2023-06-06 Hits(890)
Peptide library refers to a collection of a large number of small peptides with specific length and different sequences, which includes the arrangement and combination of various (or most) amino acid sequences in short peptides with this length. Peptide library is a powerful screening tool. It is used to screen a very small number of polypeptides with key biological activities from a large number of polypeptides.
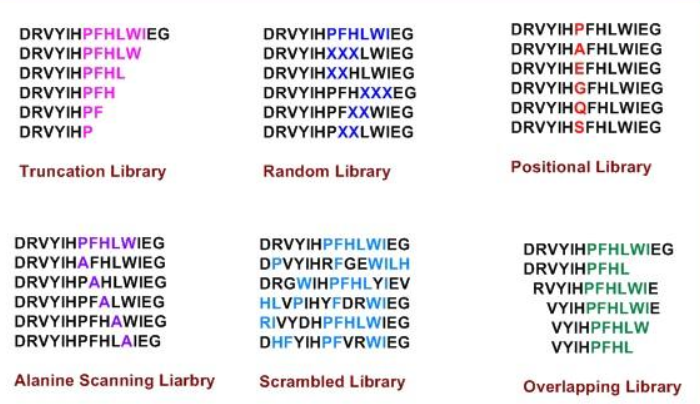
(1) Overlapping library: A single peptide can be divided into several overlapping fragments. The resulting overlapping library can then be used in processes including continuous and linear epitope mapping.
(2) Truncation library: Truncation library can be used to predict and determine the minimum length amino acid with the best epitope activity.
(3) Alanine library: Each amino acid residue is individually and systematically substituted by alanine. The library can quickly determine the contribution of each amino acid to peptide function.
(4) Random library: Random peptide library is designed as an indispensable tool for sequence optimization, and the selected position is replaced by all 20 natural amino acids at the same time, which can increase peptide activity.
(5) Scrambled library: Scrambled library has the highest variability among all peptide libraries. The obtained peptide is usually used as a negative control to show that the specific sequence is essential for the function or activity of protein. It is also a random screening tool for finding new clues.
(6) positional library: the selected sites or regions in the peptide sequence are systematically replaced by all other natural amino acids. This allows identification of amino acids that enhance peptide activity.
Peptide library is widely used in protein omics and its related fields, such as drug research and development (scientific Bevacizumab (cat:YR1001), protein-protein interaction, epitope screening, GPCR ligand screening, protein function analysis, enzyme substrate or inhibitor screening, messenger molecule research and development, and polypeptide/protein signal response.
(1) High throughput production and high screening efficiency can be achieved.
(2) Soluble antigen can be rapidly prepared.
(3) It can accurately locate the antigenic determinant and is widely used in drug development.
Based on the phage platform, KMD Bioscience has diverse libraries, as shown in figure below, which can build random 7-peptide libraries, 12-peptide libraries, 15-peptide libraries and so on for customers. The T7 phage display platform provided by KMD Bioscience is an ultra-high throughput ligand screening method. Through this technical platform, as many as 1013/ml phage-displayed polypeptides or antibody clones can be constructed, and the average number of independent clones can be 109-1010/ml. After subsequent rounds of panning, as many as 105 effective polypeptide or antibody sequences can be provided.
.png)
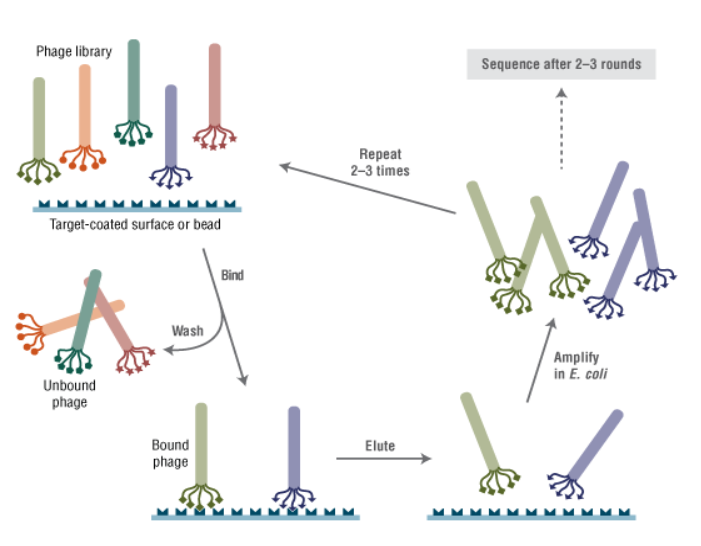
Peptide library screening is mainly divided into the following general processes: quality verification of target protein, detection of phage titer, phage expansion culture, phage panning and sequencing. The flow chart is as follows:
SDS-PAGE electrophoresis of the target protein requires that the purity of the protein is more than 95% before the next library screening.
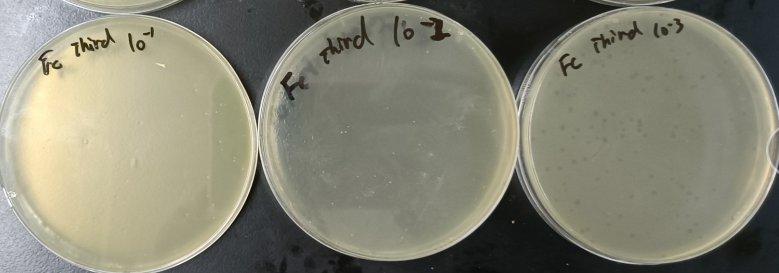
TG1 strain was inoculated into LB medium for activation culture. After agarose was added to LB medium, phage was cultured according to gradient dilution method, and the cultured phage was coated on agar plate for plaque counting.
After TG1 strain was cultured to OD600 0.4~0.6, it was inoculated into the host strain after expanded culture, and the supernatant was the phage culture.
The purified target protein was antigen coated overnight with a 96-well enzyme-labeled plate, the internal powder was defatted and sealed, the expanded phage was added for incubation, the buffer was eluted several times, the phage titer was determined, and then it was concentrated and purified, waiting for the next round of screening. Repeat the above steps twice to complete the last two rounds of screening.
Forty-eight monoclonal antibodies were selected from the bacterial plate after the third round of screening, and plasmids were extracted after amplification and culture for sequencing.