2024-08-08 Hits(273)
Phage Display Technology
Phage display technology is a technology that utilizes phage(a virus that infects bacteria)to find specific proteins or peptides of functionally binding molecules. Phage antibody library construction technology including Fab antibody library construction, scFv antibody library construction, nanobody library construction, etc., The technology has been widely used in protein engineering, drug screening, immunological studies, etc. Hage display technology can be divided into M13, T7, T4, λ, and other systems according to the type of phage; Phage display technology can be divided into phage carrier and phage granule carrier according to the difference of carrier; Phage display technology can be divided into random peptide library, cDNA library, antibody library, protein library and so on. Depending on the library. huge display technology is now well used in the application of analog epitope screening, the operation process of this technology is simple, the reagents and equipment used are low in price, and the requirements for laboratory conditions are low. However, this technique also has some limitations. The sequence expressed by phage cannot be too long, In addition, the constructed phage display library limits the molecular genetic diversity in the library so effective in vitro mutation and recombination can no longer be performed. Some molecules that are toxic to cells, such as biotoxins, are generally not expressed by phage display systems that depend on the expression of intracellular genes
Page display technology has been applied in the research and development of biomedicine at present Among them, great achievements have been made in the research and development of new vaccines (synthetic vaccines that are cheap and efficient), the development of antibody drugs (screening enzyme inhibitors), the transduction of cell signals (screening of simulated epitopes), and the research of antigen epitopes (preparation of monoclonal antibodies).
Principle
The phage transforms ssDNA into dsDNA in the presence of host enzymes after the phage infects the host, called replicative DNA (RF DNA), which is used for subsequent DNA replication (Fig. 1 A). RF DNA amplification occurs using roll-over replication, and the replication process is initiated when G2P is cleaved at a specific site on the positive strand of the parental RF DNA to create an incision and can covalently bind to the 5' end (Figure 1B). Nucleotides are added to the DNA to use the negative strand as a template at the 3' end of the cut and the synthesis of DNA continues in the presence of DNA polymerase (Fig. 1 C). The original positive strand is replaced by newly synthesized DNA and re-soul looped. converted to RF DNA or packaged into new phage genomic DNA (Fig. 1 D).
The zygotic positive strand was converted to RF DNA early in the infection, but G5P prevented the conversion of the zygotic positive strand to RF DNA, causing the single-stranded DNA to change its shape to a rod in the later stages of the infection, (Fig. 1 E). Phage DNA is covered by G5P bound to ssDNA, and the phage translocates through pores in the membrane while undergoing shell assembly (Figure 1F).
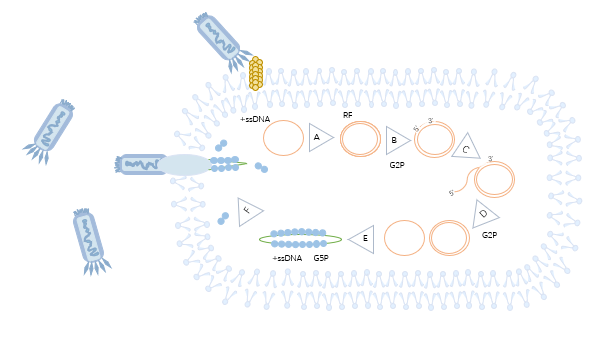
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of phage display technology
Antibody phage display library type
At present, a variety of antibody formats are used to construct antibody phage display libraries, including single-chain variable fragment (scFv), antigen-binding fragment (Fab) antibody, and camel-derived nanobody (VHH). The scFv composed of VH and VL structural domains are single-chain antibodies used to construct scFv antibody libraries. scFv is characterized by a short half-life and low immunogenicity. Fab Antibody Library consists of Fab, consisting of VH, VL, CL, and CH1, which can rapidly screen out ideal antibodies with high affinity. The smallest unit that can bind the target antigen-VHH constitutes the nanobody library currently, VHH has the advantage of a simple structure, easy to prepare and express.
Library screening methods
The success of phage display antibody preparation mainly depends on the screening of antibody phage display libraries, and the commonly used screening library methods are solid-phase screening and liquid-phase screening. Solid-phase antigen screening enriches specific antibodies through 3-4 rounds of elution to obtain antibody phage display libraries; Liquid-phase antigen screening is performed by incubating biotin-labeled target and antibody phage display libraries and capturing bound phages using magnetic beads. Solid-phase screening consumes more antigen and some antigen epitopes are destroyed. Liquid-phase screening is characterized by high efficiency and enrichment, but the antibodies obtained are less specific. The screening method of phage display antibody preparation depends on the specific experimental needs, all of which will have a certain impact on the effect of phage display antibody preparation.
Based on the above, KMD Bioscience provides library construction services such as Fab antibody library construction, scFv antibody library construction, nanobody library construction, and multi-species monoclonal antibody sources to support customers in antibody research.
In addition, KMD Bioscience also provides related services such as nanobody drug discovery, antibody in vitro expression, and functional validation.
References
[1] Ledsgaard L, Kilstrup M, Karatt-Vellatt A, et al. Basics of Antibody Phage Display Technology [J]. Toxins (Basel), 2018, 10(6): 236.
[2] Ledsgaard L, Ljungars A, Rimbault C, et al. Advances in antibody phage display technology [J]. Drug Discov Today, 2022, 27(8):2151-2169.
[3] Nur A, Schubert M, Lai JY, et al. Antibody Phage Display [J]. Methods Mol Biol. 2023, 2702: 3-12.