Service Line:+86-022-82164980
Address:FL-4, Building A5, International Enterprise Community, Tianjin, China
Email:[email protected]
KMD Bioscience offers a wide range of aptamer synthesis services, based on the SELEX screening technique, to choose from for our clients, including nucleic acid aptamer synthesis, protein aptamer synthesis, cell-SELEX aptamer synthesis, etc.
Nucleic Acid Aptamer
Nucleic Acid Aptamer is a class of single-stranded DNA or RNA molecules that can recognize specific molecules. It encompasses DNA aptamer and RNA aptamer and is produced by SELEX screening.
Because of its unique advantages, aptamers have shown wide application prospects in many fields such as biosensors, disease identification, pharmaceutical research and development, and cell imaging. For example, in the field of biosensors, nucleic acid aptamers can be used to build detection platforms with high sensitivity and specificity; In terms of disease identification, aptamers can be used to detect biological molecules such as tumor markers and pathogens. In pharmaceutical development, aptamers can be used as carriers of targeted pharmaceuticals or therapeutic agents themselves.
DNA Aptamer
DNA aptamers are aptamers composed of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). They usually have a double helix structure and are composed of four bases (adenine A, thymine T, guanine G, cytosine C) connected by phosphodiester bonds. They are single-stranded oligonucleotide sequences, typically with 56-120 bases, that bind the target sequence efficiently by recognizing specific spatial structures.
DNA aptamers are widely used in biological analysis, biomedicine, and other fields because of their stability and easy chemical modification.
RNA Aptamers
RNA aptamers are aptamers composed of ribonucleic acid (RNA). RNA aptamers occur naturally within cells and are involved in a variety of biological processes, such as protein synthesis and gene expression regulation. They have more complex structures, such as hairpin rings, pseudoknots, etc., which contribute to their high affinity binding to target molecules.
Synthesis of Nucleic Acid Aptamer
The synthesis of nucleic acid aptamers provided by KMD Bioscience is mainly achieved through in vitro aptamer screening techniques, among which SELEX (Systematic Evolution of Ligands by Exponential Enrichment) is the most commonly used. Through multiple rounds of screening and amplification, SELEX technology can screen out DNA aptamers or RNA aptamers with high specificity binding to target molecules from a large number of random sequences of DNA or RNA oligonucleotide libraries.
Protein Aptamers
Protein aptamers target proteins, also called protein-targeted aptamers, which are short oligonucleotide sequences or short polypeptides obtained by in vitro screening that bind to corresponding proteins. These aptamers, through their specific sequences and structures, form stable complexes with target proteins and thus perform various functions in living organisms.
Cell-SELEX Aptamer
Cell-SELEX Technology
The Cell-SELEX technology is a SELEX technique for screening directly at the cellular level, which is specifically designed to find aptamers that can specifically recognize molecules on the Cell surface. Cell-SELEX technology is based on the fundamental principle of SELEX technology. Through multiple rounds of affinity and elution process, aptamers with high affinity binding to specific molecules on the Cell surface are gradually screened.
Process of Cell-SELEX Aptamer Screening
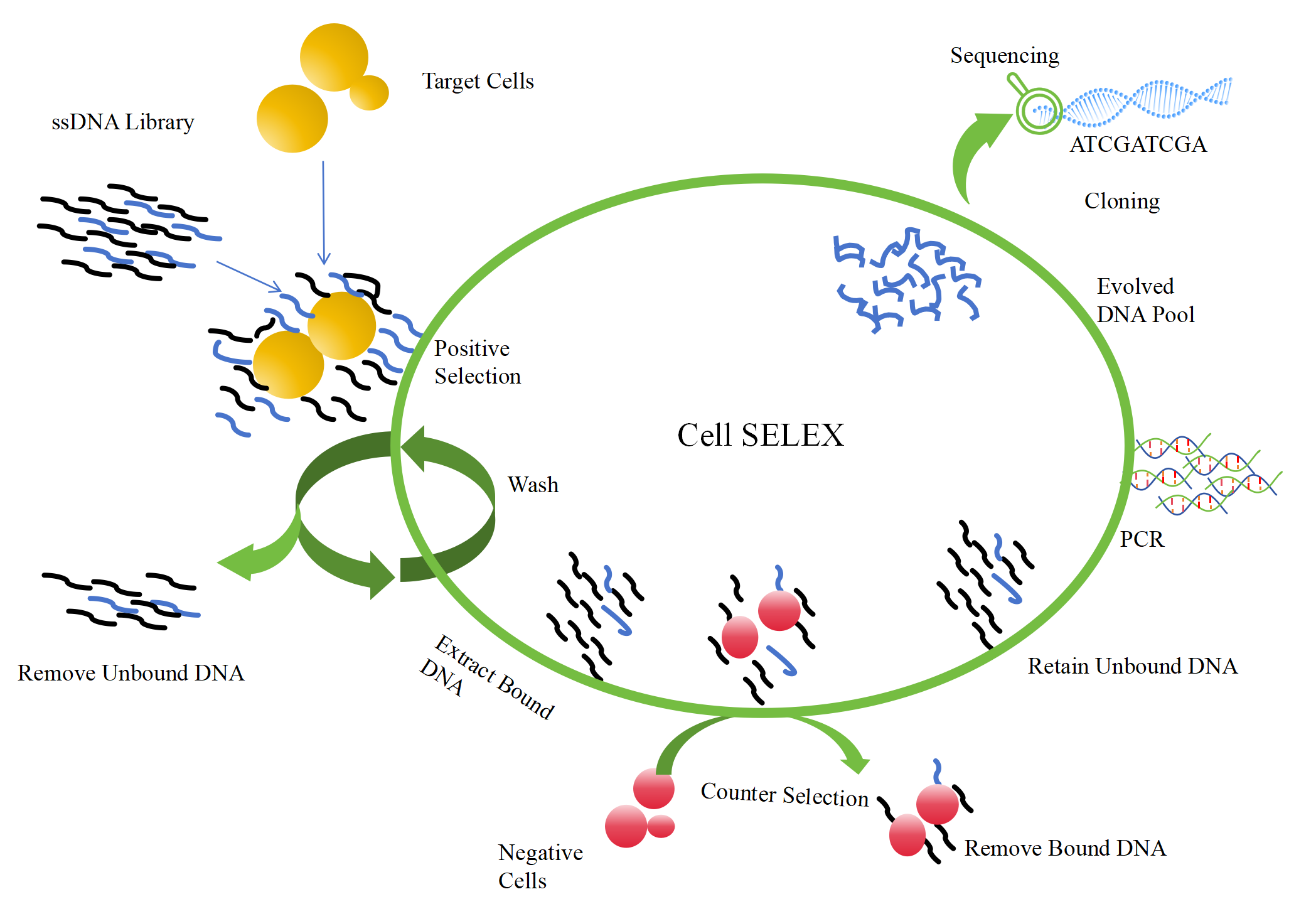
Fig.1 Process of Cell-SELEX Aptamer Screening
Initial Library Construction
Design and synthesize DNA or RNA libraries containing large numbers of random sequences. Sequences in these libraries are diverse and can cover a wide range of potential binding sites.
Target Cell Preparation
Select and culture target cells that express specific molecules on their surfaces as screening targets.
Screening Process
Binding: Nucleic acid molecules in the library are mixed with target cells, allowing them to bind to target molecules on the cell surface.
Separation: Separation of unbound nucleic acid molecules from the target cell-nucleic acid complex by physical or chemical methods (e.g., differential centrifugation, washing, etc.).
Amplification: PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification of nucleic acid molecules bound to target cells to obtain a sufficient number of specific binding sequences.
Iteration: Repeat the above binding, separation, and amplification steps several times (usually several to dozens of rounds) to gradually enrich the nucleic acid sequence with the strongest binding force to the target molecule.
Sequencing
The final enriched nucleic acid sequence was cloned and sequenced to determine its sequence information.
Aptamer identification and optimization
The binding affinity between the aptamer and the target molecule was determined by biological experiments, and the aptamer with high affinity and specificity was selected for follow-up study. The aptamer sequence was optimized to improve its binding performance and stability.
Application of Cell-SELEX
Aptamers targeting specific molecules on the surface of tumor cells are screened by Cell-SELEX technology, which can be used for early estimate and therapeutic monitoring of tumors. For example, studies have shown that aptamers screened by Cell-SELEX technology can specifically bind Frizzled-8 protein on tumor Cell surface and can be used for fluorescence imaging differential diagnosis of tumor tissues.
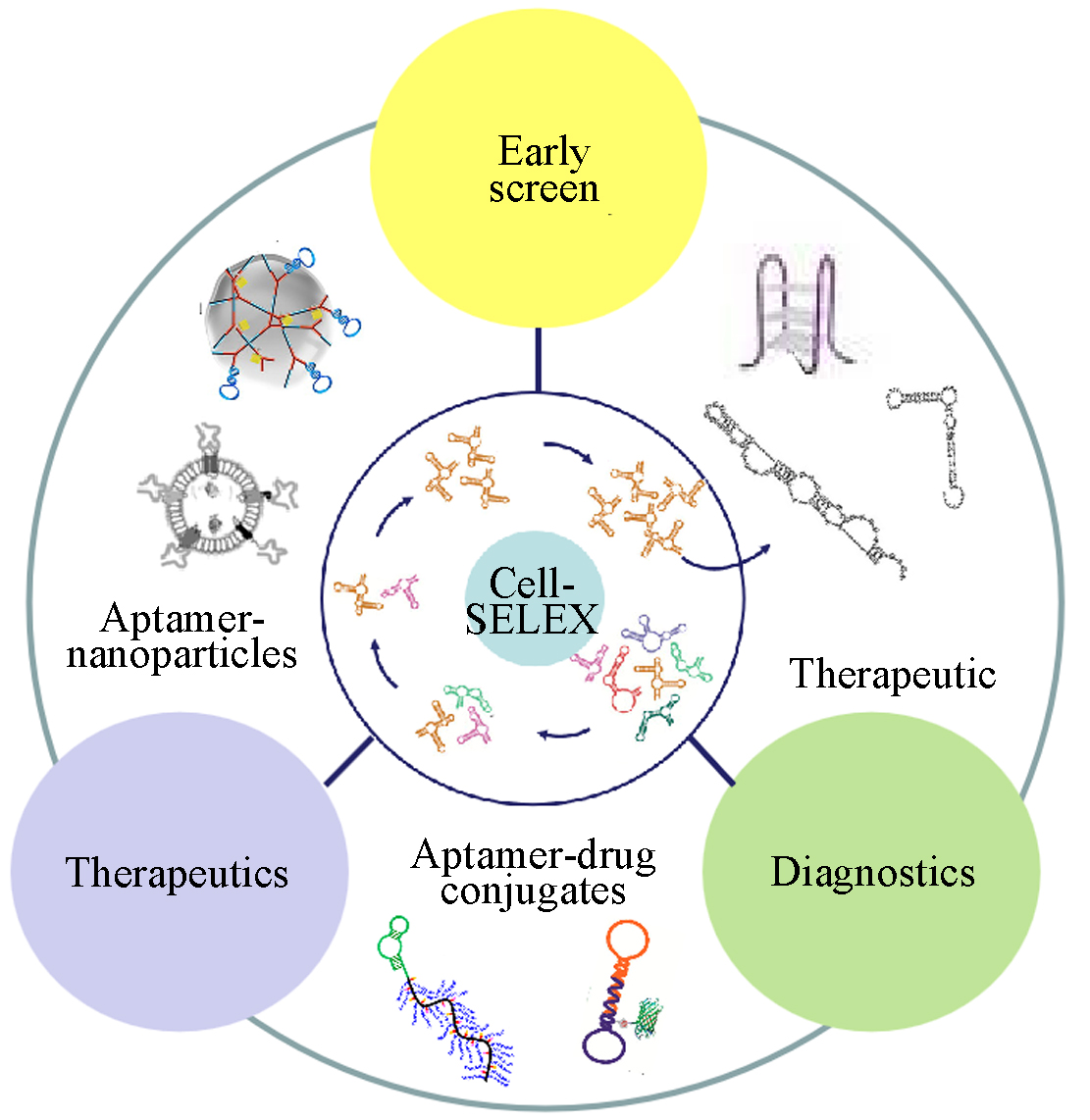
Fig.2 Application of Cell-SELEX In Cancer. (Reference Source: Progress on Aptamer for Cancer Theranostics[J].)
FAQ-Aptamer Library Construction
1. What is an aptamer?
A: Due to the low affinity of MAb therapy for biological macromolecules lipids and carbohydrates, the application of MAb has certain clinical limitations. To improve the affinity with the above biomacromolecules and lipids, carbohydrates, and other substances, the artificial ligand-aptamers are gradually produced and expanded. The aptamer is a kind of single-chain nucleic acid chain, that can be combined with a variety of different targets, with small size, low cost, uniform synthesis, custom modification, nucleic acid template properties, and other unique advantages, can expand the scope of the potential target, such as small molecule nucleic acid aptamer and ion aptamer can be used as a supplementary antibody, nucleic acid aptamer technology is now is developing rapidly. The nucleic acid aptamer is a kind of specific molecular recognition ability of single-stranded DNA or RNA molecules, by SELEX through in vitro screening, consists of 20~110 nucleotides, sequence contains random sequence and fixed sequence, by folding can form a tertiary structure, high affinity, can specifically binding target molecules of small molecule group. KMD Bioscience has completed several aptamer projects, with rich experience and mature technology. In addition, KMD Bioscience also provides customized ligand library design, antibody expression and purification, affinity determination, antibody sequencing, etc., to meet the needs of customers.
2. Steps for the aptamer library construction?
A: The basis for screening services for aptamers is the SELEX technology, The SELEX technology follows from researchers using the technology to synthesize a single-stranded oligonucleotide library in vitro, Our target molecules or target sites were then incubated in a library containing different nucleic acid sequences, Finally, the oligonucleotide without binding was washed out by the washing solution, Enabling unbound nucleotides and library separation, We then eluted the bound library before using a high concentration of the salt solution, The eluted oligonucleotides are the oligonucleotides we need that can bind to the target molecule, We then used PCR to deamplify oligonucleotides that can bind to the target molecule, Start with the next round of screening. Repeat the above steps for repeated rounds of screening, and each round involves the binding of the target molecule, isolation of the unbound sequence, and amplification of the bound sequence. As we repeated multiple screens, the higher the round of screening, the higher the specificity and affinity of our library, and eventually we can screen oligonucleotide sequences that are highly bound and highly affinity to our target molecules. However, we need to note that when screening RNA aptamers by RNA aptamer library synthesis service, we need to reverse transcription of RNA into DNA, and then conduct subsequent SELEX aptamer library screening.
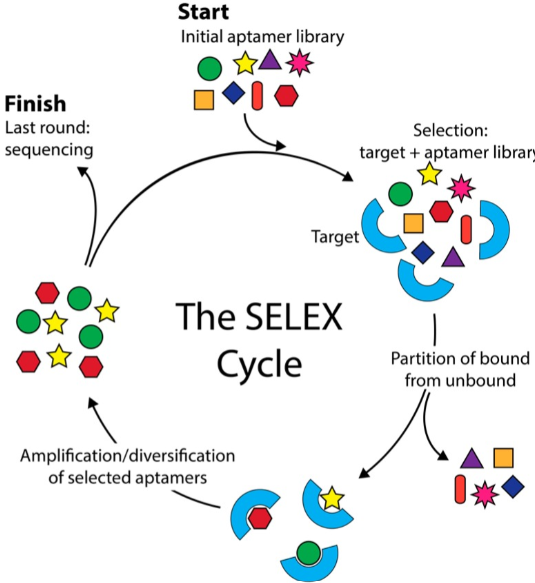
Fig 3: Steps of SELEX technology.(Reference documentation: Kinghorn AB, Fraser LA, Lang S, Shiu SCC, Tanner JA. Aptamer Bioinformatics. Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Nov 24;18(12):2516.)
3. How to solve the problem of insufficient diversity and unstable quality in the nucleic acid aptamer library service?
A: In the nucleic acid aptamer library service, we may find that the nucleic acid aptamer library sequence is not enough, and diversity cannot meet our requirements, this situation may cause our build library no way to be all possible and molecular binding sites to be identified, may appear missing phenomenon, lead to our screening to high-affinity nucleic acid aptamer probability also reduced together. At the same time, sequence errors, deletions, or contamination may occur during the construction of the aptamer library, which will also reduce the quality of our library and reduce the possibility of getting high-affinity nucleic acid aptamers. Given the above series of problems, in the library design, the library design parameters are optimized, such as the sequence length of nucleic acid, nucleic acid GC content, secondary structure, and other factors, to improve the diversity of our library construction. KMD Bioscience also uses advanced aptamer synthesis technology to ensure the randomness and diversity of our synthetic sequences and improve the efficiency of our synthetic sequences. At the same time, KMD Bioscience also strengthened the quality control in each step of building the library and improved the quality of primers, templates, and enzymes by using high-quality reagents and strictly following the standard steps. At the same time, our company also tests the sequencing quality of the aptamer libraries to ensure that the libraries delivered to customers are of high quality and stable.
4. How to solve the nucleic acid aptamer library service if faced with low library construction efficiency and poor library and target binding ability?
A: In the aptamer library service, we found that the process of building the aptamer library takes a long time, the instruments and materials are expensive, and the whole process is not efficient. At the same time, we may find that the constructed aptamer library does not bind well to the target molecule, and then the experimental screening effect is not good. The above situation may be our stumbling block in the process of building nucleic acid aptamer library, KMD Bioscience can through the process of library construction optimization and the reasonable arrangement of experimental time, then use advanced efficient aptamer synthesis technology and amplification technology, improve the efficiency of our library construction, save our experimental time and cost. At the same time, at the beginning of the aptamer library design, KMD Bioscience fully considered the characteristics of the target molecule and the need to combine with the aptamer, and the researchers designed the nucleic acid sequences with high affinity and specificity according to the above requirements. At the same time, in the process of library screening, KMD Bioscience uses various screening strategies and optimization of various screening conditions to help us improve the binding ability of the library and target.
5. How to solve the problem of low aptamer affinity encountered in the nucleic acid aptamer library service?
A: When screening nucleic acid aptamers, if the number of repeats is not enough, the specificity and affinity of our selected aptamers may be low. Therefore, with the continuous development of modern technology, the traditional SELEX aptamer library screening technology has been continuously improved and a series of related technologies have been derived. IP-SELEX is SELEX, which can be combined with immunoprecipitation; Cell-SELEX is operated at the cellular level and is generally used to screen aptamers that can identify cell surface molecules; Apta-Seq and high-throughput sequencing technology are combined to screen large-scale libraries, which greatly improves the efficiency of library screening. In addition, there are AFM-SELEX for atomic force microscope and CE-SELEX for capillary electrophoresis, which greatly improve the success rate of SELEX technology. The screening of nucleic acid aptamers enables the discovery of specific nucleic acid sequences of aptamers that bind to their target molecules with high affinity. The screening of nucleic aptamers provides new research directions for the treatment of diseases and the development of new drugs. Over the years, KMD Bioscience has been committed to providing customers with high affinity, high specificity aptamer screening technology services, for customers' subsequent aptamer function verification, drug molecule screening, and other downstream research and development support.
Reference
[1]. DONG Qian, LI Zhaoqian, PENG Tianhuan, CHEN Zhuo, TAN Weihong. Progress on Aptamer for Cancer Theranostics[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(12): 2648.
[2]. Shraim AS, Abdel Majeed BA, Al-Binni MA, Hunaiti A. Therapeutic Potential of Aptamer-Protein Interactions. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2022 Nov 4;5(12):1211-1227.
How to Order?
If you have any questions regarding our services or products, please feel free to contact us by E-mail: [email protected] or Tel: +86-400-621-6806