2025-01-15 Hits(130)
Peptide Library
Peptides are intermediate products of protein hydrolysis and are linked by peptide bonds. The compound formed by dehydration and condensation of amino acid molecules is called n peptide, so more than three peptides are usually called polypeptides. The methods of peptide synthesis include chemical synthesis and biosynthesis. At present, polypeptides are widely used in medicine, beauty, health care, and other fields, with the increasing number of medical and health problems, the demand for polypeptide products is increasing. In the hairdressing field, it is used daily as a skincare product that could anti-aging. In the medical field, it can be used to make vaccines, drugs, etc.
A peptide library consisting of large peptides of specific length and with different sequences, including most combinations of amino acid sequences. Peptide libraries can be divided into synthetic peptide libraries, native peptide libraries, and recombinant protein peptide libraries according to the source of peptides The synthetic peptide library is composed of various peptide sequences prepared by chemical synthesis. The native peptide library is composed of natural peptides in living organisms. The recombinant protein peptide library was constructed based on protein engineering technology. The synthesis methods of peptide library include phage display technology, mRNA display technology, and one-bead-one-compound high-throughput screening technology.
Targeted peptides are peptide molecules that target specific biological targets and have fine affinity. They are used in novel targeted therapies and have the advantages of strong penetration, low immunogenicity, easy chemical synthesis and modification, and high batch repeatability.
Progress of targeted peptide screening
There are many methods for targeted polypeptide molecular screening, among which the traditional combinatorial chemical screening methods have long cycles, low efficiency, time-consuming analysis and identification, and traditional phage display methods are difficult to insert or modify unnatural amino acids, which have limitations. Therefore, small molecule-targeted peptide screening methods have been developed.
Degeneracy of peptide library
The method can increase the probability of target molecules remaining in a small range of peptide libraries, it has two ways to obtain. One is to build a targeted small molecule polypeptide library that uses the degeneracy of antisense peptide and the targeting recognition principle of righteous peptide-antisense peptide. The principle of action is to use the specificity of targeted peptides to screen out peptide molecules that interact with target proteins. It is widely used in tumor diagnosis and treatment. The other is to complete the reduction of the peptide library synthesis through computer modeling technology, which can incorporate the library capacity of the peptide library, and predict whether the peptide is closely linked to the molecular target and whether it can inhibit the normal function of the target protein, which provides a basis for rapid drug screening.
High-throughput screening
Although the above method can improve the efficiency of peptide library screening to a certain extent, it has certain limitations in large-scale screening. Therefore, the high-throughput screening technology has gradually developed and is suitable for small-molecule targeted peptide screening.
New mass spectrometry is one of the tools for high-throughput screening. Based on this technology, a screening method for high-throughput glycosylated peptides has been developed, which can greatly improve the throughput and accuracy of glycopeptide identification and n-glycoproteomic analysis.
Microfluidic chip systems have also been applied in high throughput screening technology, which has the characteristics of high analysis efficiency, flexible design, automatic control, and flux integration.
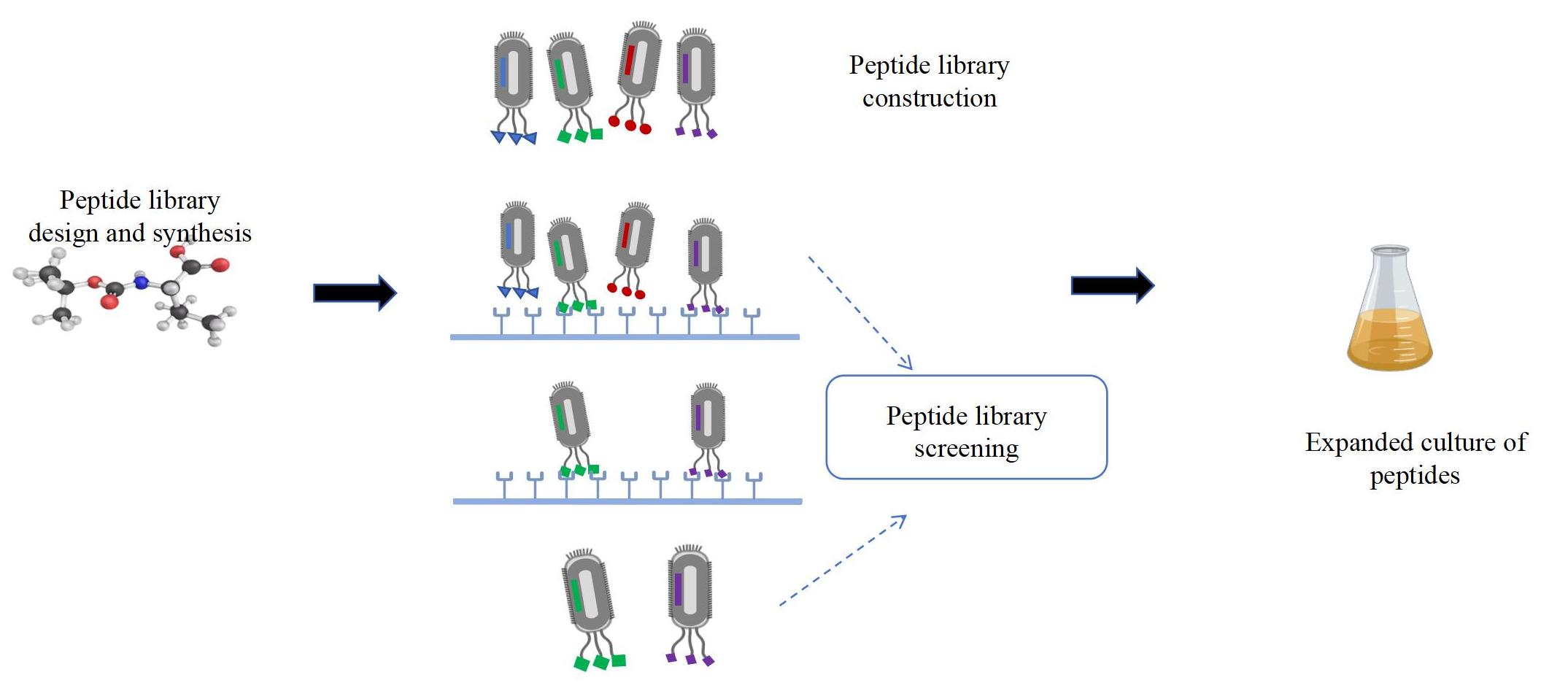
Fig 1: Peptide library construction and screening process
Application of targeted polypeptide molecules
Peptide drugs are peptide analogs synthesized from endogenous peptides and are one of the hot directions of drug development. Among them, anti-tumor peptides have attracted much attention. In recent years, cancer has become increasingly common and is one of the highest mortality diseases in the world. The current methods used to treat cancer will have different degrees of side effects, compared with this, polypeptide molecules caused by the body's adverse reactions, and strong targeting, have become a new anti-tumor drug. It has anticancer effects and is isolated from natural sources, such as venom secreted by amphibians and reptiles, which have anti-tumor activity, and short-tailed gophers, which can inhibit the proliferation of ovarian and breast cancer. Therefore, it has high selectivity and high penetration efficiency.
Through targeted drug screening, a drug that only targets specific cancer cells or proteins can be obtained. When cancer disease is treated, it only causes harm to cancer cells, and will not cause to normal cells or tissues. Therefore, the targeted drugs can improve efficacy and reduce toxic side effects.
KMD Bioscience has rich experience in antibody engineering construction and mature antibody humanization technology that can provide customers with peptide synthesis, peptide library synthesis, and screening techniques, targeting peptide screening, phage display technology, mRNA display technology, and other services. In addition, KMD Bioscience has many years of experience in phage cyclic peptide library screening, so we can also provide polypeptide library screening services, phage library screening services, and antibody customization services, including antibody expression and purification, affinity determination, antibody sequencing, etc., to meet customer needs.
References:
[1] Lin J, Wang S, Wen L, et al. Targeting peptide-mediated interactions in omics [J]. Proteomics. 2023, 23(6): e2200175.
[2] Lodola A, Giorgio C, Incerti M, et al. Targeting Eph/ephrin system in cancer therapy [J]. Eur J Med Chem. 2017, 142: 152-162.
[3] Yuan Y. Mechanisms Inspired Targeting Peptides [J]. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020, 1248: 531-546.