2025-03-26 Hits(106)
Aptamer
Nucleic acid aptamer is an oligonucleotide sequence (DNA or RNA) consisting of 20-110 nucleotides. Aptamers have high molecular recognition ability for different types of targets such as nucleic acids, proteins, cells, and some small molecules. They can also distinguish subtle differences and have high affinity and specificity, making them easy to chemically modify. Nucleic acid aptamers are typically obtained from nucleic acid molecular libraries using in vitro screening techniques, namely the Exponential Enrichment Ligand System Evolution (SELEX) technique, to obtain oligonucleotide fragments. The structure and function of nucleic acid aptamers are similar to antibodies, but they are smaller in size, shorter in production time, lower in cost, and easier to synthesize. Based on their ability to specifically bind to multiple target molecules, nucleic acid aptamers are widely used in fields such as food safety, environmental monitoring, and biomedical research. Nucleic acid aptamers can be used for drug development to design drugs targeting specific molecules. Many nucleic acid aptamers are used to make biosensors that can diagnose specific infectious diseases. Nucleic acid aptamers can serve as carriers to deliver genes to specific cells or tissues, and have certain application prospects in gene therapy. Due to the fact that nucleic acid aptamers can be prepared and screened in vitro, the possibility of contamination is relatively small, and nucleic acid aptamers do not have immunogenicity, so they will not cause rejection reactions when used as therapeutic drugs.
Screening of nucleic acid aptamers based on SELEX technology
The screening of nucleic acid aptamers is mainly based on SELEX technology. The basic principle of SELEX aptamer library screening is to synthesize a single stranded oligonucleotide library in vitro, and then incubate the target molecule in an oligonucleotide library containing approximately 10^15 different sequences. The oligonucleotides that have not bound to the target molecule are washed away with deionized water to separate them, and then eluted with a high concentration salt solution to obtain oligonucleotides that can bind to the target molecule. The oligonucleotides that can bind to the target molecule are amplified by PCR, and then the next round of screening is carried out. The above steps are repeated to achieve multiple rounds of screening, each round of screening including binding to the target molecule, separating unbound sequences, and amplifying bound sequences. The number of nucleic acid aptamers that can bind to the target molecule gradually increases with the increase of screening rounds, and the specificity also increases with repeated screening processes. Finally, oligonucleotide sequences that highly specifically bind to the target molecule are screened out. When screening RNA nucleic acid aptamers through RNA aptamer library synthesis services, RNA needs to be reverse transcribed into DNA before subsequent SELEX aptamer library screening. The advantage of DNA aptamer library synthesis service lies in the stability of DNA nucleic acid aptamers themselves, while the RNA nucleic acid aptamers prepared by RNA aptamer library synthesis service have stronger affinity and specificity for target molecules.
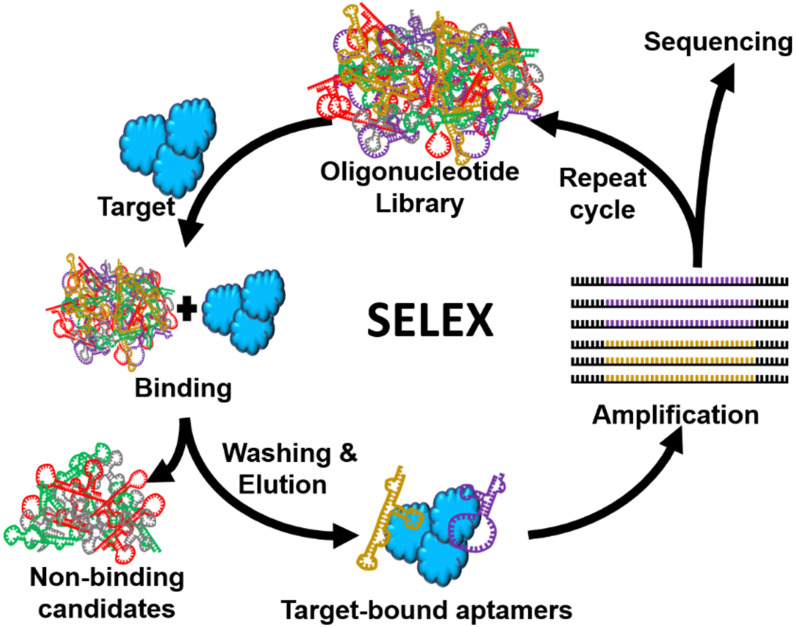
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of nucleic acid aptamer screening based on SELEX technology
When screening nucleic acid aptamers, insufficient repetition may result in lower specificity and affinity of the aptamer. Therefore, with the continuous development of technology, traditional SELEX aptamer library screening techniques have been continuously improved and a series of related technologies have been derived. IP-SELEX is a SELEX technology coupled with immunoprecipitation. Cell SELEX operates at the cellular level and is suitable for screening and recognizing aptamers for cell surface molecules. Apta Seq combines high-throughput sequencing technology to simultaneously screen large-scale libraries, greatly improving screening efficiency. In addition, AFM-SELEX using atomic force microscopy and CE-SELEX using capillary electrophoresis have greatly improved the success rate of SELEX technology. The screening of nucleic acid aptamers is mainly aimed at discovering specific nucleic acid sequences that bind with high affinity to the target molecule. The nucleic acid aptamers obtained through screening can provide new ideas for drug development in disease treatment, improve the accuracy and sensitivity of disease diagnosis, and promote further development of gene therapy technology.
Antigen types screened for nucleic acid aptamers:
The antigens that can be used for nucleic acid aptamer screening mainly include peptides, proteins, viruses, bacteria, cells, tissues, and small molecule substances. Peptides and proteins have complex structures and functions, and nucleic acid aptamers can bind to proteins with high affinity and specificity. Viruses and bacteria, as common pathogens, have complex structures and antigenic epitopes. Nucleic acid aptamers can bind to it for the detection and diagnosis of viruses and bacteria. The composition of cells and tissues is complex and there are interactions between them. Cell SELEX technology can directly screen nucleic acid aptamers that bind to specific cells or tissues, which can be used for cell recognition and disease diagnosis. Small molecule substances such as drugs and metabolites typically have lower molecular weights and simpler structures. Therefore, higher precision and specificity are necessary for designing nucleic acid aptamers that bind to small molecules.
Table 1. Comparison of different antigen types screened for nucleic acid aptamers
|
Antigen type |
Characteristic |
Difficulties in screening |
Application area |
|
Small molecule substances |
Low molecular weight and simple structure |
High precision and specificity requirements |
Drug testing, metabolite analysis |
|
Peptides and proteins |
Complex structure and diverse functions |
Specific binding |
Protein testing, disease diagnosis |
|
Viruses and bacteria |
Complex surface structure and diverse antigenic epitopes |
High affinity and high specificity binding |
Pathogen detection and treatment |
|
Cells and Tissues |
Complex composition and existence of interactions |
Nucleic acid aptamers that bind to cells or tissues are directly screened |
Cell recognition, disease diagnosis |
KMD Bioscience is committed to providing customers with high affinity and high specificity nucleic acid adapter screening technology services, which can provide strong support for downstream research and development work such as adapter function validation, in vivo function validation, and development of targeted specific molecular drugs, including affinity validation, competitive ELISA validation, in vitro targeted cell function validation, in vivo targeted inhibition function validation of aptamers, and signal pathway blockade function validation. KMD Bioscience has years of project experience and insights in SELEX technology for nucleic acid aptamer screening. After years of development, KMD Bioscience has established a comprehensive nucleic acid aptamer screening system, which can provide customers with high-quality nucleic acid aptamer screening services for targets such as proteins, peptides, amino acids, and small molecule compounds, including RNA aptamer library synthesis services and DNA aptamer library synthesis services. The nucleic acid aptamer library established by KMD Bioscience has a capacity of 10^10-10^11, which is sufficient to screen small molecule nucleic acid aptamers targeting various targets and meeting downstream experimental needs of customers. Through 6-10 rounds of pressure screening, we can obtain high affinity and high specificity nucleic acid aptamers. Based on the SELEX technology platform, the affinity of nucleic acid aptamers screened by KMD Bioscience can reach the nM-pM level. KMD Bioscience can also provide a variety of downstream validation experiments, including but not limited to affinity validation of nucleic acid aptamers, competitive ELISA validation, flow cytometry blocking validation, etc. Customers only need to provide screening targets and project requirements. KMD Bioscience's scientists provide reasonable customized solutions based on customers' project requirements to solve their scientific research problems.
Reference
[1] Wang T, Chen L, Chikkanna A, et al. Development of nucleic acid aptamer-based lateral flow assays: A robust platform for cost-effective point-of-care diagnosis. Theranostics. 2021;11(11):5174-5196.
[2] Park KS. Nucleic acid aptamer-based methods for diagnosis of infections. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018;102:179-188.
[3] Quarles JD, Livingston AT, Wood AE, et al. Preparation of Nucleic Acid Aptamer Functionalized Silver/Gold Nanoparticle Conjugates Using Thiol-Substituted Oligonucleotides. Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2709:131-147.