2024-09-19 Hits(105)
Protein Expression
Recombinant protein expression is the process of introducing exogenous genes into host cells through gene recombination technology, utilizing the host cell's biosynthetic mechanism to express the target gene within the host cell. A complete protein expression system includes target genes, vector plasmids, host cells, etc. The principle of recombinant protein expression is mainly to clone the target gene into an expression vector and transform it, and then the target protein is produced through transcription and translation. The commonly used protein expression systems include Escherichia coli expression system, mammalian cell expression system, insect cell expression system, and yeast expression system. Among them, the E. coli expression system is the primary choice for prokaryotic expression. When performing eukaryotic protein expression, the corresponding expression system will be selected based on the characteristics of eukaryotic proteins and different eukaryotic protein expression requirements. For example, the mammalian cell expression system can provide a cell environment similar to the natural cell environment and is suitable for the expression of structurally complex eukaryotic proteins. HEK293 cells have been used for transient protein expression for many years. The insect cell expression system mediated by baculovirus expression vector is now very mature. Baculovirus expression vector is a transient protein expression system based on plasmid transient gene expression. It uses insect cells with plasmid expression ability for chemical transfection to achieve virus free protein expression.
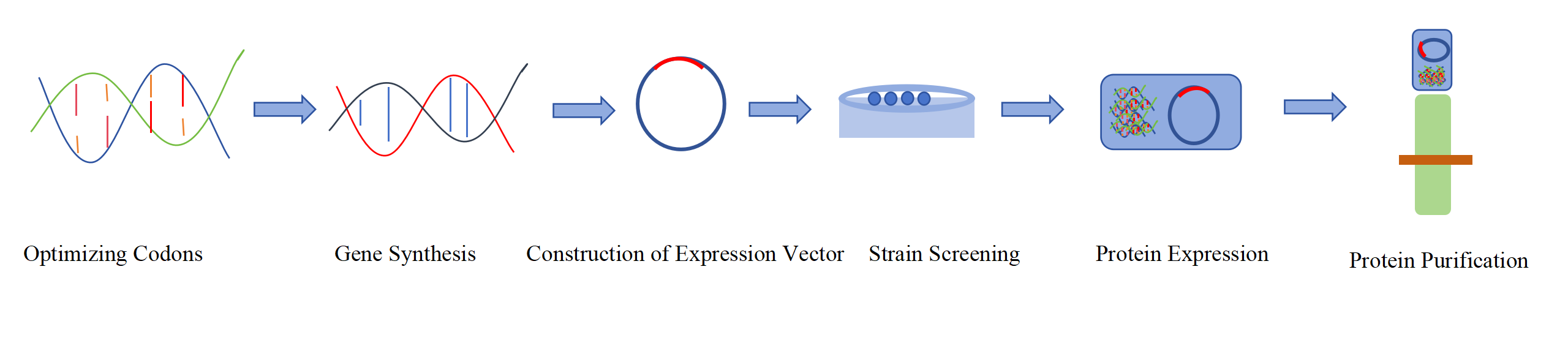
Fig. 1 Flow chart of recombinant protein expression
Types of Recombinant Protein Expression
Based on the different characteristics of protein expression, recombinant protein expression can be classified into different types. The product forms of protein expression are different, and recombinant protein expression can be divided into soluble expression and insoluble expression. The methods of protein expression are different, and recombinant protein expression can be divided into fusion expression and non fusion expression. According to whether the recombinant protein is secreted outside the cell after expression, protein expression can be divided into secretory expression and non secretory expression.
Soluble expression refers to the presence of the target protein in the host cell in a soluble form after expression, rather than forming insoluble inclusion bodies. Soluble expression is beneficial for the correct folding of the protein and the maintenance of its biological activity, and the subsequent purification process is also relatively easy. Insoluble expression, also known as inclusion body expression, refers to the formation of solid particles within cells due to incorrect folding of proteins. The target protein exists in an insoluble form, especially in the form of inclusion bodies. When proteins exist in an insoluble form, complex refolding processes are often required to restore their biological activity. However, protein solubility can be improved through fusion expression, such as using SUMO tag to promote protein dissolution, or selecting host bacteria such as Origami (DE3) and Rosetta that are conducive to forming disulfide bonds.
Fusion expression refers to the process of constructing an expression vector by connecting the gene fragment of the target protein with the gene fragment of the protein tag to form a fusion gene, and then performing fusion expression in the host cell. Fusion expression can change the physicochemical properties of the target protein, which is beneficial for soluble expression of the protein, and through the protein tag, it can simplify the subsequent purification process. Non fusion expression refers to the direct insertion of exogenous target genes into an expression vector without fusing with any protein tags, resulting in the expression of non fusion proteins similar to natural proteins. Since there is no need to remove protein tags, the purification process of non fusion expression is more direct, but its expression products are easily destroyed by proteases in host cells.
Most proteins are mainly expressed non secreted, which refers to the expression of recombinant proteins in host cells and their direct release into the cytoplasmic matrix without being secreted outside the cell. However, non secreted proteins may be degraded by host cell proteases or form inclusion bodies. Secretory expression refers to the synthesis of recombinant proteins in host cells, which are then secreted out of the cell through the secretion system, such as in culture medium. By introducing secretion signal peptide sequences into the expression vector, the target protein can be fused and expressed with the signal peptide, thereby being secreted into the extracellular space. Secretory expression can simplify the purification process of proteins and reduce the risk of expressed proteins being degraded by host cell proteases.
KMD Bioscience has established a complete integrated service for protein expression customization, protein purification, and functional validation. We have rich experience in customized recombinant protein expression and fusion protein expression purification. We have successfully prepared thousands of recombinant proteins for our customers, including recombinant antibodies, secreted proteins, transmembrane proteins, proteases, etc., with high success rates. Customers only need to provide a protein sequence, CDS or protein name, and KMD Bioscience can develop a complete fusion protein expression and purification plan in a shorter period of time. We can provide customized protein expression services based on the four major expression systems, and choose different fusion protein expression and purification strategies according to customer needs. KMD Bioscience has constructed a pCold series of vectors containing low-temperature induced expression elements, and obtained dual expression plasmids by modifying pET vectors, which can provide customers with high-quality protein expression customization services. We have rich experience in yeast protein recombinant expression, fermentation, and purification, and can quickly customize protein yeast expression strategies for customers, and provide customers with various specifications of protein yeast fermentation scales. At the same time, KMD Bioscience can provide natural protein purification and recombinant protein purification services, such as affinity purification, molecular sieve chromatography, ion exchange chromatography, and hydrophobic chromatography. With our protein purification platform, high-quality recombinant protein products can be obtained in a short period of time
Reference
[1] Schütz A, Bernhard F, Berrow N, et al. A concise guide to choosing suitable gene expression systems for recombinant protein production. STAR Protoc. 2023;4(4):102572.
[2] Assenberg R, Wan PT, Geisse S, Mayr LM. Advances in recombinant protein expression for use in pharmaceutical research. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2013;23(3):393-402.