2024-12-30 Hits(116)
Antibody Humanization
The antibody development platform of KMD Bioscience is complete, which can carry out one-stop service from antigen preparation and antibody production to antibody labeling and antibody humanization.
Antibody humanization is an important technology in the field of biomedicine. Antibody humanization aims to replace part or all of the structure of non-human antibody (such as murine monoclonal antibody) with the corresponding structure of human antibody through DNA recombination technology and protein engineering technology, so as to reduce or eliminate the immunogenicity of non-human antibody in human body. Improve its safety, efficacy and stability in human body, while retaining its original affinity and specificity. In this process, the complementary determination region (CDR) of the non-human antibody, which is the key site for the antibody to bind to the antigen, is usually retained, and the rest is replaced with the sequence of the human antibody.
The technology of humanizing antibody has experienced many stages of development, including human-mouse chimeric antibody, humanized antibody and fully humanized antibody. The main difference between these stages is the difference in the degree of humanization and the difference in the technical means used. With the continuous progress of technology, the degree of humanization of antibodies is getting higher and higher, and its safety and effectiveness in clinical applications have also been significantly improved.
Fab phage display is a method for screening and preparing Fab antibodies using phage display technology. Fab phage display is the process of inserting the Fab antibody gene into the phage genome so that the phage surface expresses the Fab antibody fragment.
1. Fab Antibody cDNA preparation: Extract RNA from appropriate cells (such as human peripheral blood lymphocytes, lymph node cells or spleen cells) and reverse transcribe it into cDNA. Then, cDNA was used as template to amplify the variable genes of heavy chain (Fd segment) and light chain.
2. Vector construction: The amplified Fd fragment and light chain fragment are connected with the phage expression vector (such as pComb3) to construct the phage expression vector containing the target antibody fragment.
3. Electric shock transformation: the connection product is electrocuted into Escherichia coli receptor cells to construct an Escherichia coli library containing targeted antibody fragments.
4. Phage library screening: The constructed phage library is incubated with target molecules (such as antigens), and phage clones that can specifically bind target molecules are screened through multiple rounds of panning and amplification.
5. Fab antibody identification and sequencing: PCR identification and sequencing of selected phage clones to confirm the correctness and specificity of their sequences.
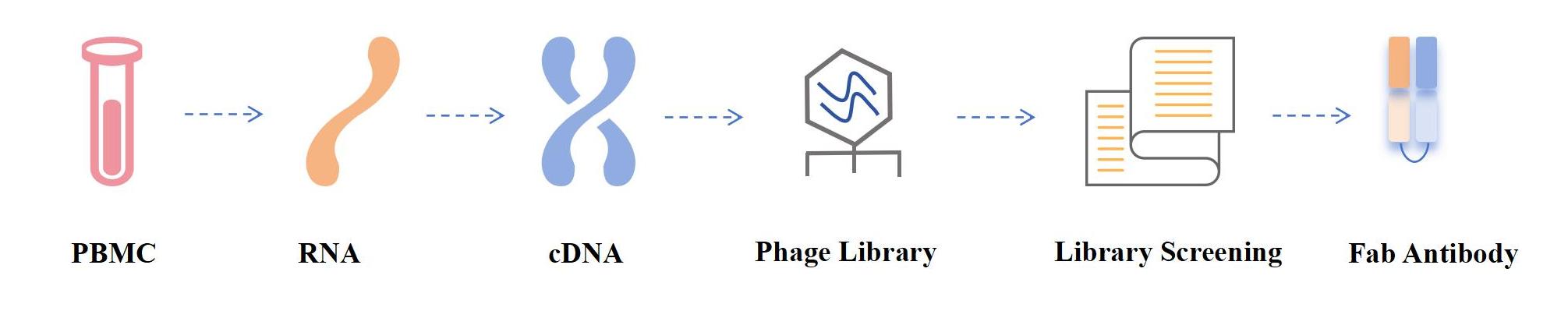
Fig.1 Fab antibody phage display process diagram
The Technique of Antibody Humanization
1. CDR transplantation
The CDR region of a non-human antibody is transplanted onto the frame region of a human antibody to preserve its antigen-binding ability. The key of this method is to select the appropriate human antibody framework region and carry out the necessary optimization to ensure that the antibody has good stability and affinity after transplantation.
2. Surface remodeling
The surface amino acid residues of a non-human antibody are modified to more closely resemble the surface properties of a human antibody. This approach helps to reduce the immunogenicity of the antibody while maintaining its antigen-binding ability.
3. SDR transplantation
Only the specific determination residues (SDRS) necessary for antigen-binding activity in the CDR sequence are transplanted onto the human antibody framework region to further reduce the immunogenicity of the antibody. This approach requires the precise identification and effective transplantation of SDRS.
KMD Bioscience uses computer modeling to randomize some frame residues into CDR grafts, and the grafted CDR is cloned into a phage display library. By screening the phage library, humanized antibodies with good affinity are screened. To further reduce the immunogenicity of humanized antibodies for CDR transplantation, KMD Bioscience can further minimize the amount of murine sources by specific determinative residues (SDR) transplantation. In addition, KMD Bioscience can also directly screen human antibodies from our prefabricated human antibody library.
Types of Humanized Antibodies
KMD Bioscience is able to provide customers with a variety of customized services for humanized antibodies.
1. Modified antibody
Modified antibodies, also known as CDR grafting antibodies, transplant the complementary determination region (CDR) of murse-derived monoclonal antibodies to the variable region of the human antibody, replacing the CDR of the human antibody. In this way, the human antibody can obtain the antigen-binding specificity of the murine monoclonal antibody, while reducing its heterogenicity.
2. Chimeric Antibody
The light and heavy chain variable region genes of allomab (such as murine MAB) were inserted into the expression vector containing the constant region of human antibody by DNA recombination technology, and then transformed into mammalian cells to express chimeric antibody. In the antibody molecule thus expressed, the V region (variable region) of the light and heavy chain is alien, while the C region (constant region) is human.
There are many types of chimeric antibodies, such as human-mouse chimeric antibodies, chimeric IgG antibodies, chimeric Fab, and F(ab')2 antibodies. Among them, human-mouse chimeric antibodies are the most common type, with variable regions derived from mouse monoclonal antibodies and constant regions derived from human antibodies.
3. Fully humanized antibody
Fully humanized antibodies are antibodies that are completely encoded by human genes and do not contain any alien components. Using gene editing technology, the antibody genes in animal somatic cells were replaced with human antibody genes, and the fully humanized antibody was produced directly after animal immunization.
Reference
[1]. Almagro JC, Fransson J. Humanization of antibodies. Front Biosci. 2008;13:1619-1633. Published 2008 Jan 1.
[2]. Jiacomini IG, Beltramino M, Boursin F, et al. An effective strategy for the humanization of antibody fragments under an accelerated timeline. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;216:465-474.
[3]. Shin SU. Chimeric antibody: potential applications for drug delivery and immunotherapy. Biotherapy. 1991;3(1):43-53.
[4]. Hyytiä H, Heikkilä T, Brockmann EC, et al. Chimeric recombinant antibody fragments in cardiac troponin I immunoassay. Clin Biochem. 2015;48(4-5):347-352.