2025-03-19 Hits(88)
Antibody Humanization
A monoclonal antibody (mAb) is a highly uniform antibody produced from a single B cell clone that targets only a specific epitope by hybridoma technology. The development of monoclonal antibodies has experienced four stages: mouse monoclonal antibody, chimeric murine human monoclonal antibody, human monoclonal antibody, and fully human antibody.
Monoclonal antibodies are widely used to prevent, diagnose, and treat diseases, especially in the clinical treatment of tumors. The world's first therapeutic monoclonal antibody (prevent kidney transplant rejection) was marketed in 1986, and since then, many monoclonal antibodies have been used to treat diseases. Humanized monoclonal antibodies and fully human antibodies have become therapeutic antibody development trends. Both of these produce anti-drug antibodies, and the production of anti-drug antibodies is related to the level of immunity in the body. Whether an allergic reaction has occurred cannot be determined by the absence of a mouse source in the antibody. The choice of the two drugs depends on the safety of the drug and the efficacy of the treatment.
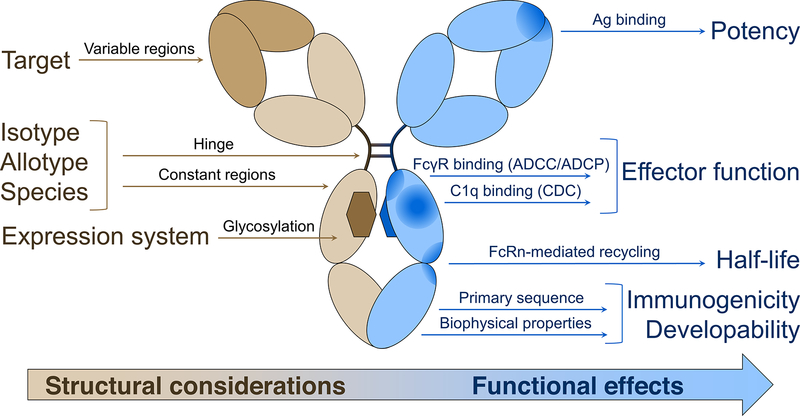
Fig 1 Therapeutic effects based on IgG1 structure. (Reference source: Considerations for the Design of Antibody-Based Therapeutics - PubMed (nih.gov))
1. Mouse Monoclonal Antibodies
The techniques of monoclonal antibody production include the hybridoma technique, phage display technique, and single B cell antibody production technique. Among them, hybridoma technology is mature and more used, and the research cost is low.
Mouse monoclonal antibodies fused B cells from immunized mice with myeloma cells to form hybridoma cells that were screened to obtain specific antibody secretion functions, and then a monoclonal antibody was obtained. The homologous antibody produced by monoclonal hybridoma cells obtained by clonal fusion, screening, and cloning of single epitope-specific B cells is called monoclonal antibody.
Mouse monoclonal antibodies don‘t contain the components of human genes, thus being recognized by the human immune system, so it’s easy to cause rejection of immune response when used to treat diseases.
2. Chimeric Murine Human Monoclonal Antibody
The chimeric murine human monoclonal antibody is the mouse antibody humanization, which is a chimeric gene splicing the V region gene of a mouse antibody and the C region gene of a human antibody, inserted into the expression vector, and then transfected into myeloma cell line to obtain the antibody. Compared with mouse monoclonal antibodies, 70% of genes derived from humans are closer to the structure of human antibodies, causing fewer adverse reactions and better therapeutic effects.
The advantages of chimeric murine human monoclonal antibody are as follows: 1. The high specificity and affinity of parent mouse antibody are retained, and the composition of human antibody is increased to about 70%; 2. The Fc segment of human antibody can mediate biological effects, such as antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity and complement-dependent cytotoxicity. 3, It can freely select antibody type, subtype, class, subclass, size, structure domain, and glycosylation site; 4, It can shorten the operation and development cycle.
3. Humanized Monoclonal Antibodies
Based on Chimeric murine human monoclonal antibody, the proportion of humanized genes was further increased, and 90% of the antibody genes were humanized antibodies derived from humans. The humanized monoclonal antibody can obtain the antigen-binding specificity of mouse monoclonal antibodies and reduce the heterogenicity. Compared with mouse monoclonal antibodies, the side effects on humans are minimal. Compared with mouse and human chimeric monoclonal antibodies, the therapeutic effect is better and the side effects are less.
Antibody humanization transformation includes CDR/SDR transplantation, surface remodeling, epitope-directed selection, and deimmunization.
4. Fully Human Antibodies
The humanized antibody was developed based on humanized antibodies, and the genes of humanized antibodies are all derived from humans. It has the advantages of high affinity and low allergenicity in that it can avoid the body's immune response, thus having higher safety and efficacy in treatment. Therefore, it is the current drug of choice for the treatment of diseases such as cancer and autoimmune diseases,
The full human antibody production includes phage display technology, yeast display technology, transgenic animal full human antibody, and single B cell antibody preparation technology.
The advantages of fully human antibodies include 1. Low immunogenicity: fully human antibodies 100% similar to the human gene will not cause a strong immune response like a mouse antibody; 2. High safety: its immunogenicity is low, resulting in fewer side effects; 3. the treatment effect is good: low immunogenicity, small side effects, better treatment effect.
In summary, the development of mouse monoclonal antibodies to fully human antibodies has experienced a transition from chimeric antibodies to humanized monoclonal antibodies, and finally realized antibodies composed entirely of human components, which greatly improved the safety and effectiveness of antibody therapy.
KMD Bioscience has rich experience in antibody engineering construction and mature antibody humanization technology that can provide customers with high-quality full human antibody production, mouse antibody humanization, antibody humanization transformation, chimeric antibody transformation, and other services. In addition, KMD Bioscience can also provide antibody expression and purification, affinity determination, antibody affinity maturation, antibody sequencing, and other services to meet the needs of different customers.
References:
[1] Waldmann H. Human Monoclonal Antibodies: The Benefits of Humanization [J]. Methods Mol Biol. 2019, 1904: 1-10.
[2] Jolliffe LK. Humanized antibodies: enhancing therapeutic utility through antibody engineering [J]. Int Rev Immunol. 1993, 10(2-3): 241-250.
[3] Qin Y, Jin J, Zhang J, et al. A fully human monoclonal antibody targeting Semaphorin 5A alleviates the progression of rheumatoid arthritis. Biomed Pharmacother [J]. 2023, 168: 115666.