2024-07-29 Hits(129)
Single-chain Variable Fragment
What is a Single-chain Variable Fragment?
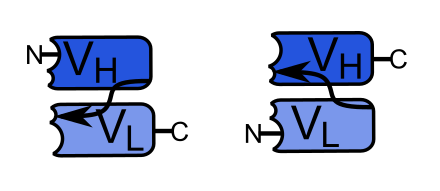
Single chain variable fragment (scFv) is composed of immunoglobulin heavy chain (VH) and light chain (VL) variable regions connected to short linking peptides of 10-25 amino acids. It has high specificity and affinity, and although it does not have a constant region or introduce short-linking peptides, it still retains the characteristics of the original immunoglobulin. Short-linking peptides usually have two connection modes, which can connect the N-terminus of VH to the C-terminus of VL and the C-terminus of VH to the N-terminus of VL, as shown in the figure.
Scfv has many uses, such as flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, and so on. SCFV can be generated through phage display technology, hybridoma technology, etc., and is generally produced in E. coli expression systems.
scFv Structure
ScFv fragments are the smallest units of immunoglobulin molecules with antigen-binding activity. Composed of a variable region of approximately 120 amino acids in the antibody heavy chain (including 3 complementary determining regions related to antigen binding), a variable region of approximately 120 amino acids in the antibody light chain (including 3 complementary determining regions), and a short linking peptide, it has a common structure (Gly ₄ Ser) 3, mainly composed of glycine and threonine, which can increase the flexibility of short linking peptides. scfv antibodies have several advantages in clinical practice, including better tumor penetration, faster blood clearance, shorter retention time in non-target tissues, and reduced immunogenicity.
Scfv also has dimer, trimer, and tetramer forms, as shown in the following figure.
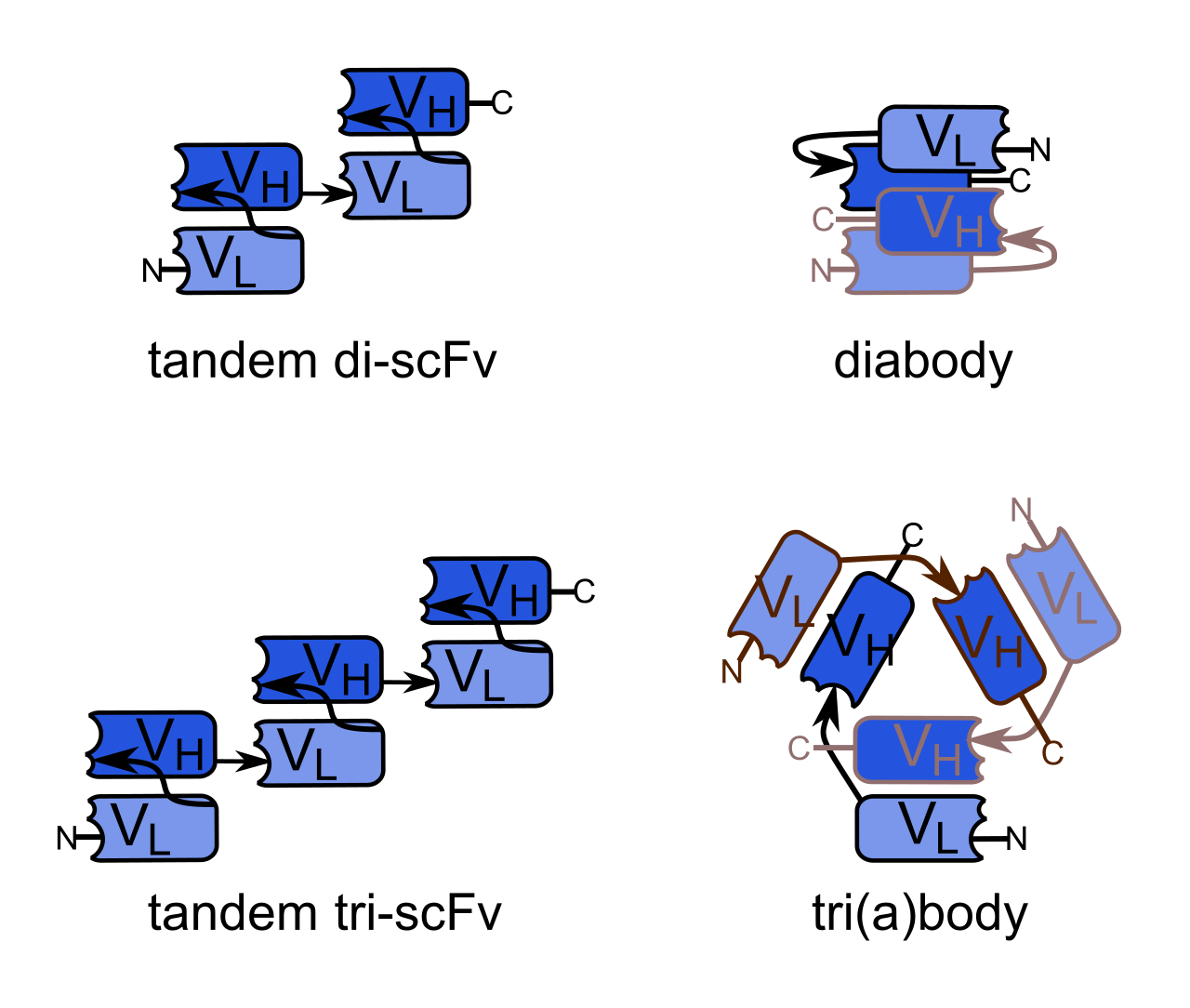
Bivalent (or bivalent) single-chain variable fragments (di scFvs, bi scFvs) can be achieved by generating a single peptide chain with two VH and two VL regions, resulting in tandem scFvs. The affinity of dual antibody targets is much higher than that of scfv antibodies. Shorter linkers (one or two amino acids) connect trimers and tetramers, with higher affinity for targeted targets.
scFv Antibody Library Construction and Screening
ScFv fragments have characteristics such as antigen binding, strong penetration, short in vivo half-life, low immunogenicity, and ease of genetic engineering operations. Currently, these antibody fragments are typically produced through phage display technology. According to the source of antibody genes, antibody libraries are generally divided into natural antibody libraries, immune antibody libraries, synthetic antibody libraries, and semi-synthetic antibody libraries.
Phage display antibody libraries are widely used for screening high-affinity antibodies and are the method that produces the most recombinant antibody fragments. The antibody library constructed by phage display technology is usually derived from RT-PCR amplification of mRNA from peripheral blood mononuclear cells, spleen cells, bone marrow cells, and tonsil cells, forming cDNA fragments. These gene fragments are spliced into bacteriophage vectors, then transferred to bacteriophages to form covalent structural proteins and displayed in vitro.
The construction process of phage display scfv antibody library
1. Plasmid design and synthesis
2. Extract RNA from PBMCs, reverse it to cDNA, use cDNA as a template, perform two PCR amplifications of heavy and light chain variable region genes using specific primers, design linkers, and use PCR overlap extension technology or other techniques to connect VH and VL genes, thereby obtaining scFv genes.
3. Plasmid construction and transformation: Select a suitable vector, connect scFv and phagemid vector, and transform them into TG1 host bacteria through electroporation to construct a scfv antibody library.
4. Identification: Randomly select 20-50 clones for PCR identification, sequencing, and antibody sequence analysis.
Screening process of phage display scfv antibody library
Fix the target antigen onto a solid surface (such as a 96-well plate or magnetic beads) for target fixation. Subsequently, the scFv library was incubated with antigens, and unbound scFvs were washed away. Finally, specific bound scFv was washed out, and further infection with Escherichia coli was amplified and screened repeatedly to obtain high-affinity scfv antibodies. The affinity was detected by SPR technology, BLI technology, ELISA technology, etc. The antibodies were produced in a suitable expression system (E. coli expression system), purified, and obtained high specificity, high affinity, and high purity scfv antibodies
scFv Application
scFv fragments have good tumor penetration, rapid blood clearance, and low retention times in non-target tissue. Generally, antibody fragments can be utilized for the preparation of immunotoxins, therapeutic gene delivery, and anticancer intrabodies. Antibody fragments can be fused to a range of toxins such as cytotoxic proteins, radionuclides, or drugs.