2024-08-29 Hits(66)
Antibody purification
Monoclonal antibodies refer to immunoglobulins produced by a single B cell that have high specificity for antigens or epitopes. Monoclonal antibodies were initially prepared as mouse antibodies using hybridoma technology. Specifically, by fusing spleen cells from immunized mice with myeloma cells from humans or mice, hybridoma cells are formed, which secrete specific antibodies. The generated mouse monoclonal antibodies are mainly used in animal research and disease diagnosis after purification services. However, the human body will produce an immune response to foreign mouse proteins, so there are significant limitations in the clinical application of mouse monoclonal antibodies. Later, people used "humanization" to prepare monoclonal antibodies from mice, and used genetic engineering technology to modify mouse antibodies to have a constant region of human immunoglobulin to reduce their immunogenicity. This type of antibody is also known as humanized monoclonal antibody. In addition, using human cells to produce monoclonal antibodies is called whole human monoclonal antibody preparation. Monoclonal antibodies are widely used in biomedical and clinical applications. In medical research, monoclonal antibodies can be used as immunomodulators, therapeutic monoclonal antibodies can be used for cancer chemotherapy and viral infection treatment, and the development of monoclonal antibody conjugates is mainly used for cancer treatment.
Classification of monoclonal antibody samples
According to different sources and monoclonal antibody preparation methods, monoclonal antibody samples are classified into different types, such as ascites, hybridoma supernatant, etc. Among them, the sample obtained by injecting hybridoma cells into the abdominal cavity of animals and using the physiological environment of the animal's abdominal cavity to produce antibodies is called ascites sample. The hybridoma cells injected into the animal's abdominal cavity can proliferate and secrete monoclonal antibodies in the abdominal cavity, and the antibodies accumulate in the ascites. Due to the high concentration of monoclonal antibodies accumulated in ascites, these monoclonal antibodies are suitable for large-scale antibody production and purification. But these antibodies may contain impurities, such as animal proteins, hormones, etc., which need to be removed through purification. For example, mouse monoclonal antibody purification services can remove impurities from mouse ascites antibodies.
The liquid containing monoclonal antibodies collected from the culture medium during the cultivation of hybridoma cells is called hybridoma supernatant. Due to the combination of the secretory function of B lymphocytes and the unlimited proliferation ability of myeloma cells, monoclonal antibodies are often secreted into the culture medium during the in vitro cultivation of hybridoma cells. Although the concentration of monoclonal antibodies in the hybridoma supernatant is relatively low, the purity of monoclonal antibodies in the hybridoma supernatant is relatively high because it does not come from the complex physiological environment in animals. The hybridoma supernatant is suitable for small-scale antibody production, but further purification is required for large-scale preparation.
Purification methods and applications of antibodies
High purity antibodies can be isolated from the complex by purifying the antibodies. Common antibody purification methods include antibody affinity purification and antibody separation and purification, including Protein A/G purification, ion exchange chromatography, gel filtration, precipitation, and hydrophobic interaction chromatography. Among them, Protein A/G affinity purification service is an antibody affinity purification method widely used in the purification of various antibodies. It purifies antibodies by specifically binding Protein A of Staphylococcus aureus or Protein G of Streptococcus to the Fc segment of the antibody. Moreover, Protein A has high affinity for IgG from various species, and Protein G also has strong antibody binding ability. Protein A or Protein G is loaded into the chromatography column, and then the sample containing the antibody is loaded into the chromatography column. The antibody can bind to Protein A or Protein G. After washing the chromatography column with buffer, unbound impurities will be washed away. Then, the antibody is eluted with acidic buffer, and the pH of the eluent is adjusted to neutral to obtain purified antibody. Protein A/G affinity purification service is easy and fast to operate, suitable for large-scale antibody purification.
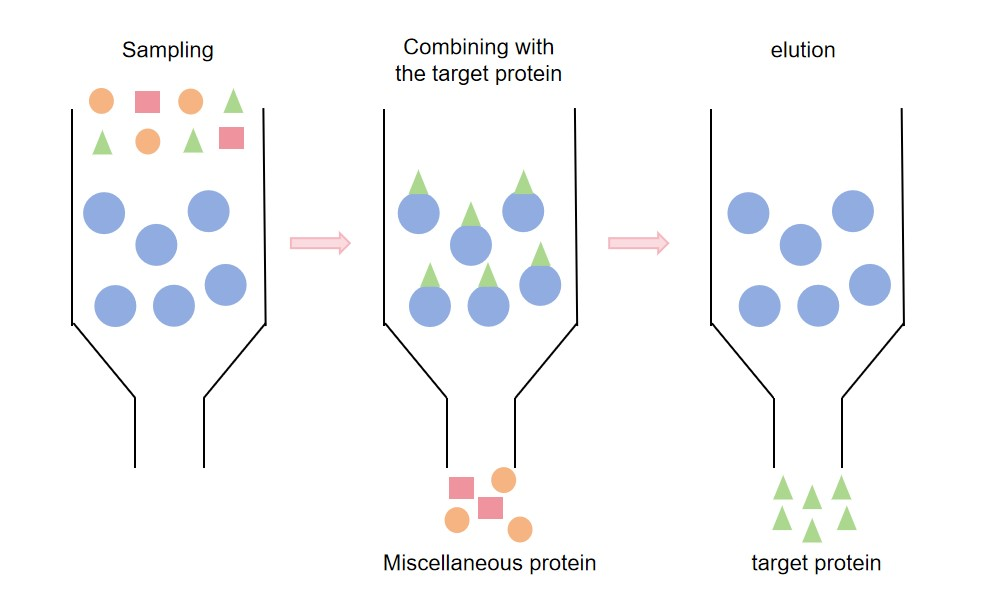
Fig. 1 Principle diagram of antibody affinity purification
Antibodies are essentially immunoglobulins composed of amino acids with acidic or alkaline side chains that can be ionized into ions in a buffer solution at a certain pH. Ion exchange chromatography is a method of separating and purifying antibodies by adjusting the pH and salt concentration of the ion exchange column, allowing them to interact with the stationary phase on the column. This method is suitable for removing impurities and obtaining high-purity antibodies.
The pore size of gel filtration column is different. Antibodies as macromolecules move slowly in the gel filtration column, while salts and small molecular impurities move faster. Antibodies can be separated and purified through different molecular sizes. The gel filtration purification method is suitable for separating macromolecular proteins, such as antibodies and some enzymes, from mixtures.
There are certain differences in physical or chemical properties between antibody proteins and other proteins. Precipitation method can change physical or chemical conditions, such as increasing salt ion concentration, adding organic solvents, etc., to precipitate antibodies in the form of precipitation and separate them from other impurities. The ammonium sulfate precipitation method is a commonly used precipitation method, suitable for preliminary purification or concentration of large amounts of antibodies.
The hydrophobic groups on the surface of antibodies will bind to the hydrophobic ligands on the stationary phase in high salt solutions. Hydrophobic interaction chromatography is a method of elution and purification of antibodies by gradient reduction of salt concentration, commonly used for the purification of high-purity monoclonal antibodies.
KMD Bioscience has been committed to antibody production research for many years, providing customers with quality assured antibody and recombinant protein products and services. We can customize antibodies with high efficacy, strong specificity, and good stability. KMD Bioscience has a variety of antibody purification instruments and equipment, which can provide antibody purification services from various sources such as rabbit, sheep, chicken, and mouse monoclonal antibodies, as well as Protein A/G affinity purification services and antibody separation and purification services. And we will choose the purification method based on the specific purpose of the customer. Based on the comprehensive platform system construction of antibody platform, protein platform, etc., we cover the upstream and downstream services of antibody production, and can provide technical services from antibody preparation, antibody affinity purification and antibody separation and purification, antibody sequencing, etc.
Reference
[1] Fishman JB, Berg EA. Antibody Purification and Storage. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2019;2019(5).
[2] Hober S, Nord K, Linhult M. Protein A chromatography for antibody purification. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2007;848(1):40-7.
[3] J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2007;848(1):19-27.