2025-04-08 Hits(70)
Western Blotting
Introduction to Protein Western Blot
Western Blot (WB) is one of the commonly used techniques for qualitative and quantitative detection of protein expression. The main purpose of Western Blot is to detect whether a certain protein (i.e. the target protein) is expressed in the sample (tissue or cells) and the relative abundance of expression. Specific antibodies are used to identify and bind target proteins in cells or biological tissue samples treated by gel electrophoresis.
This technique combines the high resolution and high specificity of both SDS-PAGE and solid phase immunoassay, and is a convenient and reliable research tool in the field of protein research.
The Principle of Protein Western Blot
The method uses SDS-PAGE technology to separate protein molecules on a gel according to their molecular weight in a biological sample, and then transfer these proteins to a solid phase membrane by means of electrical transfer. The protein on the solid phase membrane acts as an antigen and reacts with the corresponding antibody, which then reacts with an enzyme-labeled second antibody. Finally, the proteins expressed by specific target genes isolated by electrophoresis are detected by means of substrate color development or fluorescence imaging .
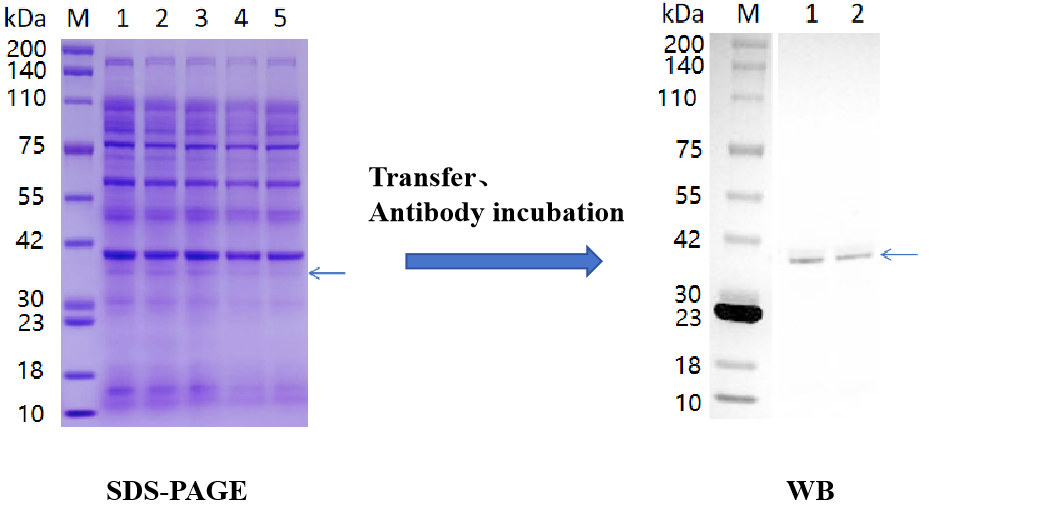
Figure 1:Results of major curlin subunit protein expression identification
\
Western Blot Protocol
(1) Sample preparation: Cells containing the target protein must be completely lysed to ensure adequate protein release while removing non-protein components. Good sample preparation ensures that the target protein is intact for downstream analysis.
(2) Electrophoresis: SDS-PAGE electrophoresis separates proteins in samples and can be used to estimate the molecular weight of proteins.
(3) Transfer: The protein separated by electrophoresis is transferred from the gel to the imprinted membrane and immobilized. Electrotransfer is the most common transfer method in protein immunoblotting, even though an electric field force drives the protein to elution from the gel to the membrane. In this process, the membrane and gel are placed together and filter paper is placed between the two electrodes. When a voltage is applied between the electrodes, the protein migrates to the membrane under the action of an electric field force.
(4) Antibody incubation: After transferring the protein from the gel to the membrane, the target protein antibody (primary antibody) is incubated with the membrane to enable the primary antibody to recognize its target. Then, a second incubation is performed with a secondary antibody (labeled) that can bind to the primary antibody for color analysis.
(5) Image acquisition: The physical signal on the imprinted membrane is converted into a visual protein strip, and then the molecular weight and relative abundance of the protein strip are analyzed. The traditional method is to use film to capture the protein signal on the imprinted membrane, which is generated by colorimetry or a chemiluminescence substrate. The naked eye can only estimate the relative protein abundance roughly, and the film image needs to be converted into a digital image for more accurate analysis in computer software. Digital imagers skip the film imaging step and capture imprinted images directly digitally.
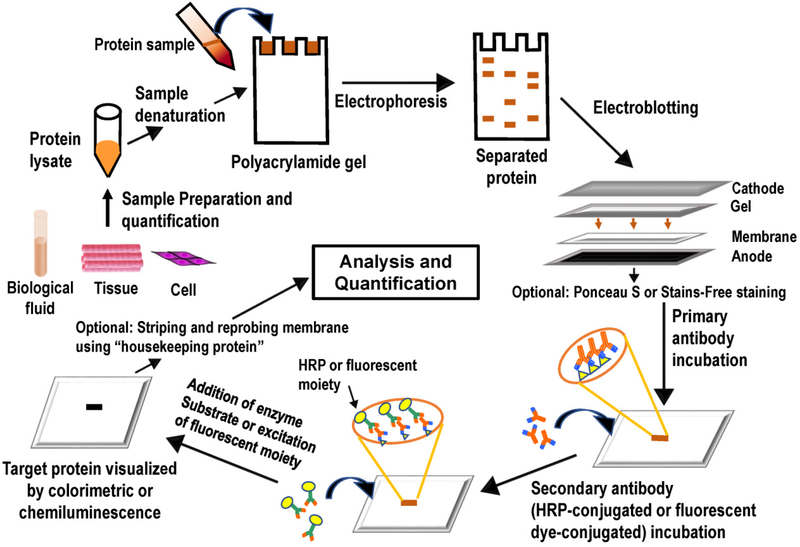
Figure 2:Western Blot process. (Figure source: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28974114/.)
Application of Western Blot
Western Blot is often used to detect the presence, expression level and molecular weight of specific proteins in the sample, which mainly includes the following aspects:
(1) Basic research
Protein expression analysis: Determine the expression of specific proteins in different cell types, tissues, or organs.
Protein modification studies: such as phosphorylation, glycosylation, etc., to study the effects of these modifications on protein function.
Protein interactions: Interactions between proteins are studied by co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) in combination with Western Blot.
(2) Clinical diagnosis
Detection of disease markers: detection of disease-related protein markers in serum, urine, or other body fluids for diagnosis and prognosis of disease.
Pathogen detection: The detection of protein components of specific pathogens for the diagnosis of infectious diseases.
(3) Drug development:
Drug mechanism of action studies: The study of how drugs affect the expression or function of specific proteins.
Biological product quality control: In the biopharmaceutical process, to ensure the purity and activity of the target protein in the product.
Western Blot Common Problems and Solutions
Western Blot common problems can be divided into the following four categories:
(1) No target protein detected. No target protein was present in the sample; The protein is degraded, and PMSF needs to be added to inhibit the protease activity; The antibody can not recognize the target protein, check the antibody information, whether the antibody selection is correct, and whether it can be used for WB verification.
(2) Striped but high background. It may be that the sealing is insufficient, and the solution is to replace the fresh sealing fluid and extend the sealing time. Or washing is not sufficient, the solution is to increase the number of washing and time. This problem can also occur if the concentration of the primary antibody is too high, and the solution is to dilute the antibody to the appropriate concentration. Or if there is a problem with the sample, the solution is to check the purity and quality of the protein sample, and it is recommended to use fresh samples.
(3) Faint bands. Low concentrations of antibodies or antigens may cause weak signals. Increasing exposure time makes the bands clearer.
(4) There are patches or uneven spots on the imprinting. Plaques and uneven spots on imprints are usually caused by improper metastasis. If there are bubbles between the gel and the film, it will appear darker on the film. It is also important to use an oscillator during all incubation processes so that uneven spots do not appear during incubation.
References
[1] Yicheng W , Amp Z Y , Culture C ,et al.Studied on antigens of Toxoplasma gondii cultured in PK-15 cell by SDS-PAGE and Western blot[J].ACTA AGRICULTURAE ZHEJIANGENSIS, 1997.
[2] Richard P .A Reanalysis of IgM Western Blot Criteria for the Diagnosis of Early Lyme Disease[J].Journal of Infectious Diseases, 1999(4):1021-1024.DOI:10.1086/314651.
[3] Cooper S T , Lo H P , North K N .Single section Western blot: Improving the molecular diagnosis of the muscular dystrophies[J].Neurology, 2003, 61(1):93-97.DOI:10.1212/01.WNL.0000069460.53438.38.
[4] Mishra M, Tiwari S, Gomes AV. Protein purification and analysis: next generation Western blotting techniques. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2017 Nov;14(11):1037-1053. doi: 10.1080/14789450.2017.1388167. Epub 2017 Oct 13. PMID: 28974114; PMCID: PMC6810642.