Service Line:+86-022-82164980
Address:FL-4, Building A5, International Enterprise Community, Tianjin, China
Email:[email protected]
| Catalog Number | KMP2416 |
|---|---|
| Product Name | Mouse CD244 Protein, His Tag |
| Product Description | The Mouse CD244 Protein(KMP2416) is produced in HEK293 Cells and the target gene encoding Gln20-Asn221 is expressed with a 6His tag at the C-terminus. |
| Molecular Weight | 23.55 kDa |
| Alias | Natural killer cell receptor 2B4, CD244 |
| Species | Mouse |
| Host | HEK293 Cells |
| Size | 50ug, 100ug, 200ug |
| Purification | Affinity purification |
| Purity | >95% as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin | <1.0 EU/ug determined by the LAL method |
| Buffer | PBS, pH7.4 |
| Uniprot | Q07763 |
| SDS-PAGE | 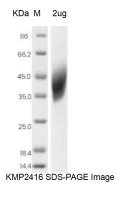 |
| Function | Heterophilic receptor of the signaling lymphocytic activation molecule (SLAM) family; its ligand is CD48. SLAM receptors triggered by homo- or heterotypic cell-cell interactions are modulating the activation and differentiation of a wide variety of immune cells and thus are involved in the regulation and interconnection of both innate and adaptive immune response. Activities are controlled by presence or absence of small cytoplasmic adapter proteins, SH2D1A/SAP and/or SH2D1B/EAT-2. Acts as activating natural killer (NK) cell receptor (PubMed:8326140, PubMed:12734329, PubMed:19648922, PubMed:20962259). Activating function implicates association with SH2D1A and FYN. Downstreaming signaling involves predominantly VAV1, and, to a lesser degree, INPP5D/SHIP1 and CBL. Signal attenuation in the absence of SH2D1A is proposed to be dependent on INPP5D and to a lesser extent PTPN6/SHP-1 and PTPN11/SHP-2. Stimulates NK cell cytotoxicity, production of IFN-gamma and granule exocytosis (PubMed:8326140, PubMed:15169881, PubMed:15998796, PubMed:22683124). Optimal expansion and activation of NK cells seems to be dependent on the engagement of CD244 with CD48 expressed on neighboring NK cells (PubMed:15905190). Regulation of NK cell activity by adapters Sh2d1b and Sh2d1b2 is reported conflictingly (PubMed:16127454, PubMed:16425036). Acts as costimulator in NK activation by enhancing signals by other NK receptors such as NCR3 and NCR1. At early stages of NK cell differentiation may function as an inhibitory receptor possibly ensuring the self-tolerance of developing NK cells (By similarity). Involved in the regulation of CD8+ T-cell proliferation; expression on activated T-cells and binding to CD48 provides costimulatory-like function for neighboring T-cells (PubMed:11739483). Inhibits inflammatory responses in dendritic cells (DCs) (PubMed:25643613). |
| Background | Natural killer cell receptor 2B4(2B4/CD244)is a 66 kDa type I transmembrane glycoprotein in the SLAM subgroup of the CD2 protein family. SLAM family proteins have an extracellular domain(ECD) with two or four Ig-like domains and at least two cytoplasmic immunoreceptor tyrosine-based switch motifs(ITSMs). 2B4 interacts with CD48, while other SLAM family proteins interact in a homophilic manner. The mouse 2B4 cDNA encodes a 397 amino acid(aa) precursor that includes a 19 aa signal sequence, a 207 aa ECD with one Ig-like V-type and one C2-type Ig-like domain, a 21 aa transmembrane segment, and a 150 aa cytoplasmic domain with four ITSMs. Within the ECD, mouse 2B4 shares 46% and 68% aa sequence identity with human and rat 2B4, respectively. 2B4/CD48 signaling cooperates with other receptor systems to either promote or inhibit NK and CD8+ T cell activation. The inhibitory activities are distinct from those of MHC I restricted inhibitory NK cell receptors. Ligation of 2B4 with antibodies or CD48 constructs can directly trigger inhibitory signaling or disrupt an inhibitory interaction, leading to cellular activation. 2B4 can also induce signaling through CD48. |
| Storage | Aliquot and store at -20℃ to -80℃. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing cycles. |
| Note | This product is for research use only. |
| References | 1.J. Immunol. 167:6706-6710 (2001) 2.J. Immunol. 170:4881-4885 (2003) 3.Mol. Cell. Biol. 24:5144-5156 (2004) 4.J. Exp. Med. 202:181-192 (2005) 5.Nat. Immunol. 6:1002-1010 (2005) 6.Immunogenetics 58:15-25 (2006) |