Service Line:+86-022-82164980
Address:FL-4, Building A5, International Enterprise Community, Tianjin, China
Email:[email protected]
KMD Bioscience has been dedicated to protein interaction research for many years. Protein interaction, an important direction in protein structure and function research, can reveal the interaction mode between molecules. KMD Bioscience, which can express recombinant proteins with GST, Myc-tag, Flag-tag, HA-tag and other tags in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic expression systems, has rich experience in recombinant protein expression. KMD Bioscience has sophisticated testing equipment and mature technology that are from Kyoto University, Japan. The co-immunoprecipitation and Pull Down technologies of KMD Bioscience come from Kyoto University's IPS laboratory in Japan, which ensures the accuracy of the experiments. KMD Bioscience, which insists on providing customers with high quality pull down assay service, is able to provide one-stop technical services from recombinant protein preparation to dna protein pull down, rna protein pull down to meet the needs of different customers.
Pull Down assay experiment, a technology to detect molecular interactions in vitro conditions, which is used to verify protein-protein interactions or to screen for target proteins. Pull down assay experiment is similar to co-immunoprecipitation technology, except that co-immunoprecipitation technology uses antibodies to cross-link magnetic beads or agarose, whereas this technology utilizes protein-protein and protein-other biomolecule (dna protein pull down, rna protein pull down) interactions for the capture and study of the target molecules. The principle is that the tagged bait protein is captured by a solidified affinity ligand that specifically binds to the tag, generating a "secondary affinity support" that is used to purify other proteins that interact with the bait protein. Proteins interacting with the decoy protein can be detected by SDS-PAGE electrophoresis, or by further characterization of the purified and eluted protein complexes in combination with Western blot validation and LC-MS/MS.
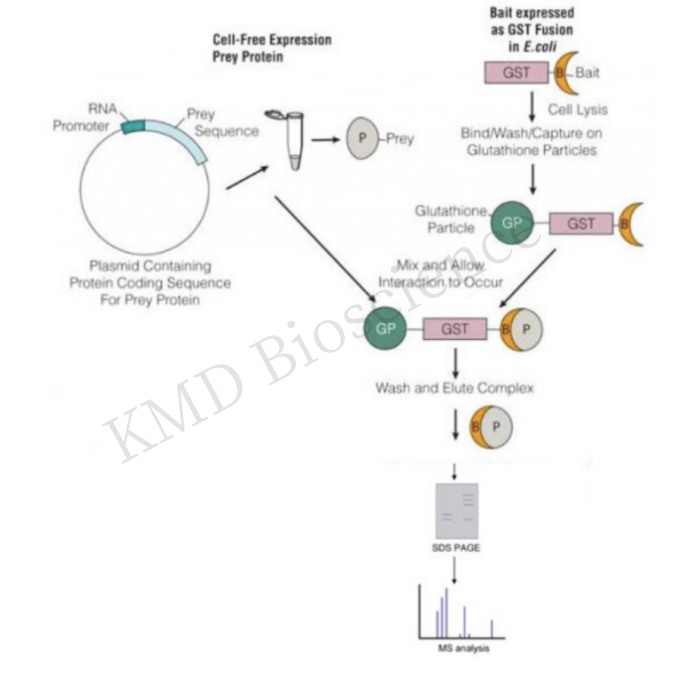
KMD Bioscience has established and improved the GST pull down assay technology, streptomycin labeling pull-down technology, CO-IP technology, Chip-qPCR technology and other immunology-based detection technology service system, among which pull down technology and streptomycin labeling pull-down technology are used for protein and nucleic acid research, DNA pull down, RNA pull down, respectively.
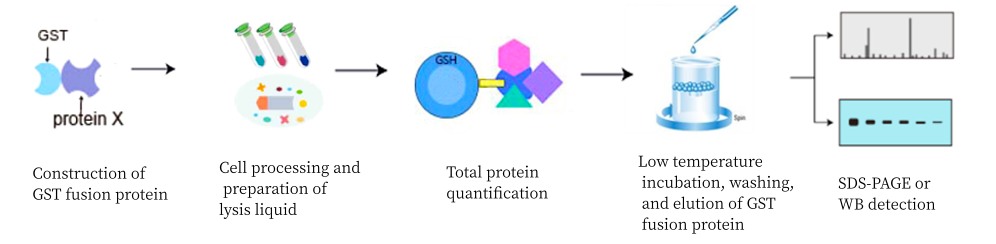
GST Pull down, also called protein binding assay in vitro, is a method of verifying or finding interactions between proteins under in vitro conditions.
|
GST Pull Down Assay Experiment |
|
|
Experimental principle |
This technology utilizes the affinity of GST for glutathione (GSH)-coupled spherical beads, firstly, recombinant expression technology is used to express "bait" proteins tagged with GST (glutathione transferase), and then the bait proteins are incubated with cell lysates to capture target molecules able to bind to the bait proteins, and then agarose beads tagged with GSH are added, and the GSH catalyzes the linkage of the protein complexes onto agarose beads under the catalytic effect of GST, and then low-speed centrifugation is used to collect the above complexes for subsequent analyses, such as SDS-PAGE. |
|
Applications |
*Demonstrate predicted possible protein-protein interactions *Search for unknown molecules that interact with known proteins |
|
Advantages |
*Mostly use labeled (e.g., GST) antibodies for detection, which is widely applicable *Simple to use and an effective method for direct detection of protein interactions |
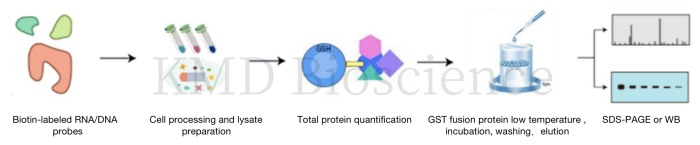
RNA pull down and DNA pull down are important technique for studying RNA or DNA-protein interactions under in vitro conditions.
|
RNA/DNA Pull Down Experiment |
|
|
Experimental principle |
*The technique involves the in vitro transcription of a portion or the full length of the target RNA, labeled with a biotin-labeled RNA/DNA probe, and incubated with cytoplasmic protein extracts to form RNA/DNA-protein complexes. The above complexes are then separated from the cell lysate using streptavidin-labeled magnetic beads or agarose beads. Then elution, SDS-PAGE or silver staining are performed to verify the target molecules |
|
Applications |
*Verification of whether a protein interacts with the target RNA/DNA *Purified proteins can be screened for binding to target RNA by mass spectrometry identification |
|
Advantages |
*The technique is a common method for capturing RNA/DNA-protein complexes *Enables validation or screening of interacting proteins for target RNA or DNA, such as validation or searching for transcription factors for specific genes |
F1: How to distinguish the expression of proteins?
A1: After the ultrasonic bacterial solution was observed, the bacterial solution expressed in the supernatant was clear and less precipitated; In the case of inclusion bodies, the bacterial fluid is cloudy and precipitated, and eventually SDS-PAGE results prevail.
F2: The expression mode of protein is inclusion body, can we continue the GST pull down assays
A2: The functional conception of the protein can be restored and subsequent experiments can be continued. Protein denaturation is refolded by removing denaturants through the high concentrations of urea and guanidine hydrochloride.
F3: GST pull down the background of the result
A3: It may be related to non-specific binding. ------->Solution: Increase the number of elution steps and change the elution conditions.
F4: GST pulls down the banding blur of the result
A4: It was related to insufficient elution conditions or low protein purity. ------->Solution: Increase the concentration of eluent to increase the protein content. You can also improve the purity of the protein to prevent this from happening.
F5: Why do false positives appear in GST pull down
A5: Related to non-specific adsorption. ------->Solution: Add more non-ionic detergent, and pre-treat GST beads with a specific pH buffer, 0.1% Tween-20 (or other detergent).
F6: The Co-IP verification results showed protein interaction, but the GST pull-down verification proteins did not interact
A6: Co-IP can only verify the protein interaction in vivo. If the interaction is not detected, other proteins may participate; GST pull-down verifies the direct interaction of two proteins in vitro, if any Protein participations, GST pull-down can’t be verified.
F7: Can complementary strands of DNA be used to verify each other in DNA pull-down assays
A7: The DNA-pull down assays are to study the interaction between DNA and proteins, and can’t be used to verify that DNA and complementary DNA strands are fishing each other.
F8: Whether double-stranded or single-stranded DNA is used in the DNA-pull down experiment
A8: The conventional approach is to use DNA double strands as probes.
F9: Treatment of samples in RNA Pull down
A9: To avoid RNA degradation and affect the accuracy of experimental results. ------->Solution: Adding protease and RNase inhibitors during cell lysis, repeated freezing and thawing 2-3 times. Ultrasonic treatment of plant tissue samples. The above reagent consumables need to be treated with RNA enzyme.
F10: How to determine the result of mass spectrometry identification
A10: The protein identified by mass spectrometry is mainly screened according to the score. ------->Solution: The proteins sent for mass spectrometry detection are all the proteins screened by the pull-down experiment. If the proteins are sequenced for detection, the number of characteristic peptide segments of the identified proteins is generally used as a reference.
If you have any questions regarding our services or products, please feel free to contact us by E-mail: [email protected] or Tel: +86-022-8216-4980;