2025-01-03 Hits(92)
Fab Antibody
Fab antibody is the cleavage product of the antigen-binding part of the antibody molecule, which is produced by the immunoglobulin G (IgG) produced by B cells after enzymatic hydrolysis or genetic engineering. It contains the variable region of the antibody molecule, namely the variable region (VL) of the light chain and the variable region (VH) of the heavy chain, as well as the constant region fragment CH1 of the heavy chain. The light and heavy chains are connected by a disulfide bond, giving Fab antibodies a stable double-stranded structure. Each Fab antibody molecule contains an antigen-binding site that binds specifically to the antigen.
Fab antibodies produced by KMD Bioscience are highly sensitive, capable of detecting very low concentrations of antigens or antibodies, and highly specific, able to specifically recognize and bind to the target antigen. KMD Bioscience is able to provide complete Fab antibody preparation services, which typically include Fab antibody labeling steps in addition to the basic antibody production and purification process to facilitate subsequent detection, localization or analysis. Antibody labeling is an important biotechnology that aims to use chemical or physical methods to attach specific markers (enzymes, fluorescein, isotopes, biotin, etc.) to antibody molecules, thereby giving antibodies new properties or functions. At present, antibody labeling technology has been widely used in medical pathology, immunohistochemistry, molecular biology, biopharmaceutical and other fields of analytical research and technical determination.
Fab Antibody Expression
The process of Fab antibody expression can be realized by a variety of methods, including enzymatic hydrolysis and preparation by expression system.
Fab fragments were obtained by direct enzyme digestion on the basis of monoclonal antibody. It is fast and simple, but it first requires monoclonal antibody raw materials, which are generally limited in quantity and expensive, and the obtained Fab often loses a certain amount of immune reactivity.
The preparation method using the expression system is mainly through genetic engineering technology, the gene encoding Fab fragment is introduced into the host cell for expression. KMD Bioscience already has two mature Fab antibody expression systems: E. coli expression system and mammalian expression system.
E.coli expression system: It has the advantages of low production cost and fast production speed, but it lacks post-translational modification, easy to form inclusion bodies, and difficult to guarantee the activity after renaturation. The expression process involves gene synthesis, vector construction, transformation and culture, expression and purification.
Mammalian expression systems, such as HEK293 or CHO cells, are relatively expensive to prepare and have a long growth cycle, but they are well modified after translation, and the expressed Fab fragments have good activity. Mammalian expression systems are the most widely used systems that preserve the natural properties of Fab antibodies. Fab antibody expression in mammalian system usually includes gene cloning, expression vector construction, cell culture and transfection, expression and screening, purification and identification.
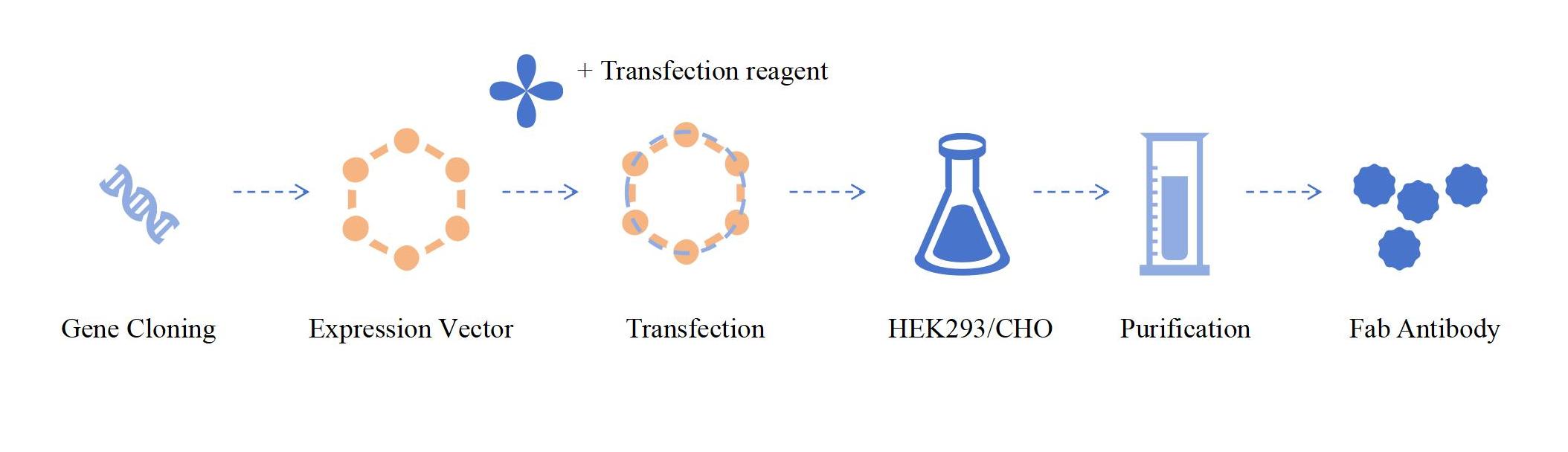
Fig.1 Fab antibody preparation process of mammalian expression.
Fab Antibody Labeling
KMD Bioscience based on fluorescein, isotopes, biotin and other markers, can provide a variety of Fab antibody labeling services. These markers can be detected by various precision instruments, so as to realize the qualitative, localization and quantitative study of antigen and antibody reactions.
1. Antibody biotin labeling
The principle of antibody biotin labeling is based on the high affinity interaction between biotin and biotin-binding proteins. Biotin is a small molecular organic substance (also known as vitamin H) that binds tightly to biotin-binding proteins. In the labeling process, biotin can be chemically linked to the amino group of the antibody to form a covalent bond, so as to generate biotin-labeled antibody. This connection does not change the immune activity of the antibody, and enables the biotin-labeled antibody to bind to the corresponding antigen.
2. Antibody HRP labeling
Antibody HRP labeling refers to the binding of horseradish peroxidase (HRP) to antibodies. HRP is a 44,000 molecular weight glycoprotein, which is composed of colorless enzyme proteins combined with dark brown iron porphyrins, usually from the horseradish plant. The basic principle of antibody HRP labeling is to use the enzyme activity of HRP to produce color reaction in the presence of substrate, so as to realize the detection and localization of antibodies.
3. Antibody Isotope labeling
Isotopes are atoms that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons, which have the same chemical properties but may have different physical properties. In antibody isotope labeling, an atom in an antibody molecule is usually replaced with its isotope to achieve antibody labeling. This labeling method is based on the stability of the isotope in the chemical reaction, that is, the antibody molecule can still maintain its original biological activity after isotope substitution. There are two kinds of isotopes, radioactive and non-radioactive, and radioisotopes are commonly used in biology at present, which has the characteristics of convenient detection and high sensitivity.
Reference
[1]. Wang C, Hong J, Yang Z, et al. Design of a Novel Fab-Like Antibody Fragment with Enhanced Stability and Affinity for Clinical use. Small Methods. 2022;6(2):e2100966.
[2]. Wu X, Sereno AJ, Huang F, et al. Fab-based bispecific antibody formats with robust biophysical properties and biological activity. MAbs. 2015;7(3):470-482.