one of the most commonly used monoclonal antibodies, which is widely used in the fields of tumor diagnosis and treatment, cell surface antigen detection, and body trace component determination. Therefore, the generation of antibodies with high specificity and mass production is the main demand of scientific research users. Kamed Bio has accumulated sufficient experience and expertise in antibody generation, and can provide you with complete upstream and downstream services for customization of murine monoclonal antibodies.