Service Line:+86-022-82164980
Address:FL-4, Building A5, International Enterprise Community, Tianjin, China
Email:[email protected]
Phage display technology utilizes a phage-based display library to identify and develop particular protein and antibody interactions and is now one of the most potent and widely used laboratory technologies for the study of antibody discovery. KMD Bioscience specializes in advanced phage display technologies for a variety of service projects. With the mature antibody production platform we have built up, we can offer high-quality phage display library construction and custom phage display library screening services to meet various customer needs. KMD Bioscience now offers multi-species monoclonal antibody production services, covering humans, rats, rabbits, chickens, sheep, geese, pigs, bovine, horses, donkeys, camels, alpacas, etc. With skilled technology, our scientists can offer high-quality phage display library construction and custom antibody library screening services to meet our client’s different requirements.
Phage display service has many applications in drug development, such as identifying new drug targets, designing new therapeutic proteins, and developing vaccines for infectious diseases. It is also used in research applications to study protein-protein interactions, protein-DNA interactions, and protein-ligand interactions. KMD Bioscience is devoted to providing one-stop technical services including protein expression, affinity analysis, antibody humanization, antibody affinity maturation, and related services to save you time. With the time saved, you can achieve more in your research. Backed by a wealth of experience and advanced platforms, KMD Bioscience can provide comprehensive phage display library construction services.
Antibody Phage Display Library Platform
Phage display technology (PDT) is a molecular diversity technology that allows the presentation of large peptide and protein libraries on the surface of filamentous phage. In 1985, Smith, G.P. proposed inserting exogenous genes into the modified phage shell protein and expressing fusion proteins containing exogenous proteins or polypeptides, called fusion phages. Through repeated adsorption-elution-amplification processes, phages that specifically bind to target proteins are screened from phage libraries. Then enrichment, amplification, and gene sequencing were performed to infer the amino acid composition of exogenous proteins. A crucial advantage of this technology is the direct link between the experimental phenotype and its encapsulated genotype, which allows the evolution of the selected binders into optimized molecules. It has been successfully applied to epitope analysis, monoclonal antibody screening, and determination of protein functional antagonist polypeptides or mimetic peptides and plays an essential role in drug screening, vaccine design, etc.
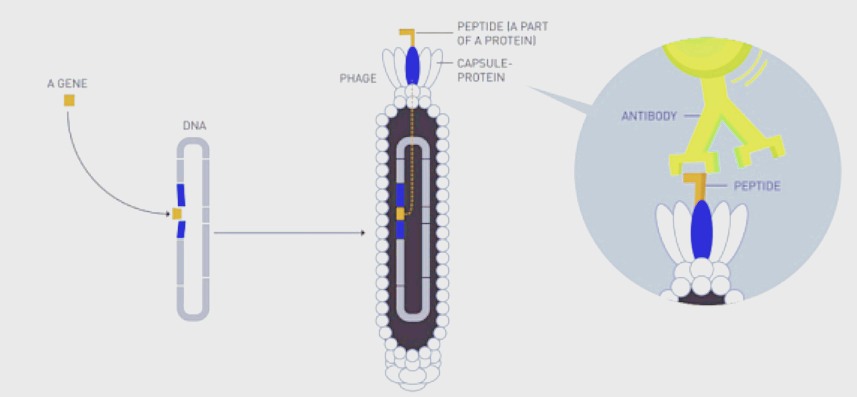
Fig 1: Diagram of phage display technology
Phage Display Technology Process
In general, filamentous bacteriophages (e.g. M13 phage) are the most popular choice for phage display and are extensively used in many research fields. Using M13 filamentous phage shell protein pIII and PVIII display technologies, KMD Bioscience can construct different kinds of natural or immune phage antibody display libraries for our clients, and the library capacity can reach 10^11.
Specific polypeptides can be efficiently screened by the affinity between displayed polypeptides and target proteins (mainly refers to antibodies, antigens, some growth factor receptors, etc.) or other biological macromolecules. First, the target protein is solidified, e.g. by binding to a plastic plate (96-well plate), then the phage libraries are added and reacted with it. After washing, the unbound phages were washed out and the affinity phages were captured. The captured phages were eluted and then infected with E. coli for further amplification. Such an "adsorption-elution-amplification" enrichment process is called panning. A round of panning can enrich 103 folds of the phages. Typically, short peptides interacting with target proteins can be screened from the phage libraries of 109-1010 after 3-4 rounds of panning.
.jpg)
Fig 2: Workflow of phage display technology
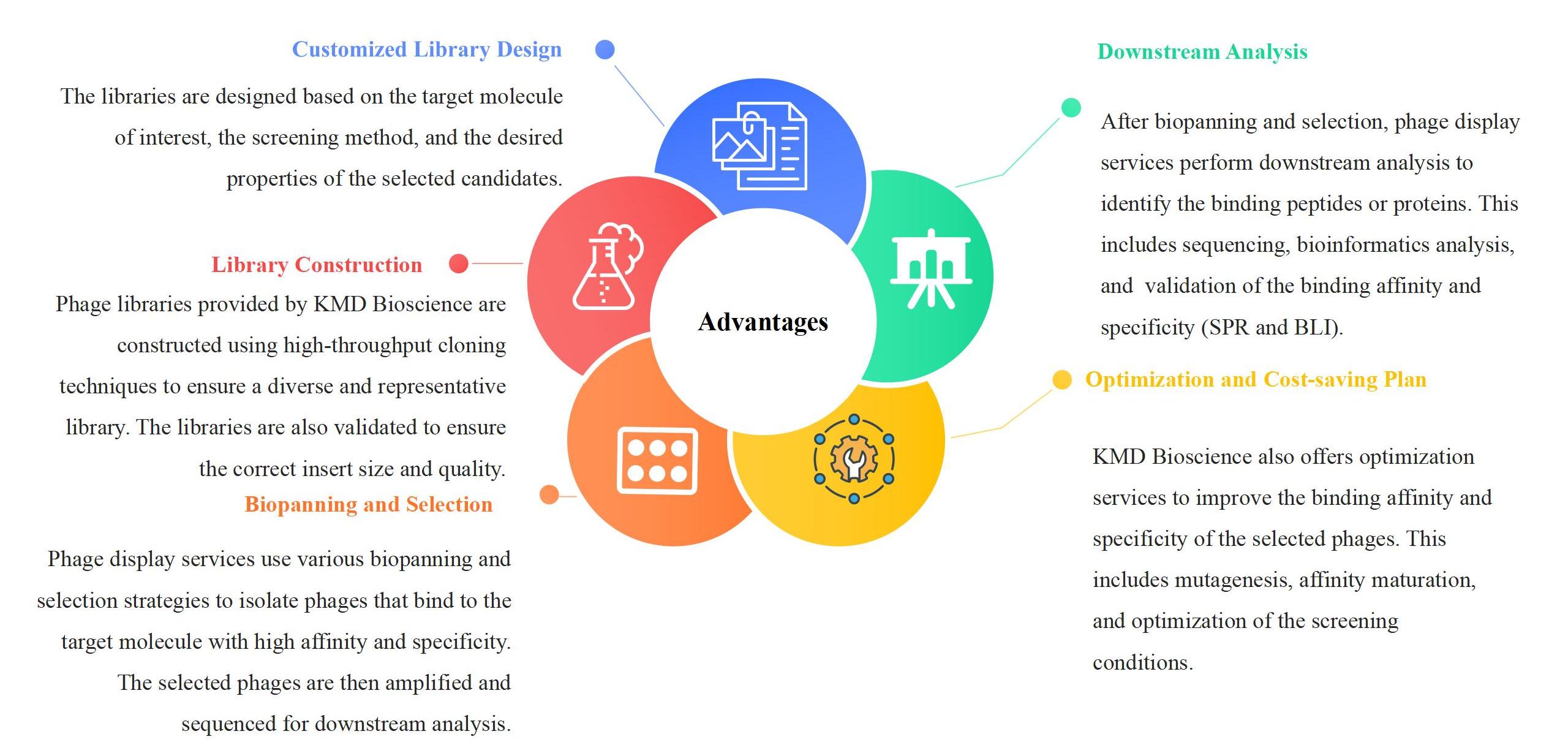
Phage Display Platform Highlights
How to Order?
If you have any questions regarding our services or products, please feel free to contact us by E-mail: [email protected] or Tel: +86-400-621-6806