2024-08-28 Hits(135)
Phage Display Technology
Phage display technology is an in vitro screening technique that can select target peptides from a large library of peptides and display them on the surface of bacteriophages. The M13 phage display system, which consists of five capsid proteins, is currently widely used for display. The function of capsid protein pIII is mainly screening, and the target peptide gene can be inserted into pIII, and its applicable vector range is also very wide. In 1985, phage display technology was created as a technique for studying antigenic epitopes. Phage display mainly involves inserting exogenous genes into phage capsid proteins through genetic engineering technology, so that the peptides encoded by exogenous genes can be displayed as fusion proteins without changing their structure and activity. Afterward, multiple rounds of screening are conducted to select highly specific antibodies or peptides that can bind to the target molecule. In 1990, a random 6-peptide library based on phage display technology was created. After years of development, phage display technology has been applied not only in the study of antigen epitopes, but also in areas such as cell signal transduction, protein recognition sites, and drug development. With the widespread use of phage display technology, many diseases have been identified through phage display technology. For example, a short peptide associated with ankylosing spondylitis was discovered through a phage random 12 peptide library, and a peptide that may be a biomarker of colon cancer was also discovered in the serum of colon cancer patients through phage display technology. The peptide library established based on phage display technology has a capacity of billions. In terms of screening peptide markers, phage display peptide libraries have the advantages of speed, relatively low cost, and large library capacity. By screening bacteriophage peptides that bind to specific antigens, new antibodies can be developed or existing antibodies can be improved. Phage display peptides can also be used for vaccine development, cancer diagnosis, biosensor development, and more.
Classification of phage display peptide libraries
There are multiple categories of phage display peptide libraries, which can be classified based on the type of phage, carrier type, and library type. According to the different types of bacteriophages, bacteriophage display peptide libraries are divided into M13 bacteriophage display system, T7 bacteriophage display system, T4 bacteriophage, λ bacteriophage display system, etc. Among them, the M13 phage display system includes a blue-white spot system and an auxiliary phage system. The blue-white spot system uses genetic engineering technology to insert a reporter gene, such as the lacZ gene, into a phage vector. When an exogenous gene is inserted and can be expressed, the expression of the reporter gene will be interfered with, forming white colonies in the host bacteria. When the inserted exogenous gene is not expressed correctly, the expression of the reporter gene will not be interfered with, and blue colonies will be formed in the host bacteria. The blue-white spot system is beneficial for the rapid screening of bacteriophages containing exogenous genes. The auxiliary phage system is mainly used to support the synthesis and screening of phage display peptide libraries. It can provide the necessary gene products for phage display technology, such as proteins required for phage replication and packaging processes, to ensure the normal operation of the phage display system. The T7 phage display system is capable of a high-copy display of peptides or proteins and can be used for screening proteins with different molecular weights and affinities.
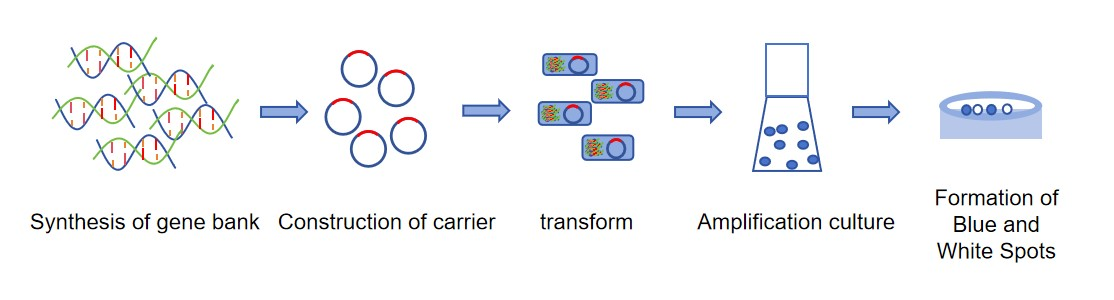
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of M13 phage display system
The carriers of phage display peptide libraries include phage vectors and phagemid vectors. Phage vectors can generate infectious phage particles, which can be used to display larger peptides or protein fragments. Phage particles are hybrids of bacteriophages and plasmids, possessing the packaging and infectivity of bacteriophages, as well as the stability and operability of plasmids. Phage particle vectors can be used to display smaller peptides or protein fragments.
According to different library types, phage display peptide libraries are divided into random peptide libraries, cDNA libraries, antibody libraries, and protein libraries. Among them, a random peptide library is a library generated by chemical or genetic synthesis methods containing a large number of random sequence peptides, mainly used to screen peptides that bind to specific target molecules. The mRNA extracted from specific tissues or cells and the cDNA generated by reverse transcription can be inserted into phage vectors to construct cDNA libraries, which can be used to express and display corresponding protein or peptide fragments. The antibody library contains a large number of antibody gene sequences, which can be inserted into phage vectors and screened for antibodies targeting specific antigens through phage display technology. The protein library contains a large number of different protein or peptide sequences that can be displayed on the surface of bacteriophages for screening proteins with specific functions or properties.
KMD Bioscience is committed to providing customers with high-quality peptide library construction technology services, providing strong support for downstream research and development work such as peptide library synthesis and screening, targeted peptide drug discovery, specific blocking peptide drug development, and specific lead sequence development. KMD Bioscience has rich project experience and insights in peptide library construction. After years of development, KMD Bioscience has established a comprehensive peptide library construction system, including the M13 phage display system relying on the M13 auxiliary phage, the M13 KE phage display system, the T7 phage display system, etc. It can provide customers with high-quality linear peptide libraries (including but not limited to 6-peptide library, 7-peptide library, 12 peptide library, 15 peptide library) and various types of peptide library construction services such as cyclic peptide libraries (cyclic 6-peptide library, cyclic 7-peptide library, cyclic 10 peptide library, etc.). The M13 phage peptide library established by KMD Bioscience has a storage capacity of up to 10^8 and a titer of up to 10^13 phage display peptide particles/ml. The T7 phage peptide library has a storage capacity of up to 108 and a titer of up to 10^11 phage display peptide particles/ml, which is sufficient to support customers in screening targeted peptides for various targets and meeting downstream experimental needs in the future. KMD Bioscience can provide one-stop technical services including peptide gene library design and synthesis, peptide library construction, matching peptide library screening, affinity validation, in vitro cell validation, etc. Customers only need to provide specific project requirements, and KMD Bioscience scientists will design the best library construction method and phage system based on customer project requirements to meet their project needs.
Reference
[1] Jaroszewicz W, Morcinek-Orłowska J, Pierzynowska K, et al. Phage display and other peptide display technologies. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2022;46(2):fuab052.
[2] Chen PC, Liu WR. The Construction of a Genetically Encoded, Phage-Displayed Cyclic-Peptide Library. Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2355:219-230.
[3] Gao Q, Chen L, Jia C, et al. Selection and identification of a specific peptide binding to ovarian cancer cells from a phage-displayed peptide library. Biotechnol Lett. 2022;44(8):951-960.