Service Line:+86-022-82164980
Address:FL-4, Building A5, International Enterprise Community, Tianjin, China
Email:[email protected]
Apolipoprotein (Apo) is the protein associated with the largest component of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) and plays the most important role in lipoprotein metabolism, such as participating in the transport of plasma aqueous mediators, hydrophobic molecules on the cell surface, and binding to specific receptors to correctly direct lipids as well as target organs and body tissues. The five main classes include A, B, C, D, and E. Most of them are synthesized in the liver (some in the small intestine). The most important of these are Apolipoprotein A and Apolipoprotein B. The two main types measured are ApoAI and ApoB.
Apolipoprotein AI (ApoAI), the 11th most abundant protein in human serum, is the major structural scaffold and binding ligand for high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-CHOL), representing approximately 45% of the molecular weight. With 15 different protein forms, human serum apolipoproteins help transport excess cholesterol from peripheral tissues back to the liver for metabolism, known as reverse cholesterol transport (RCT), and play a central role in lipid metabolism. Like HDL-CHOL, ApoAI is strongly associated with cardiometabolic health indicators and coronary heart disease (CHD) risk, mediating cholesterol transport and inflammatory, immune and vasodilatory pathways. Survival or risk can be assessed in patients with heart disease and peripheral vascular disease.
Apolipoprotein B (ApoB) is synthesized by the liver, and more than 90% of plasma apoB is present in LDL. apoB accounts for approximately 95% of the structural components of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-CHOL), and therefore the total apoB concentration inversely and better reflects the sum of the potentially atherogenic (AS) particles in the coronary arteries.
KMD Bioscience provides high-quality antibody discovery services starting from phage antibody display technology platform, and establishes stable cell line construction and screening, natural protein extraction and fermentation, recombinant protein customized expression services, and multi-species antibody discovery platform. As a raw material supplier of in vitro diagnostics, KMD Bioscience is committed to the rapid development and large-scale production of proteins and antibodies for in vitro diagnostics. Based on the above platforms, KMD Bioscience successfully develops many recombinant proteins, antibodies, antibody drug target proteins, industrial enzymes, diagnostic raw materials and other related reagents for scientific research and new drug discovery. KMD Bioscience adheres to independent innovation and breakthroughs in key technologies, and has successively obtained the national patent pilot unit and laboratory ISO9001:2015 quality management system certification and adheres to the continuous optimization to effectively ensure the quality stability of the products in the production process and final delivery. All antibodies provided by KMD Bioscience are rigorously tested to ensure their purity and sensitivity for use in a variety of different diagnostic platforms, such as LFIA, ELISA, CLIA, POCT, and so on.
Molecular structure of ApoAl and ApoB
Apolipoprotein Al (ApoAl) in human serum is a single polypeptide chain consisting of 243 amino acid residues, with an N-terminal of aspartate and a C-terminal of glutamine, and a molecular mass of 28.3 kDa. ApoAl contains more than 55% a-helical structure, i.e., bound lipids. It consists of 22 amino acid residues in a tandem repeating helical fragment with proline linkage between the fragments. In addition, ApoA1 contains 2 repeats consisting of 11 amino acid residues.
Apolipoprotein B (apoB) is a class of larger glycoproteins synthesized in the human small intestine and liver and is a structural and functional component essential for the assembly of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins. It is present in plasma in two main forms: apoB-48 and apoB-100, both encoded by a single gene with a long mRNA. apoB-48 is produced as a result of editing of the apoB-100 m RNA and is one of the apolipoproteins of celiac microsomes (CM), and apoB100 is one of the apolipoproteins of very-low-density-lipoprotein (VLDL) and low-density-lipoprotein (LDL). LDL) one of the apolipoproteins. The ApoB we usually measure usually refers to ApoB100.
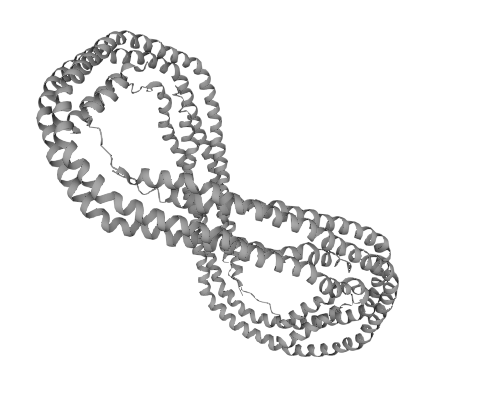
Figure 1 Molecular structure of ApoAI
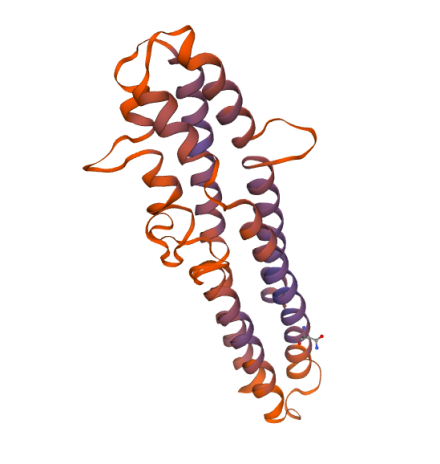
Figure 2 Molecular structure of ApoB
Biological functions of ApoAl and ApoB
The most important function of apolipoprotein Al (ApoAl) is to interact with intracellular receptors and participate in cholesterol esterification, transport and lipoprotein metabolism. Activation of lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) plays an important role in the removal of lipids from tissues and in the fight against atherosclerosis. Plasma aPOAI levels are negatively correlated with coronary heart disease and atherosclerosis, making ApoAl a test for atherosclerosis.
Apolipoprotein B (apoB) plays an important role in lipid metabolism, cholesterol transport, absorption and metabolism as a carrier for transporting triglycerides and cholesterol. Lipoproteins containing apoB are biomarkers for cardiovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis. Mutations in this gene or its regulatory region can lead to hypobeta-lipoproteinemia, normotriglyceride hypobeta-lipoproteinemia, and hypercholesterolemia.Apo B is superior to LDL-CHOL in predicting ischemic heart disease, myocardial infarction, any ischemic cardiovascular event, and any nonfatal ischemic cardiovascular event.
Biological significance of the ApoB/apoAI ratio
ApoB/apoAI ratio: a marker of cardiovascular disease risk factors and a target for therapy.
The ratio of low-density to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C/HDL-C) usually represents the balance of pro- and anti-atherogenic lipids. The ratio of ApoA I and ApoB, as the main components of HDL and LDL, respectively, simply and accurately reflects the level of cholesterol transport in the body. The higher the ratio, the higher the level of cholesterol expression in the blood circulation, which leads to more cholesterol deposition in the blood vessel wall, accelerating the progression of atherosclerosis and the occurrence of cardiovascular events. And the predictive value of this ratio for coronary heart disease is better than traditional lipid indicators.
KMD Bioscience has many years of experience in the research of monoclonal antibody drugs. KMD Bioscience gathers a group of scientists with advanced technology in the field of monoclonal antibodies, and is committed to providing good service for our customers' drug research. Our monoclonal antibody drugs are developed using recombinant antibody technology, using the same sequence as therapeutic antibodies and tested to ensure specific binding to the same target molecules, making them a suitable choice for drug research or analytical development. All antibody products we offer are subject to stringent QC validation and all antibodies are rigorously tested to ensure high purity and quality. Meanwhile, KMD Bioscience's research experts are always looking for newer targets and are committed to providing customers with a wide range of antibody products.
KMD Bioscience independently develops a variety of monoclonal antibody drugs for different targets. KMD Bioscience's monoclonal antibody drugs are only used for scientific research and cannot be used for other purposes.