2024-12-20 Hits(83)
Aptamer
Small molecule aptamers refer to DNA or RNA single strand oligonucleotide sequences with high affinity and high specificity to specific small molecule targets that are screened from random sequence libraries by SELEX technology, and can also be peptides. After years of development, KMD Bioscience has great technical advantages in aptamer selection.
With the continuous development and improvement of aptamer technology, the application prospect of small molecule aptamer in the field of biomedicine and medicine research and development will be broader. Small molecule aptamers have important application value in medicine research and development. By obtaining highly specific aptamers for specific small molecules, it can provide important basis for medicine design and optimization, and accelerate the development process of new medicines. In the targeted therapy of diseases such as cancer, aptamers can bind specifically to specific antigens or receptors on the surface of tumor cells, thus achieving precise treatment. KMD Bioscience can provide customized peptide aptamer screening services according to the different experimental and application needs of customers.
Aptamer Type
According to the type of molecule, aptamers can be divided into two main categories: nucleic acid aptamers and peptide aptamers. Nucleic acid aptamers can be divided into DNA aptamers and RNA aptamers. Both nucleic acid aptamers and peptide aptamers have high specificity and affinity for target molecules.
|
Type |
Constitution |
|
DNA Aptamers |
Consists of short strands of single-stranded DNA molecules. Can be folded to form a specific three-dimensional structure. |
|
RNA Aptamers |
Consists of short strands of single-stranded RNA molecules. Can be folded to form a specific three-dimensional structure. |
|
Peptide Aptamers |
A short peptide composed of amino acids. It is usually fixed on a stable protein scaffold (such as thioredoxin) to increase its binding force and stability with the target. |
Aptamer Selection
Small molecule aptamer screening techniques generally include the following steps:
A. Initial library design: Build a DNA, RNA or peptide library containing a large number of random sequences that have the potential to bind to small target molecules.
B. Screening process: The main steps include target binding to the library, isolation and purification of the binding target molecule aptamer PCR amplification, iterative screening and so on. After each round of screening, the screening results can be verified and analyzed through technologies such as sequencing.
C. Optimization and validation: The selected aptamers were optimized to improve their affinity, specificity and stability. Subsequently, a series of experiments were carried out to verify its binding ability and application effect.
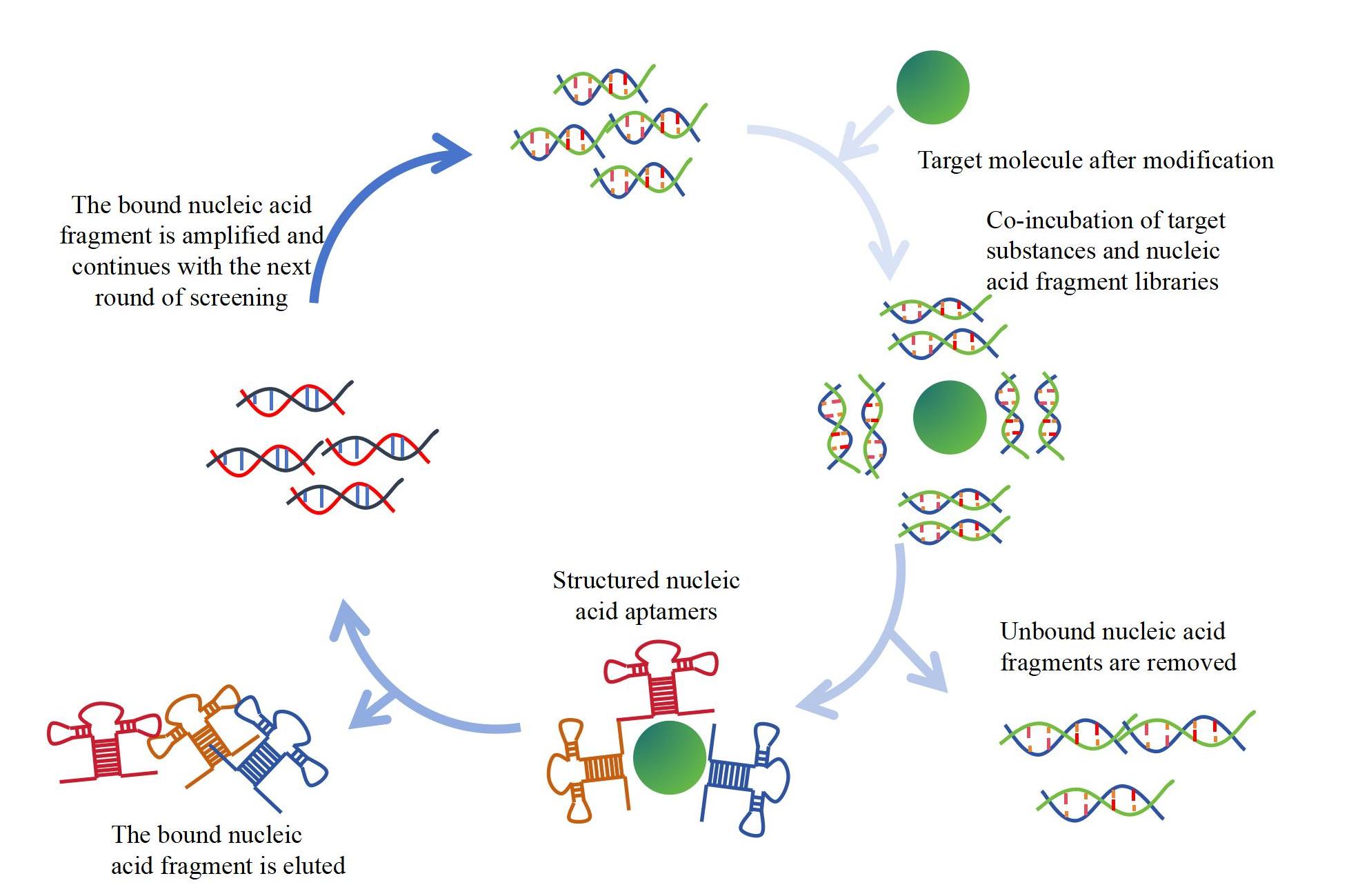
Aptamer Screening Techniques for Small Molecule
Small molecule aptamer screening techniques can be used in a variety of specific ways, Including the following content:
A. SELEX technology
SELEX technology is an in vitro screening technique. Through multiple screening processes, aptamer sequences (peptide aptamers, DNA aptamers, RNA aptamers) that can efficiently bind to target small molecules can be selected from initial libraries containing a large number of random sequences. This technique has become a classic method for aptamer selection since it was proposed by Tuerk and Ellington in 1990.
Features:
a. High specificity.
b. High affinity.
c. Suitable for many types of small molecule targets.
B. Solid phase adsorption and elution techniques
It is often used for aptamer screening of soluble small molecules. The library was fixed on a solid phase carrier, incubated with the target small molecule, washed away the unbound sequences, and collected the bound aptamers for subsequent analysis.
Features:
a. Easy to operate.
b. Efficient screening.
c. Wide application.
C. Centrifugal precipitation method
Aptamer screening for larger particles such as cells, bacteria and viruses. The aptamer is obtained by separating the particles with aptamer by centrifugation.
Features:
a. Fast and efficient.
b. Easy operation.
c. High degree of automation.
D. FluMag-SELEX technique
A method for screening fluorescent aptamers by combining magnetic beads with SELEX technique. The method requires a small number of targets and the amount of binding aptamers can be directly measured by fluorescence, which is suitable for the screening of small molecule targets.
Features:
a. Small number of targets.
b. Intuitive.
c. High efficiency.
Capillary electrophoresis SELEX (CE-SELEX) can screen high-affinity aptamers in 2-4 rounds, and is often used to screen proteins, lipopolysaccharides, polypeptides and other macromolecules. This method utilizes the difference in electrophoretic mobility caused by the difference in charge to mass ratio between different components to achieve separation. By adjusting electrophoresis conditions and screening parameters, aptamers with high affinity binding to the target can be screened.
Features:
a. Fast separation.
b. High sensitivity.
c. Multiple rounds of screening.
.png)
Development Prospect of Peptide Aptamer
With the continuous progress of biotechnology and computing technology, small molecule aptamer screening technology will play an important role in more fields. For example, in drug development, aptamers can be used as potential drug targets or drug carriers to improve the targeting and bioavailability of drugs. In disease diagnosis and treatment, aptamers can be used as biomarker detection tools or targeted therapeutic drugs. In biosensing technology, aptamer sensors can achieve highly sensitive and selective detection.
Small molecule aptamer screening technology is a technology with important application value, and its continuous development will bring more innovations and breakthroughs for biomedical research and clinical applications.
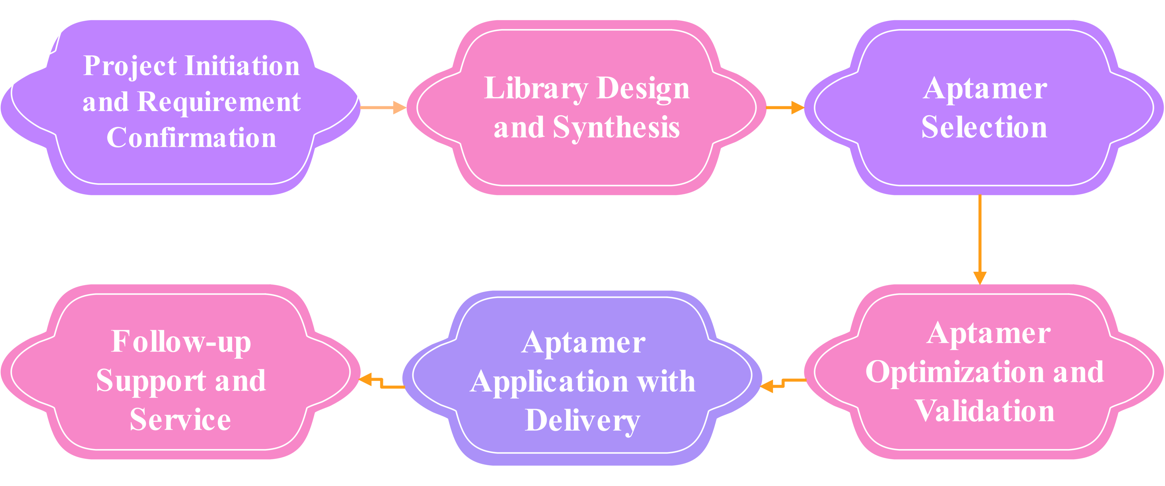
Aptamer Screening for Small Molecule Service Process
Reference
[1]. Chauveau F, Pestourie C, Tavitian B. Les aptamères ou l'évolution moléculaire dirigée: sélection et applications [Aptamers: selection and scope of applications]. Pathol Biol (Paris). 2006;54(4):251-258.
[2]. Yu H, Alkhamis O, Canoura J, Liu Y, Xiao Y. Advances and Challenges in Small-Molecule DNA Aptamer Isolation, Characterization, and Sensor Development. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021;60(31):16800-16823.
[3]. Dong Y, Zhang T, Lin X, et al. Graphene/aptamer probes for small molecule detection: from in vitro test to in situ imaging. Mikrochim Acta. 2020;187(3):179. Published 2020 Feb 19.