2023-08-23 Hits(525)
Vector construction is one of the common means for molecular biology research, using this technology to insert foreign DNA fragments into artificially constructed plasmids, to transport the ligated DNA molecules to recipient cells for replication and amplification for subsequent scientific experiments.
At present, commonly used vector construction techniques include overlapping extension PCR, traditional digestion ligation and homologous recombination. The traditional digestion ligation method is to digest the plasmid and DNA containing the fragment of interest with the same restriction enzyme to obtain linear DNA with the same sticky end or flat end, purify the digestion product, and then use the DNA ligase fragment to connect with the carrier to obtain a recombinant plasmid. The recombinant plasmid is transferred into competent cells for subsequent screening and expansion. Homologous recombinant cloning technology reorganizes two linearized vectors and inserts with the same end sequence into recombinant plasmids through homologous recombinase, which are also transferred to competent cells for screening and amplification.
Prokaryotic system expression vector: The E. coli expression system requires that the vector contains an SD sequence, a strong promoter and its regulatory sequences on both sides, a correct reading framework between the promoter and the foreign gene, and a transcriptional termination region downstream of the foreign gene. The most commonly used vectors are the pET series and the pGEX series. KMD Bioscience achieves efficient expression of recombinant proteins through codon optimization, modification of expression vector elements, and diversity selection of fusion tags and hosts.
Mammalian cell expression vector: including prokaryotic sequence, promoter, enhancer, selection marker gene, terminator and polynucleotide signal and other control elements, vector selection is mainly pcDNA3.1 series and pcDNA4 series. KMD Bioscience designs high-expression vectors that provide customers with high-expression levels of recombinant protein mammalian cell expression and preparation services.
Yeast plasmid vectors: supported by selection markers (such as nutritional deficiency screening marker HIS3, antibiotic screening marker chloramphenicol, etc.) and regulatory sequences (including promoter, ARS, 2μM plasmid, yeast centromeric segment, etc.), the vector selection is mainly pPIC9 series and pPIC3.5 series. KMD Bioscience can provide customers with a variety of protein yeast fermentation specifications and protein purification platforms at the same time, and obtain high-quality recombinant proteins in a short time.
Insect expression vector: The baculovirus expression vector uses Sf9 and Sf21 cell lines and silkworms as expression hosts, clons foreign genes on transfer vectors, co-transfects cells with viral DNA, and obtains recombinant viruses through homologous recombination and screening. The carrier selection is mainly pFastBac1 series and pFastBacHT series. KMD Bioscience optimizes codons for you free of charge based on the codon preference of Sf9, Sf21, Hi-5 and S2 insect cells to effectively increase the expression of recombinant proteins.
Select appropriate vectors according to the purpose of constructing recombinant plasmids, and analyze the target fragments and the digestion sites contained in the vectors.
It can be specifically bound to the fragment of interest and amplified, with a primer length of about 18-25 bp and a GC content between 40% and 60%, and two suitable digestion sites need to be added.
Using the DNA/cDNA of the research subjects as a template, the target fragments were amplified by PCR, and the target gene bands were detected and recovered by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis.
Using the appropriate restriction enzyme, perform a double digestion experiment on the fragment of interest and the plasmid vector. The sample was performed on ice throughout the dosing, the sample was blown well with a pipette, the bubbles were removed by flicking the bottom of the tube, and then the sample was thrown to the bottom of the tube with a palm centrifuge, and finally, the enzyme was digested in a water bath at 37°C for 1.5 h. After the reaction, the product is subjected to 1% agarose electrophoresis, and if the band position is correct, the product is recovered.
T4 DNA Ligase was used to enzymatically link the recovered product after digestion. The enzyme is highly efficient for viscous end ligation at 16°C, and the enzyme can be fully ligated overnight.
Bacterial solution PCR: The monoclonal colonies were selected into 1.5 ml EP tubes containing the corresponding resistance and cultured for 4~5 h, and each component was added according to the PCR system used to amplify the target fragment, in which the template DNA was the bacterial solution (volume 1 μl), and the negative control group with water as the template and the amplified target fragment were set as the positive control group. After the reaction, all samples were electrophoresis in a 1% agarose gel, and whether the enzyme connection was successful was preliminarily judged according to the brightness and position of the band.
Digestion verification: The double digestion group of the target fragment was used as the positive control and the unloaded double digestion group was used as the negative control, and the 1% agarose gel electrophoresis was performed on the reaction. If the sample group has two bands that are in the same position as the positive control group and the negative control group, it is further evidence that the recombinant plasmid is successfully ligated.
Sequencing verification: Send it to the sequencing company for verification of the comparison results.
(1) Vector linearization: Use restriction endonuclease digestion or reverse PCR amplification to select appropriate cloning sites to linearize the vector.
(2) Acquisition of inserts: Introduce the homologous sequence of the two ends of the linearized vector at the 5' end of the forward and reverse amplification primer of the insert, so that the 5' and 3' ends of the amplified insert have the same homologous sequence corresponding to the two ends of the linearized cloning vector (15-20 bp, excluding the digestion site).
(3) Recombinant reaction: Recover the agarose gel electrophoresis product, and calculate the amount of linearized vector required for recombination reaction and the amount of DNA required for insertion according to the measured concentration.
(4) Transform the competent state.
(5) Identification of recombinant reaction products: bacterial PCR, sequencing.
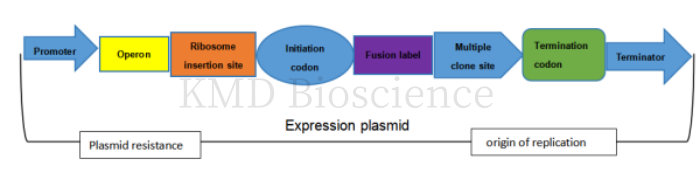
Figure 1 Diagram of the expression plasmid
The homologous recombination method has low dependence on the digestion site, the construction time is short, and the simple construction process can save a lot of effort, but the false positive rate is slightly higher.
The traditional enzyme digestion method has a long application time and mature technology, but it depends on the selection of digestion sites, the digestion efficiency and ligation efficiency are low, and the construction process is cumbersome.
(1) Construct cloning vectors for amplifying target genes; (2) Construct expression vectors for expressing target genes; (3) Construct gene-editing vectors for editing genes; (4) Construct viral packaging vectors for transfection of cells.
KMD can provide a variety of vector construction services, including conventional protein expression vector construction (E. coli, mammals, yeast, insects), vector element replacement and modification, etc., to provide customers with accurate consulting services, detection technology and scientific research services with a professional and dedicated attitude.