2024-09-24 Hits(113)
Antibody Humanization
As an important part of the immune system, antibodies play an important role in medical diagnosis, treatment, and scientific research, and provide strong support for progress in medicine and life sciences. The earliest appearance of antibodies can be traced back to China's inoculation of "human pox" to prevent smallpox, and the first therapeutic CD3 monoclonal antibody approved by the FDA in modern times is OKT3, which is used to treat anti-rejection reactions in organ transplantation. CD3 monoclonal antibody is a murine monoclonal antibody, because it does not contain human gene components, and can be recognized by the human immune system, so it is easy to cause an immune response when used to treat diseases. With the development of molecular biology technology, the new humanization technology of antibody and the modification of murine monoclonal antibody are overcoming this problem, and the antibody humanization service is emerging, especially the fully human antibody drug discovery service:
The method of humanized antibody modification
The modification of humanized antibody is based on the chimeric monoclonal antibody of humans and mice. The methods of humanized antibody are as follows:
Chimeric IgG antibody
The principle is to obtain the V region gene of the target antibody from hybridoma cells producing a certain mouse monoclonal antibody, recombine with the human C region gene clone it into a suitable vector, and then transfer it to the recipient cell for expression.
Reopro, Sylant, Rituximab, Infliximab, and other chimeric monoclonal antibody have been marketed.
Chimeric Fab and F (ab ') 2 antibody
Due to the low affinity and small molecular weight of the antibody, it is easy to be filtered by the glomeruli and disappear from the blood, which isn’t suitable for clinical treatment alone.
CDR transplantation
The principle is to clone the human FR sequence to the corresponding part of the antibody-based on retaining the mouse CDR sequence.
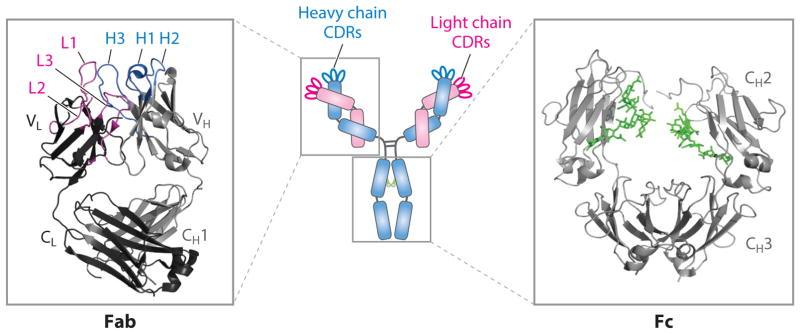
Fig 1 Molecular structure of IgG1 antibody
SDR transplantation
SDR transplantation also known as specific determination of disability transplantation which the SDR region refers to the existence of CDR region contact with the antigen of the amino acid sequence. The SDR region can produce immunogenicity transplanted into the human antibody framework.
Frame area reconstruction
Frame region remodeling is based on FR screening that includes surface remodeling, which humanizes amino acid residues, and glycosylation modification, which changes the glycosylation site. The technology can improve antibody affinity.
Transgenic mouse technology
Transgenic mouse technology is the technology of transferring the optimized human antibody DNA sequence into the mouse genome. Because the immune system is the mouse, the antibodies are not the same as those of the human body.
The marketed Nivolumab, Denosumab and Panitumumab were all produced by transgenic mice.
Antibody library technology
An immune antibody library is established by single-cell cloning technology after immunizing the body.
The non-immune antibody library consists of a semi-synthetic antibody library, a fully synthetic antibody library, and a natural antibody library.
This technique is limited by the capacity of the antibody library and host modification of amino acids. Necitumumab and Adalimumab as a drug were screened by phage banks.
Necitumumab and Adalimumab were screened through phage display technology.
Ribosome display technology
This technique works by displaying the target gene on the surface of the ribosome, forming an MRNa-protein-ribosome complex, and then adding antigens to the mixture for screening. Compared with phage display technology, this method has a higher storage capacity.
mRNA display technology
mRNA display technology is an improvement and extension of ribosome display technology, which is more conducive to screening.
Yeast display technology
Yeast display technology uses yeast as a carrier to locate foreign genes on the surface of yeast cells through fusion expression, to screen them. It can also label cells with substances such as fluorescein and perform timed and quantitative screening by flow cytometry.
Single-cell technique
Single cells can be screened from the established antibody library according to cell surface marker molecules, then the heavy chain and light chain genes of antibodies can be obtained by RT-PCR after cell enrichment.
The advantage of humanized antibody modification
Humanized antibodies are conducive to the fully human antibody drug discovery, which has the following advantages: 1. Higher safety: Because the whole human antibody drugs are more similar to the antibodies produced by the human body, they can reduce the immune response and allergic reaction caused by the body; 2, the treatment effect is better: the whole human antibody drug has a higher binding affinity; 3, wider application: Fully human antibody drugs can be used to treat a variety of diseases, such as cancer, autoimmune diseases, etc., uncomplicated or difficult to treat diseases provide more treatment options and possibilities.
KMD Bioscience has rich experience in antibody engineering construction and mature antibody humanization technology that can provide customers with high-quality humanized Modification methods of humanized antibodies, humanized antibody service, humanized monoclonal antibody production services, and other services. In addition, KMD Bioscience can also provide monoclonal antibody production, antibody expression and purification, affinity determination, antibody affinity maturation, antibody sequencing, and other services to meet the needs of different customers.
References
[1] Zinn S, Vazquez-Lombardi R, Zimmermann C, et al. Advances in antibody-based therapy in oncology [J]. Nat Cancer. 2023, 4(2): 165-180.
[2] Nagano K, Tsutsumi Y. Phage Display Technology as a Powerful Platform for Antibody Drug Discovery [J]. Viruses. 2021, 13(2): 178.
[3] Waldmann H. Human Monoclonal Antibodies: The Benefits of Humanization [J]. Methods Mol Biol. 2019, 1904: 1-10.