2024-10-10 Hits(132)
Phage Display Technology
Antibodies are immunoglobulins produced by B lymphocytes that can participate in humoral immunity. They consist of variable domains, light chain variable regions (VL), and heavy chain variable regions (VH), and antibodies recognize target antigens through their variable fragments. In the 1980s, BIRD et al. designed single-chain antibodies (scFv) as a genetic fusion of VL and VH, unlinked by short flexible peptides. ScFv is the smallest binding unit with antibody activity. Due to its lack of Fc domain, its volume is small, about 25 kDa. Compared with full-length antibodies, antibody scFv penetrating tissue barriers and tumor tissues is easier. It can be applied to targeted cancer therapy drugs and is important in detecting reagents. In addition, based on the characteristic of antibody scFv not containing Fc fragments, its immunogenicity is low, and the risk of causing immune reactions in the human body is also relatively small. ScFv can also be efficiently expressed in various expression systems, including prokaryotic and eukaryotic expression systems, such as E. coli, yeast, insect cells, mammalian cells, etc.
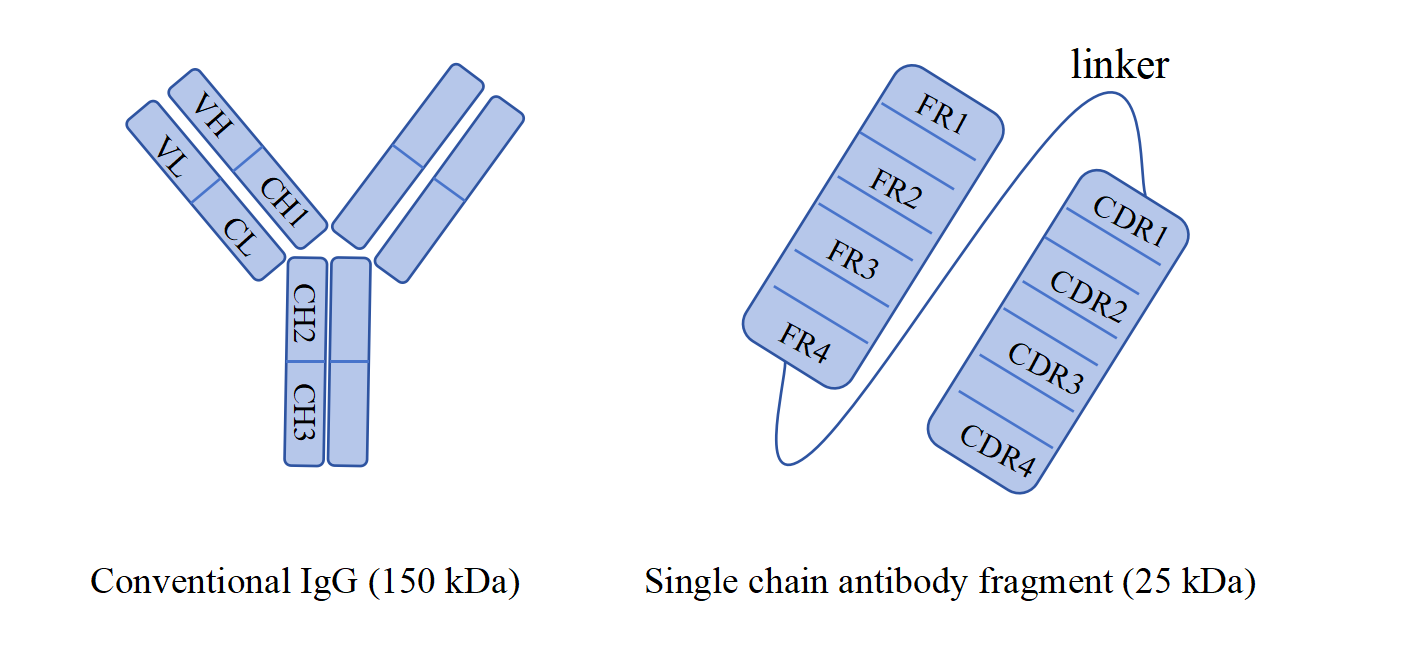
Fig. 1 Comparison of Traditional Antibody and Single Chain Antibody Structures
Application of single-chain antibodies
scFv can be linked to chemical toxins to form immunotoxins, which can then target and kill tumor cells. In addition, antibody scFv can also be linked to T cells to construct chimeric antigen receptor T cells (CAR-T) for cancer treatment. scFv can neutralize specific antigens on the surface of the virus, thereby inhibiting virus replication and transmission. scFv can be fused with markers such as fluorescent proteins for early diagnosis and localization of diseases. Phage library construction technology can display scFv on the surface of bacteriophages, making drug screening more convenient and efficient by constructing single-chain antibody libraries.
Construction of scFv antibody library
Firstly, peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) are isolated from the peripheral blood of immunized animals, and total RNA is extracted from PBMCs. During the extraction process, attention should be paid to the integrity and purity of RNA. The extracted RNA is used as a template and then reverse-transcribed into cDNA. Afterwards, VH and VL genes are amplified by PCR using cDNA as a template. Generally, two rounds of PCR amplification are performed to improve the specificity and yield of antibodies. Specific linker sequences are used to connect VH and VL genes to form a complete scFv gene. The scFv gene is inserted into a phagemid vector to construct an expression vector, which can contain promoters, terminators, replication origins, etc., to ensure the correct expression of the scFv gene in the host cell. The constructed expression vector is transformed into host cells such as Escherichia coli, yeast, or mammalian cells. The expressed scFv antibody is based on phage library construction technology, and a single-chain antibody library is constructed. Solid-phase antigen and antibody libraries can be used for incubation, and after several rounds of washing, elution, and amplification processes, single-chain antibodies with specificity and affinity can be screened. Positive clones were selected from the screened single-chain antibody library and sequenced to verify whether the sequencing results were consistent with the expected scFv gene sequence.
Animals capable of preparing scFv antibodies
Animals of different species have differences in their immune systems and antibody characteristics, which can affect the efficiency and specificity of single-chain antibody production. The commonly used animals for producing single-chain antibodies are rabbits, sheep, and rats. Among them, rabbit IgG has high sensitivity and specificity in immune response, and its structure is relatively simple and stable. Therefore, rabbits are an ideal choice for preparing high-affinity and high-specificity single-chain antibodies. Rabbit single-chain antibodies are widely used in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases that require high sensitivity and specificity. Rats are one of the commonly used experimental animals, and their IgG has multiple subtypes. Different subtypes also have certain differences in structure and function. The immune system of rats can produce diverse antibodies, so rats are widely used for the production of single-chain antibodies with specific functions and characteristics. In experimental studies simulating human disease states, rat single-chain antibodies are the most common. Sheep IgG also has multiple subtypes, and the sheep immune system can target multiple antigens. Sheep single-chain antibodies have potential application value in livestock disease prevention and control.
Table 1. Comparison of animals capable of preparing single-chain antibodies
|
Animal species |
Advantage |
Disadvantage |
Application area |
|
rabbit |
Sensitivity, high specificity, and structural stability |
The preparation cost is relatively high |
Disease diagnosis, treatment, and research |
|
sheep |
The immune system is diverse and capable of producing multiple antibodies |
Relatively less research and application |
Disease prevention and control in animal husbandry |
|
rat |
Diversified immune system and abundant antibody subtypes |
There may be species-specific issues |
Drug development, disease diagnosis |
KMD Bioscience has a mature single-chain antibody library construction system, which can prepare scFv antibody libraries for immune animal spleen cells and human B lymphocytes. We will conduct a comprehensive analysis of scFv antibody sequence information and validate it through various experiments, such as EC50 determination, affinity analysis, flow cytometry blockade verification, etc. We have multiple phage antibody library construction platforms including M13, T4, T7, and λ phages, which can meet the different needs of customers and provide personalized antibody discovery and single-chain antibody library construction services. KMD Bioscience specializes in constructing different types of scFv phage display libraries, such as immune libraries, natural libraries, semi-synthetic libraries, synthetic libraries, etc. The scFv antibody library we have constructed has a large capacity and can produce high-affinity scFv antibodies. We can provide customers with various bacteriophage vectors including pMECS, pComb3X, and pCANTAB 5E. We have strains such as TG1 Escherichia coli, XL1 Blue, and ER2738, which can be used for phage infection after expanded cultivation. The antibody library we have built has a large capacity of up to 109, with a high insertion rate of the target fragment, which is beneficial for screening scFv antibodies that satisfy customers. We can also express and purify the screened scFv according to customer needs. In addition to prokaryotic expression systems, we also have various eukaryotic expression systems for antibody proteins, such as mammalian cells, yeast cells, plant and insect cell expression systems, etc., which can provide high-quality antibody discovery services and produce high-quality scFv antibodies for customers.
Reference
[1] Boucher LE, Prinslow EG, Feldkamp M, et al. "Stapling" scFv for multispecific biotherapeutics of superior properties. MAbs. 2023 , 15(1):2195517.
[2] Kato M, Hanyu Y. Enzymatic Assembly for scFv Library Construction. Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1575:31-44.
[3] Bemani P, Mohammadi M, Hakakian A. ScFv Improvement Approaches. Protein Pept Lett. 2018, 25(3):222-229.