Service Line:+86-022-82164980
Address:FL-4, Building A5, International Enterprise Community, Tianjin, China
Email:[email protected]
The Phage display technology provides the basis for the development of fully humanized therapeutic antibodies, which is of great significance to antibody medicine research. KMD Bioscience has been researching in the field of antibodies for over 10 years. Our phage display services cover a wide range of library types, as well as customized peptide synthesis services and flexibly effective phage display peptide library screening services according to customers' needs.
Except for diverse premade antibody libraries, KMD Bioscience also carries multiple well-tailored premade peptide libraries ranging from 3- to 20-mer. Currently, we are glad to present our professional service of premade phage display peptide library screening for our customers around the world.
Applications of Phage Display Peptide Library
The Screening of Small Peptides
Small peptides, such as enzyme inhibitors, activators or antagonists of receptors, etc., have important values for basic research and application. Therefore, the search and study of these small peptides has been popular research in biochemistry and pharmacology. Usually, these small peptides can be synthesized by rational in vitro design or isolated from chemically synthesized mixtures. However, the former requires detailed molecular structure information, and the latter is laborious and expensive. In contrast, the phage random peptide library technique allows easy and efficient screening of highly active small peptides and can be performed without knowledge of molecular structure, enriching the desired ligands by specific affinity screening only. This method has been successfully used to screen a variety of molecules for short peptide ligands, such as several highly active enzyme inhibitors: type IV collagenase inhibitors and elastase inhibitors, etc. In addition to the screening of specific enzyme inhibitors, this technique also has applications in the screening of activators of some cytokine receptors.
Antigen Epitope Studies
The antigen epitope is the active center where the antigen binds to the antibody. The study of specific antigen active centers is beneficial to reveal the mechanism of antigen-antibody interaction and lay the foundation for the design of some bioactive medicines. The epitope recognized by anti-peptide antibody usually is the 5-6 amino acid residues in the antigen molecule. Therefore, screening the epitope recognized by an antibody with a phage random peptide library is a very effective method. The antigenic determinant cluster can be generally divided into two cases: linear, in which the binding site of the antigen to the antibody is a continuous sequence of amino acids; and spatial, in which the binding center of the antigen to the antibody is a few amino acids that are close to each other in the spatial conformation of the molecule but discontinuous in the primary structure. In the first case, small peptides that can bind specifically to them can be screened directly from the peptide library with the corresponding antibody, and structural similarity groups can be found from them by sequence analysis of these small peptides. In the second case, the structural analog obtained by antibody screening cannot be directly judged as antigenic mimic epitopes and must be determined by functional analysis.
Synthesis of Artificial Antibodies
The synthesis of monoclonal antibodies has been popular research in antibody engineering. Phage display peptide library technology can get rid of the murine origin of antibody synthesis by hybridoma, make antibody molecules "miniaturized", and can synthesize and screen cloned antibodies without immunization. Currently, there are two main approaches to constructing a phage antibody library. The first is to insert the heavy chain and light chain variable region genes encoding the antibody molecule into the expression vector, and during phage assembly, their expression products are combined to become functional antibodies and displayed on the phage surface. The second is to link the heavy chain and light chain variable region gene fragments with an oligonucleotide encoding a flexible short peptide and insert them into the expression vector, whereupon the products are displayed on the phage surface as heterogeneous single chain antibodies. The second approach is now commonly used.
Phage Display Peptide Library Technology
The phage display peptide library belongs to the biosynthetic peptide library, in which an infectious filamentous phage is used as a vector, and a fragment of a synthetic random DNA sequence is inserted into the gene encoding the shell protein of the vector by genetic engineering. The peptide encoded by this exogenous DNA fragment can be displayed as a fusion protein together with the phage shell protein on the surface coat of a live phage, in addition, maintains relatively independent spatial conformation and biological activity without affecting the ability of this recombinant phage to infect the host bacterium. Only one exogenous random peptide can be displayed on the surface of each phage viral particle, and the collection of all phages displaying different peptides constitutes the phage display peptide library. The constructed phage display peptide library is affinity screened by the target protein (e.g., monoclonal antibody) and then enriched for those recombinant phages that bind to the target protein (i.e., the corresponding phage antigenic peptide). Such phages exhibiting antigenic peptides can proliferate in E. coli. So once a recombinant phage exhibiting a specific peptide is obtained, then this phage can become an unlimited source of specific peptides.
The main advantage of phage display peptide libraries is their low cost, the ability to amplify them in vitro, and the ability to obtain large numbers of target phage peptides simply and rapidly. Theoretically, a phage display peptide library can be screened for any desired peptide sequence from it if it is large enough, and it is possible to screen for certain sequences that simply do not exist in nature.
M13 Phage Display System
Among many phage vehicles currently in application, M13 filamentous phage has always been a more popular option and extensively used in various types of research. M13 is one template bacteriophage of E. coli with a typical long rod appearance containing a single-strand DNA (6407 bp) genome. The viral coat is composed of five different capsid proteins, major capsid pVIII (2700 copies), and four minor capsids (pIII and pVI at one end while pVII and pIX at the other end). Unlike T4 and T7, M13 is a lysogenic phage that is assembled in the periplasm and secreted out of the bacterial membrane without causing host lysis.
M13's multiple capsid proteins provide comprehensive display choices that can be employed to display a variety of peptides and proteins with distinctive characteristics. All five capsids have successfully exhibited foreign domain libraries, each of which makes a unique vector for different features. However, in most cases, pIII and pVIII are the preferred choices for M13 phage display.
Using the M13 filamentous phage capsid protein pIII and PVIII display technology, KMD Bioscience can construct various types of premade phage display peptide libraries containing Dodecapeptide library (12 peptides), Heptapeptide library (7 peptides), and a Cyclic Heptapeptide library (C7C peptide library).
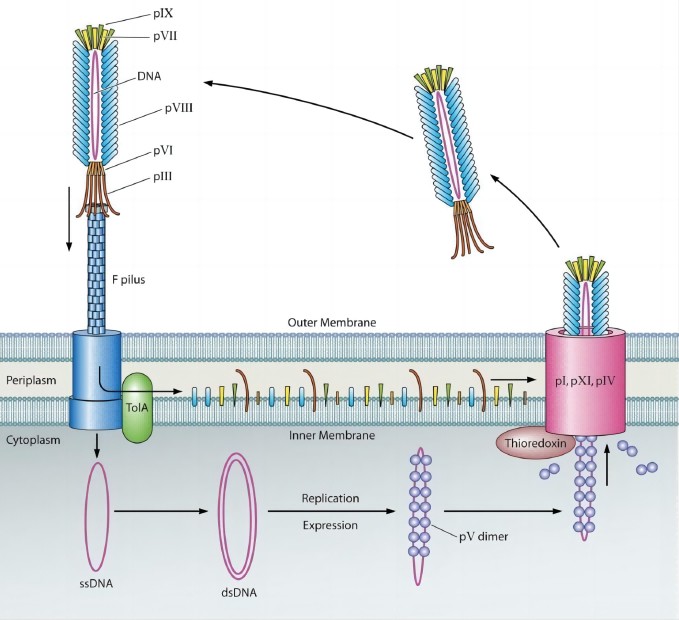
Fig.1 The life cycle of filamentous phages.
Phage Display Peptide Library Screening Services
KMD Bioscience has several carefully prepared premade peptide libraries ranging from 3 to 20 polymersomes. KMD Bioscience offers premade phage display peptide library screening expertise to many clients. KMD Bioscience’s phage display peptide library screening service is an effective means of identifying peptides that bind target molecules and modulate their function. Phage display peptide library can be used for (i) B- and T-cell epitope mapping. (ii) selection of bioactive peptides that bind to receptors or proteins, disease-specific antigen mimics, peptides that bind to non-protein targets, cell-specific peptides, or organ-specific peptides. (iii) development of peptide-mediated medicine delivery systems and other applications.
Phage Display Peptide Library Construction Workflow
|
Process |
Services Content |
|
Nucleotide Sequence Synthesis |
Random synthesis of nucleotide sequences of customer-specified length |
|
Polymerization and Digestion |
Polymerization and digestion of the synthesized DNA sequence |
|
Electroconversion Libraries Preparation |
ER2738 host bacteria were prepared, and then E. coli was transformed with the well-constructed recombinant plasmid |
|
Peptide Library Size and Diversity Detection |
Detection of peptide library size by colony counting and peptide library diversity by sequencing |
|
Phage Display Peptide Library Preparation |
By infecting the M13 phage packaging peptide library |
Phage Display Peptide Library Screening Process
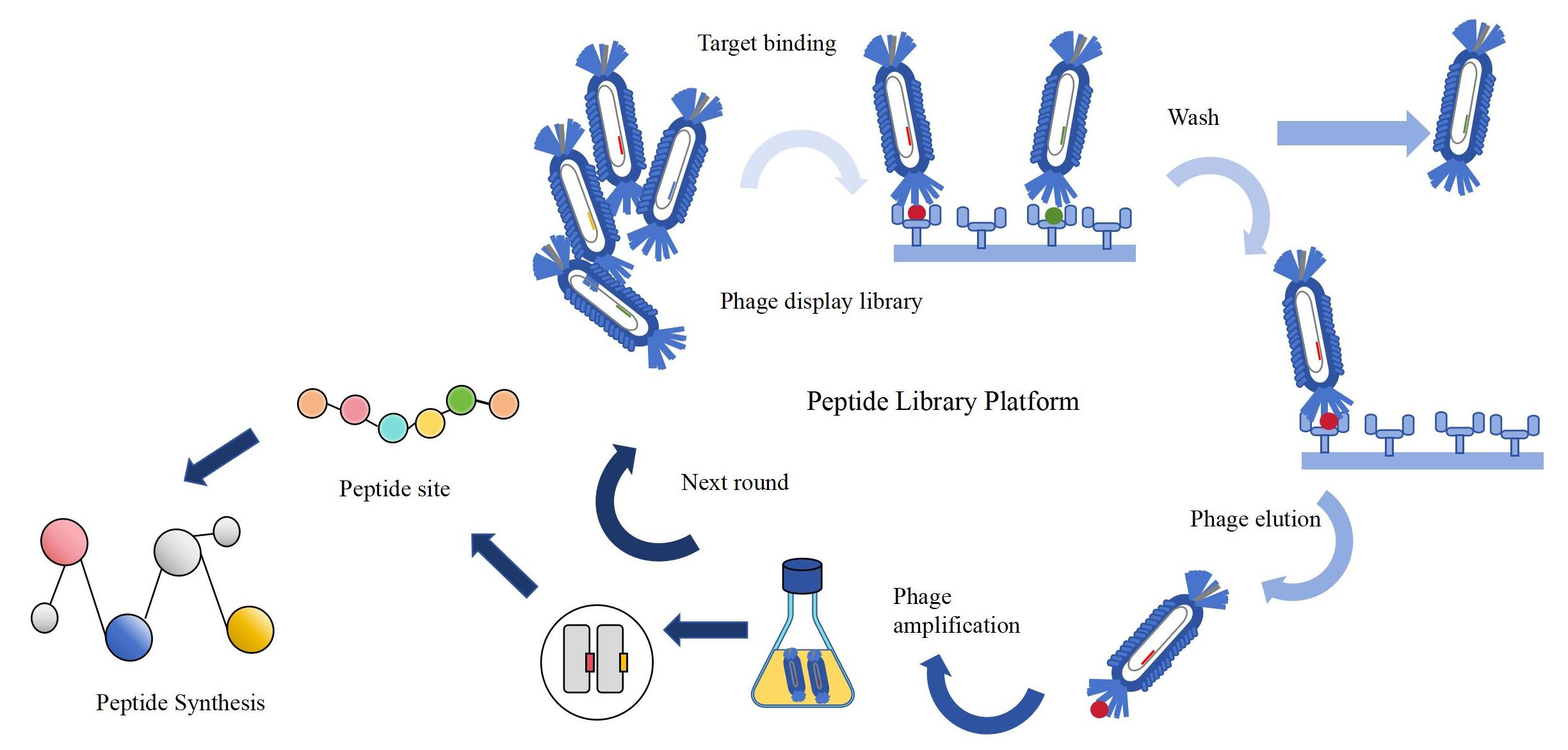
Fig.2 Phage display peptide library screening process
Peptide Library Screening Service Workflow
|
Services Process |
Service Content |
Timeline |
|
Quality Control of Antigens |
Antigen purity testing by SDS-PAGE |
1 week |
|
Peptide Library Screening |
Positive clones recognizing antigen by 3-4 rounds of screening |
2 weeks |
|
Antibody Sequencing |
Positive clone sequencing |
1 week |
|
Antibody Quality Control |
Expression of target antibody in E.coli, followed by quality control by ELISA |
1 week |
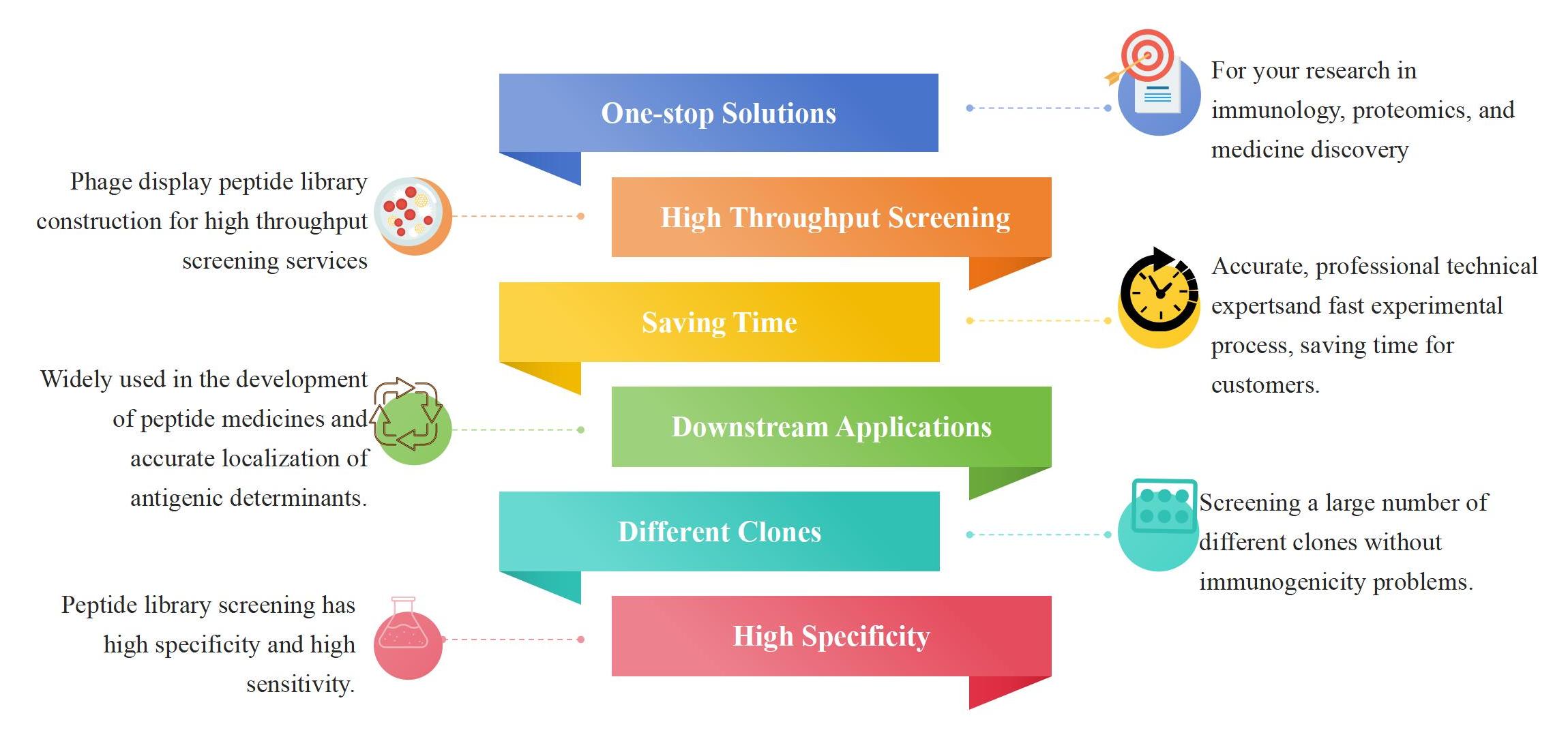
Advantages Of Phage Display Peptide Library Service:
How to Order?
If you have any questions regarding our services or products, please feel free to contact us by E-mail: [email protected] or Tel: +86-400-621-6806