Service Line:+86-022-82164980
Address:FL-4, Building A5, International Enterprise Community, Tianjin, China
Email:[email protected]
The phage display peptide platform provided by KMD Bioscience is a high throughput antibody screening and peptide custom synthesis platform. The phage display antibody library platform can construct up to 10^13/ml peptides or antibody clones displayed on phage. After subsequent rounds of high throughput screening, KMD Bioscience can provide up to 10^5 validated peptide or antibody sequences, providing a solid research foundation for searches of subsequent enzyme substrate, protein-ligand, and high-specificity antibodies. Based on the phage display antibody library platform, KMD Bioscience can construct a heptapeptide library (7 peptide library), dodecapeptide library (12 peptide library), and cyclic heptapeptide library (cyclic 7 peptide library), etc. for customers.
Cyclization modifications can confer several advantages to peptides that cumulatively make them more medicine-like. Constraining peptides via cyclization is a common strategy to mimic protein secondary structures (e.g. peptide rings) or to create peptides with enhanced conformational stability compared to their linear analogs. KMD Bioscience constructed a premade cyclic heptapeptide phage display peptide library, aiming to construct top-quality cyclic peptide libraries.
Applications of Cyclic 7 Peptide Library-Random Peptide Library Screening
Phage display of cyclic peptide libraries to discover macrocyclic inhibitors of protein−protein interactions
Cyclic peptides are well suited for targeting protein−protein interactions. Due to their constrained structures, cyclic peptides benefit from lower entropic penalty upon binding and often show high affinity and specificity. They further phage display antibody library increased stability and cell permeability in comparison to linear peptides. Well-known natural product-derived cyclic compounds such as cyclosporin A have inspired research in the field. Genetically encoded libraries of cyclic peptides are increasingly used to find cyclic compounds. Such libraries can be generated through a variety of approaches like phage display library, yeast display library, mRNA display, and split-intein circular ligation. Bicyclic peptide phage libraries can further be generated by chemical cross-linking. Phage display antibody libraries benefit from large library sizes and ease of experiments. Highly diverse cyclic M13 peptide-phage display antibody libraries can be generated by designing randomized peptide sequences flanked by cysteine residues. However, the reversible nature of the disulfide bond limits the applicability of these cycles in an intracellular milieu.
Applications in enzyme inhibitors
Cyclic peptides have been reported for the inhibition of proteases, phosphatases, proteasomes, HIV integrases, and dam methyltransferases. Cyclization peptides have been emphasized by academics in the area of inhibition of enzyme activity. Numerous groups have investigated the cyclization of peptides to enhance their inhibitory activity. As an example, the NS2b-NS3 protease of the Dengue virus is a serious viral infection transmitted by mosquito bites. There is no specific treatment available.NS2b-NS3 protease is a good antiviral target because it is required for viral maturation and infectivity.
Applications in RNA-Protein interaction inhibitor.
RNA-protein binding processes can be interfered with by cyclic peptides. In laboratory studies, several groups have found that cyclic peptides can disrupt multiple processes of RNA-protein interactions, including translation initiation, elongation, pre-mRNA splicing, and viral replication.
Cyclic 7 Peptide Library-Random Peptide Library Construction Service
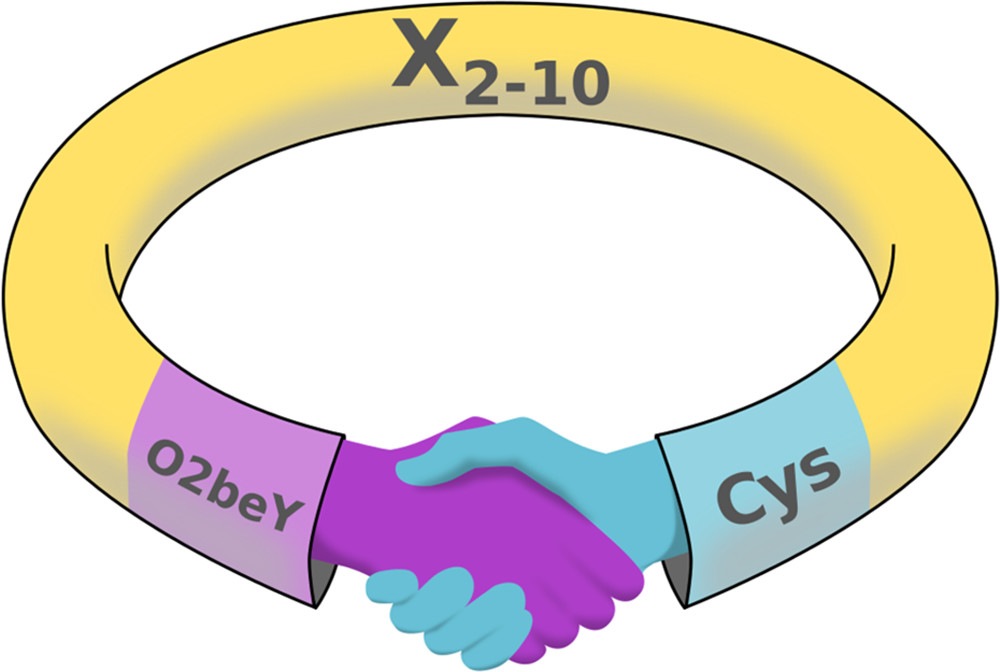
Fig.1 Structure of the cyclic peptide
The cyclic heptapeptide phage display library is based on combinatorial peptide libraries of random peptide libraries fused to a minor coat protein (pIII) of the M13 phage. The displayed peptide is expressed at the N-terminus of pIII, i.e., the first residue of the mature protein is the first randomized position. The peptide is followed by a short spacer (Gly-Gly-Gly-Ser) and then the wild-type pIII sequence.
Cyclization peptides more are resistant to proteolysis, increase the protein permeability, and can augment their affinities while preserving their selectivity. This is why cyclic peptides represent an increasingly interesting scaffold for studying and modulating protein−protein interactions.
Random oligonucleotide fragments of the cyclic 7-mer peptide were synthesized by chemical synthesis and then inserted into the gene encoding the shell protein of the phage vector and transformed into E. coli by genetic engineering recombinant technology. The proliferated and generated phages carry exogenous peptides on their surface, and each phage expresses one exogenous peptide on its surface. All these phages constitute a premade cyclic heptapeptide phage display library.
Cyclic 7 Peptide Library-Random Peptide Library Screening
The target molecule provided by the customer is used to obtain a monoclonal antibody that can bind to the target molecule with high affinity after a screening, amplification, and selection step from the whole premade cyclic heptapeptide phage display library. By determining the DNA sequence of this phagemid, the amino acid sequence of the peptide carried by the phage can be known. The enriched cyclic peptides display a high affinity for the target protein and may serve as inhibitors of endogenous protein-protein interactions (PPIs).
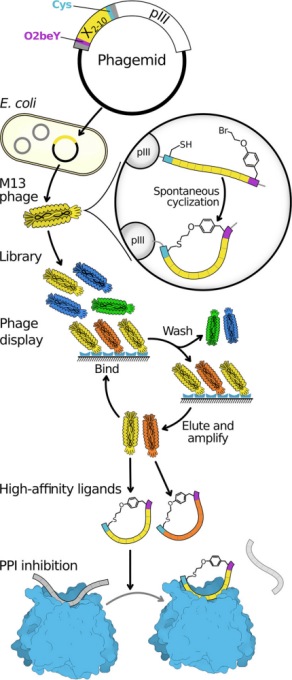
Fig 2 Peptide library synthesis and screening of phage display cyclic heptapeptide library.
Cyclic Heptapeptide Library-Random Peptide Library Screening Workflow
|
Services Available |
Service Content |
Service Time |
|
Support Multiple Provision Forms |
-Purified protein -Unpurified protein (provides purification services) -Targeted targets |
|
|
Quality Control of Antigens |
Antigen purity testing by SDS-PAGE |
3 days |
|
Peptide Library Screening |
Positive clones recognizing antigen by 3-4 rounds of screening |
2 weeks |
|
Antibody Sequencing |
Positive clone sequencing |
1 week |
|
Antibody Quality Control |
Expression of target antibody in E.coli, followed by quality control by Elisa |
1 week |
|
Delivery |
Experimental report and >10 independent peptide clones |
Depends on express |
Advantages Of High Throughput Antibody Screening Service
How to Order?
If you have any questions regarding our services or products, please feel free to contact us by E-mail: [email protected] or Tel: +86-400-621-6806;