2025-01-17 Hits(233)
Antibody Humanization
Immunogenicity refers to the ability of a substance (such as a drug or biological product) to cause the body's immune system to produce an immune response. The occurrence of polypeptide immunogenicity is related to the drug itself (for example, the drug production from the mouse or human, molecular structure and modification, polymer formation, mixed with impurities, etc.), and the patient itself or the treatment regimen (the patient's immune status, allergy history, genetic background; Route, dose and frequency of administration). Thus, polypeptide immunogenicity is an important safety consideration in drug development, as excessive immunogenicity can lead to immune reactions or side effects on the immune system. Therefore, antibody immunogen production is crucial.
At present, monoclonal antibody drugs are the largest category in the global biological drug market, including mouse monoclonal antibody, chimeric monoclonal antibody, humanized antibody, and fully human monoclonal antibody, among which humanized antibody and fully human monoclonal antibody have overcome the problem of strong immune response caused by mouse monoclonal antibody in the treatment of diseases, and have become the leading model in the field of therapeutic antibodies. With the continuous growth of global medical demand, more monoclonal drugs will be developed that provide important technical support for treating complex diseases.
CDR transplantation
The principle is to clone the human FR sequence to the corresponding part of the antibody-based on retaining the mouse CDR sequence.
SDR transplantation
SDR transplantation also known as specific determination of disability transplantation which the SDR region refers to the existence of CDR region contact with the antigen of the amino acid sequence. The SDR region can produce immunogenicity transplanted into the human antibody framework.
Frame area reconstruction
Frame region remodeling is based on FR screening that includes surface remodeling, which humanizes amino acid residues, and glycosylation modification, which changes the glycosylation site. The technology can improve antibody affinity.
Fully Humanized Antibody Development
Transgenic mouse technology
Transgenic mouse technology is the technology of transferring the optimized human antibody DNA sequence into the mouse genome. Because the immune system is the mouse, the antibodies are not the same as those of the human body.
The marketed Nivolumab, Denosumab, and Panitumumab were all produced by transgenic mice.
Antibody library technology
An immune antibody library is established by single-cell cloning technology after immunizing the body.
The non-immune antibody library consists of a semi-synthetic antibody library, a fully synthetic antibody library, and a natural antibody library.
This technique is limited by the capacity of the antibody library and host modification of amino acids. The marketed Necitumumab and Adalimumab were screened by phage display technology. We provide corresponding Biosimilar antibody products for scientific research purposes.
|
Catalog Number |
Product Name |
Application |
Size |
| YR1006 | Anti-Human EGFR Recombinant Antibody(Necitumumab) | ELISA, IF, IP, FuncS, FCM, ICC |
1mg, 5mg |
| YR1005 | Anti-Human TNFA Recombinant Antibody(Adalimumab) | FCM, IP, ELISA, Neut, FuncS | 1mg, 5mg |
Ribosome display technology
This technique works by displaying the target gene on the surface of the ribosome, forming an MRNa-protein-ribosome complex, and then adding antigens to the mixture for screening. Compared with phage display technology, this method has a higher storage capacity.
mRNA display technology
mRNA display technology is an improvement and extension of ribosome display technology, which is more conducive to screening.
Yeast display technology
Yeast display technology uses yeast as a carrier to locate foreign genes on the surface of yeast cells through fusion expression, to screen them. It can also label cells with substances such as fluorescein and perform timed and quantitative screening by flow cytometry.
Single-cell technique
Single cells can be screened from the established antibody library according to cell surface marker molecules, then the heavy chain and light chain genes of antibodies can be obtained by RT-PCR after cell enrichment.
Humanized single-domain antibody
Single-domain antibodies (sdAbs) exist in the variable region of heavy chain antibodies in camels and sharks, and have great advantages compared with full-length conventional antibodies: 1. Rapid blood clearance, strong ability to penetrate tissues and tumors, and can be used as non-invasive imaging agents; 2. The half-life is long, and the prospects for treating chronic diseases are wide; 3. It can target the recognition of antigens in living cells.
Although sdAbs have many advantages, they can cause a certain immune response when treating diseases, so the humanized single-domain antibody is gradually emerging. Common methods of humanized single-domain antibody include:
(1) A synthetic sdAb library was constructed using humanized or fully humanized sdAb scaffolds.
(2) Separate VHH from rare molecules with VHH sequence characteristics.
(3) By transgenic animals to produce HCAbs that are fully human variable domains.
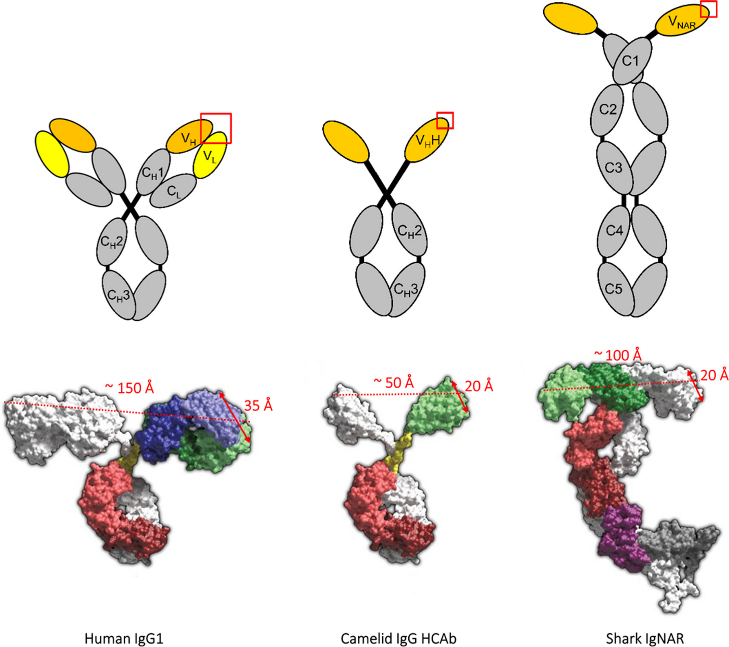
Fig1: Domain structures of conventional vertebrate tetrameric IgG1, camelid heavy chain-only IgG, and shark IgNAR.(Reference source: Immunogenicity and humanization of single-domain antibodies)
KMD Bioscience has rich experience in antibody engineering construction and mature antibody humanization technology that can provide customers with high-quality antibody immunogen production, humanized Modification methods of humanization antibody, humanized single-domain antibody, humanized antibody production services, and other services. In addition, KMD Bioscience can also provide monoclonal antibody production, antibody expression and purification, affinity determination, antibody affinity maturation, antibody sequencing, and other services to meet the needs of different customers.
References
[1] Rossotti MA, Bélanger K, Henry KA, Tanha J. Immunogenicity and humanization of single-domain antibodies [J]. FEBS J. 2022, 289(14): 4304-4327.
[2] Nagano K, Tsutsumi Y. Phage Display Technology as a Powerful Platform for Antibody Drug Discovery [J]. Viruses. 2021, 13(2): 178.
[3] Lu RM, Hwang YC, Liu IJ, Lee CC, Tsai HZ, Li HJ, Wu HC. Development of therapeutic antibodies for the treatment of diseases [J]. J Biomed Sci. 2020, 27(1): 1.