2025-02-21 Hits(64)
Recombinant Protein
At present, commonly used protein expression systems include Escherichia coli expression system, mammalian cell expression system, insect cell expression system, and yeast expression system. Among them, mammalian cell expression systems can provide the closest transcription and translation environment to the natural state for customized recombinant proteins. At the same time, mammalian cell expression systems can perform correct post-translational modifications on expressed proteins, such as glycosylation, phosphorylation, etc., making the expressed proteins closer to the structure and function of natural proteins. This is also a major advantage of mammalian cell expression systems. The mammalian cell expression system can express a large number of proteins, which is suitable for large-scale customization of recombinant proteins. In addition, proteins expressed by mammalian cells can be secreted outside the cell, making the process of recombinant protein expression and purification simpler. Based on the powerful post-translational modification function of mammalian cell expression systems, mammalian protein expression is also closer to the structure of human derived proteins. Therefore, mammalian protein expression systems are commonly used for therapeutic recombinant protein customization.
In 1986, human tissue type plasminogen activator produced in Chinese hamster ovary cells (CHO cells) entered clinical applications. Since then, more and more recombinant proteins have been customized using CHO cell protein expression or other mammalian cell expression systems. Moreover, the recombinant protein and antibody prepared by CHO cell protein expression have low pathogenicity and are relatively safe for humans. The cells can be cultured in serum-free medium, ensuring the safety of the production process. Therefore, using CHO cell protein expression system to produce drugs has become a trend, especially in the production of monoclonal antibodies. Mammalian protein expression systems can be customized for recombinant proteins through transient expression systems or stable cell lines, which have different requirements for mammalian expression vectors. Transfecting recombinant genes from mammalian expression vectors into cells is often the first step in the process of mammalian protein expression, therefore, culturing mammalian cells is an indispensable step.
Precautions for Mammalian Cell Culture
In the process of cell culture, cell contamination is the most important issue that needs attention. Depending on the source of contamination, cell contamination can be mainly divided into physical contamination, chemical contamination, and microbial contamination. The cultivation of cells requires strict control of temperature and carbon dioxide content. The temperature for mammalian cell cultivation is generally controlled at 37 ℃. However, if the temperature is not suitable, such as too cold or too hot, it can cause changes in the cell state and even lead to cell death. During the cultivation process, it is advisable to avoid exposing cells to radiation and radiation. Radiation and ultraviolet radiation can damage the DNA structure of cells, leading to cell death or genetic variation. Therefore, when performing ultraviolet sterilization, it is important to avoid direct exposure of ultraviolet radiation to cell culture bottles. In addition, the cell culture incubator should be placed in a stable location, as strong vibrations around it may cause mechanical damage to the cells.
In the environment of cell culture, there may be some harmful chemicals to cells, such as culture medium, water, reagents, etc. Impurities or concentration issues of certain components in the culture medium may affect cell growth and even have toxic effects. During the process of cell culture, impurities in water or reagents mixed into cells can cause changes in cell state or lead to cell death. If the reagents, enzymes, serum, etc. used in processing cells are of poor quality, they can also affect the growth of cells.
Microbial contamination is a relatively common and serious contamination in the process of cell culture, which can be divided into bacterial contamination, fungal contamination, mycoplasma contamination, and viral contamination according to the type of microorganisms.
Tab 1. Types and Characteristics of Microbial Pollution
|
Types of Microbial Pollution |
Characteristic |
The impact on cells |
|
Bacterial contamination |
Many types of pollution sources, The pollution rate is fast and easy to detect |
The culture medium becomes turbid and yellow, and cell growth is inhibited |
|
Fungal contamination |
White or light yellow dots appear on the culture medium, and filamentous, tubular, or branched hyphae can be seen under the microscope |
Cell growth is inhibited, and contamination spreads between the wells of the culture plate |
|
Mycoplasma contamination |
Invisibility |
Cell metabolism and growth are inhibited |
|
Virus contamination |
There is no significant change in cell morphology |
Cell growth is affected |
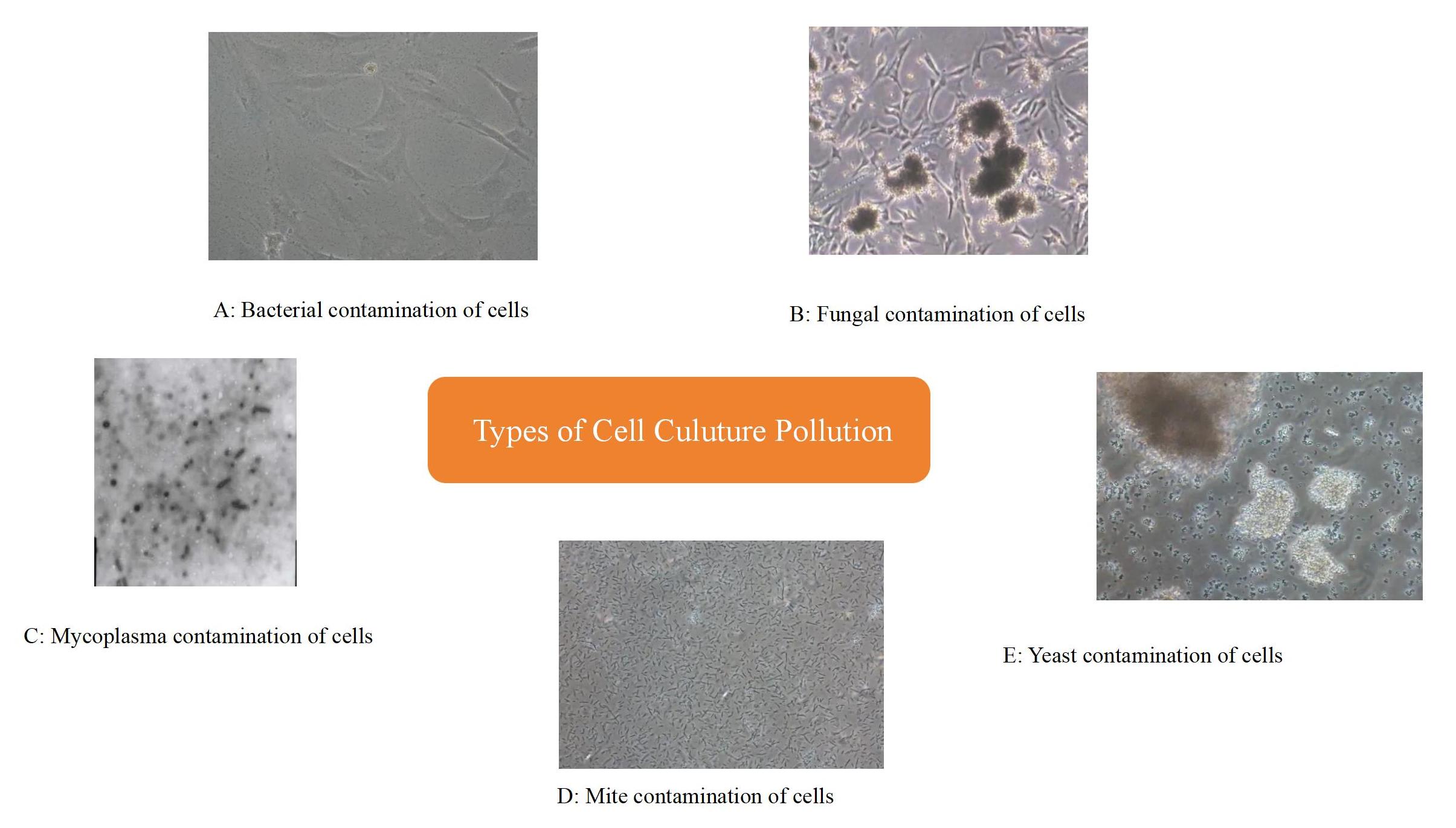
Fig 1: Types of Cell Culuture Pollution
Once cells are contaminated, it will affect their state, prolong the cell culture cycle, and affect experimental results. Therefore, it is necessary to maintain a clean and tidy cell culture environment, regularly disinfect it, and strictly follow relevant regulations during the operation to ensure sterile operation.
Selection of culture medium for mammalian cells:
In the process of cell culture, culture medium is often used, which provides a growth environment for cells and determines the physical conditions for cell growth. The culture medium will contain some essential nutrients for cell growth, such as amino acids, vitamins, inorganic salts, etc. In addition, many culture media require the addition of serum to provide other nutrients necessary for cell growth. Different types of cells (primary cells, adherent cells, suspension cells, cell lines, etc.) have different nutritional requirements, so the suitable culture medium is different. Mammalian cells usually grow in suspension, DMEM is a commonly used culture medium, CHO cells are usually cultured in serum-free medium, and other mammalian cells are mostly cultured in serum containing medium, such as HEK293 cells and Sp2/0 cells.
KMD Bioscience has established a comprehensive recombinant protein mammalian expression system, including but not limited to FreeStyle 293-F cell line, Expi 293-F cell line, Expi-CHO-K1 and Expi CHO-S cell lines, which can be combined with KMD Bioscience's designed mammalian expression vector (containing full-length CMV promoter and optimized secretion signal peptide sequence) to provide customers with higher expression levels of recombinant protein mammalian cell expression and preparation services. We have a complete set of purified fillers and equipment provided by GE, large-scale fermentation, disposable cell fermentation factories for cell culture and protein expression preparation, and can provide customers with high-quality recombinant proteins in bulk. In addition, the integrated service of recombinant protein expression and purification provided by KMD Bioscience can shorten the experimental cycle and save customers time. We have a mature vector cell transfection efficient expression system, which can easily obtain stable antibody production.
Reference
[1] Zhu J. Mammalian cell protein expression for biopharmaceutical production. Biotechnol Adv. 2012;30(5):1158-70.
[2] O'Flaherty R, Bergin A, Flampouri E, et al. Mammalian cell culture for production of recombinant proteins: A review of the critical steps in their biomanufacturing. Biotechnol Adv. 2020;43:107552.
[3] Kühn T, Ihalainen TO, Hyväluoma J, et al. Protein diffusion in mammalian cell cytoplasm. PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e22962.