Service Line:+86-022-82164980
Address:FL-4, Building A5, International Enterprise Community, Tianjin, China
Email:[email protected]
The phage display peptide platform provided by KMD Bioscience is an ultra-high throughput library screening platform. The phage display technology platform can construct up to 10^13/ml peptides or antibody clones displayed on phage. After subsequent rounds of biopanning, KMD Bioscience can provide up to 105 validated peptide or antibody sequences, providing a solid research foundation for searches of subsequent enzyme substrate, protein-ligand, and high-specificity antibody. Based on the phage display peptide platform, KMD Bioscience can build a heptapeptide library (7 peptide library), dodecapeptide library (12 peptide library), and cyclic heptapeptide library (cyclic 7 peptide library), etc. for customers.
Applications of Heptapeptide Library - Random Peptide Library Screening
Tumor-targeting therapy can be an efficacious way to cure a malignant tumor in clinical trials. Phage display technology is a molecular diversity technology that allows the presentation of a large number of peptides or proteins on the surface of filamentous phage for various applications. The study reported on using phage display technology to generate peptide libraries that bind to colon cancer tissues. To accomplish this, they developed a library screening protocol that contained 3 rounds of in vitro positive panning on colon cancer cells (SW480) and 2 rounds of subtractive screening in vitro on normal human intestinal epithelial cells with a phage display-heptapeptide library. After several rounds of panning, both phage titer and recovery efficiency were significantly improved. Through a cell-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, immunofluorescence, in vivo binding assay, immunocytochemical staining, and immunohistochemical staining, peptide CP15 (VHLGYAT) was demonstrated to be the most effective peptide in targeting tumor cells (SW480 and HT29 cells) and tumor tissues but not the normal human intestinal epithelial cells and control colon tissue. These studies suggest that peptide CP15 may be a promising lead candidate in the development of a useful colon tumor diagnostic and targeted medicine delivery agent.
Heptapeptide Library-Phage Display Library Construction Service
Random oligonucleotide fragments of the heptapeptide were synthesized by chemical synthesis and then inserted into the gene encoding the shell protein of the phage vector and transformed into E. coli by genetic engineering recombinant technology. A random heptapeptide was fused to the M13 phage minor coat protein (pIII) to form a combinatorial library. The heptapeptide shown is expressed at the N terminus of pIII, i.e., the first amino acid of the mature protein is the first amino acid of the random heptapeptide, and the heptapeptide is followed by a short stretch of spacer polypeptide consisting of Gly-Gly-Gly-Ser followed by the wild-type pIII protein. The proliferated and generated phages carry exogenous peptides on their surface, and each phage expresses one exogenous peptide on its surface. All these phages constitute a premade random heptapeptide library.
The target molecule provided by the customer is used to obtain a phage clone that can bind to the target molecule with high affinity after a screening, amplification, and selection step from the whole premade peptide library screening. By determining the DNA sequence of this phage, the amino acid sequence of the peptide carried by the phage can be known.
Premade Peptide Library Screening-Heptapeptide Library
Phage display describes a selection technique in which a library of peptide or protein variants is expressed on the outside of a phage virion, while the genetic material encoding each variant resides on the inside. This creates a physical linkage between each variant protein sequence and the DNA encoding it, which allows rapid partitioning based on binding affinity to a given target molecule (antibodies, enzymes, cell-surface receptors, etc.) by an in vitro selection process called panning. In its simplest form, panning is carried out by incubating a library of phage-displayed peptides on a plate (or bead) coated with the target, washing away the unbound phage, and eluting the specifically bound phage (Fig. 1). The eluted phages are then amplified and taken through additional binding/amplification cycles to enrich the pool in favor of binding sequences. After 3-4 rounds, individual clones are characterized by DNA sequencing and binding assays.
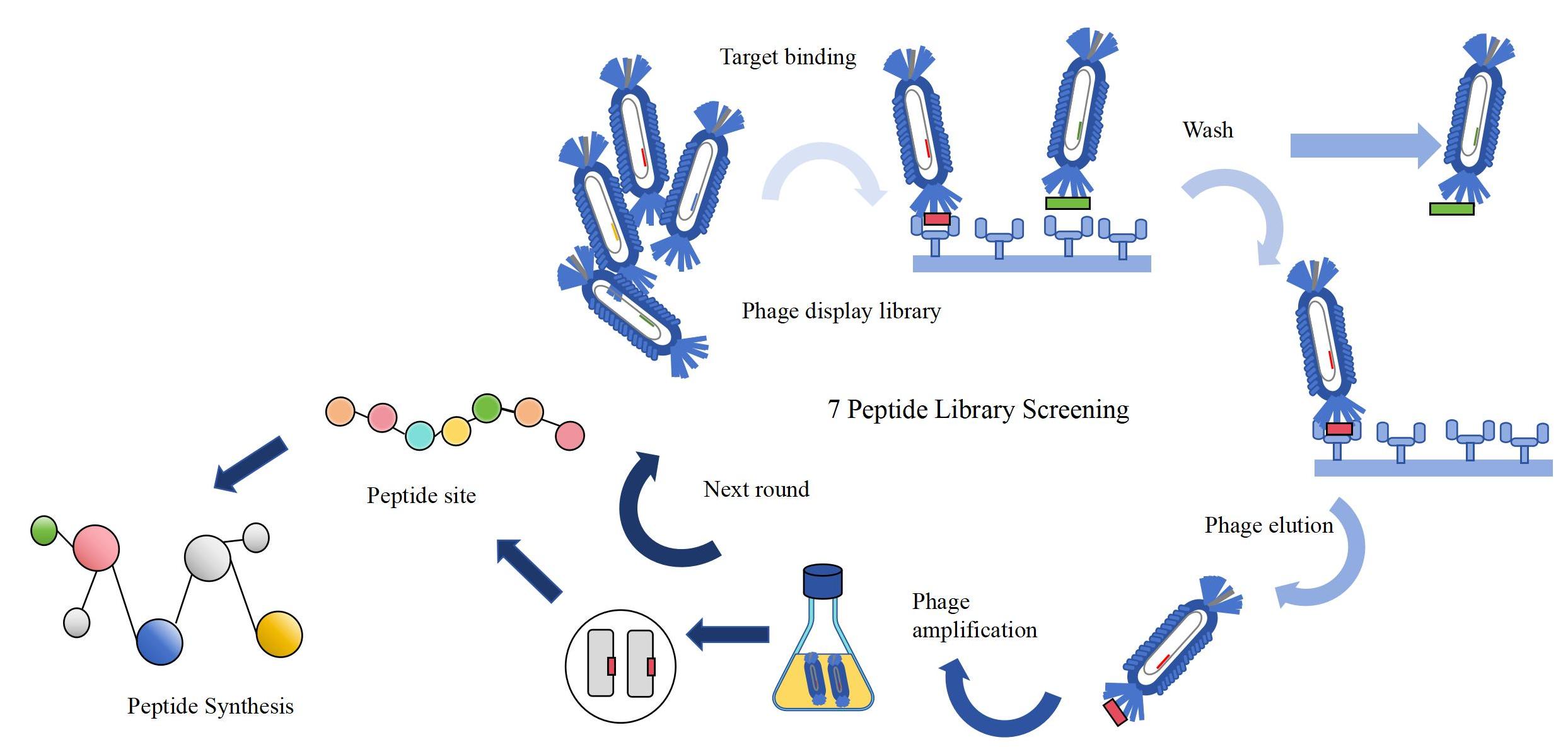
Fig. 1 Phage Display Peptide Discovery
Heptapeptide Library - Random Peptide Library Screening Workflow
|
Services Process |
Service Content |
Service Time |
|
Support Multiple Provision Forms |
-Purified protein -Unpurified protein (provides purification services) -Targeted targets |
- |
|
Quality Control of Antigens |
Antigen purity testing by SDS-PAGE |
1 week |
|
Peptide Library Screening |
Positive clones recognizing antigen by 3-4 rounds of screening |
2 weeks |
|
Antibody Sequencing |
Positive clone sequencing |
1 week |
|
Antibody Quality Control |
Expression of target antibody in E.coli, followed by quality control by ELISA |
1 week |
|
Result Delivery |
Experimental report and >10 independent peptide clones |
Depends on express |
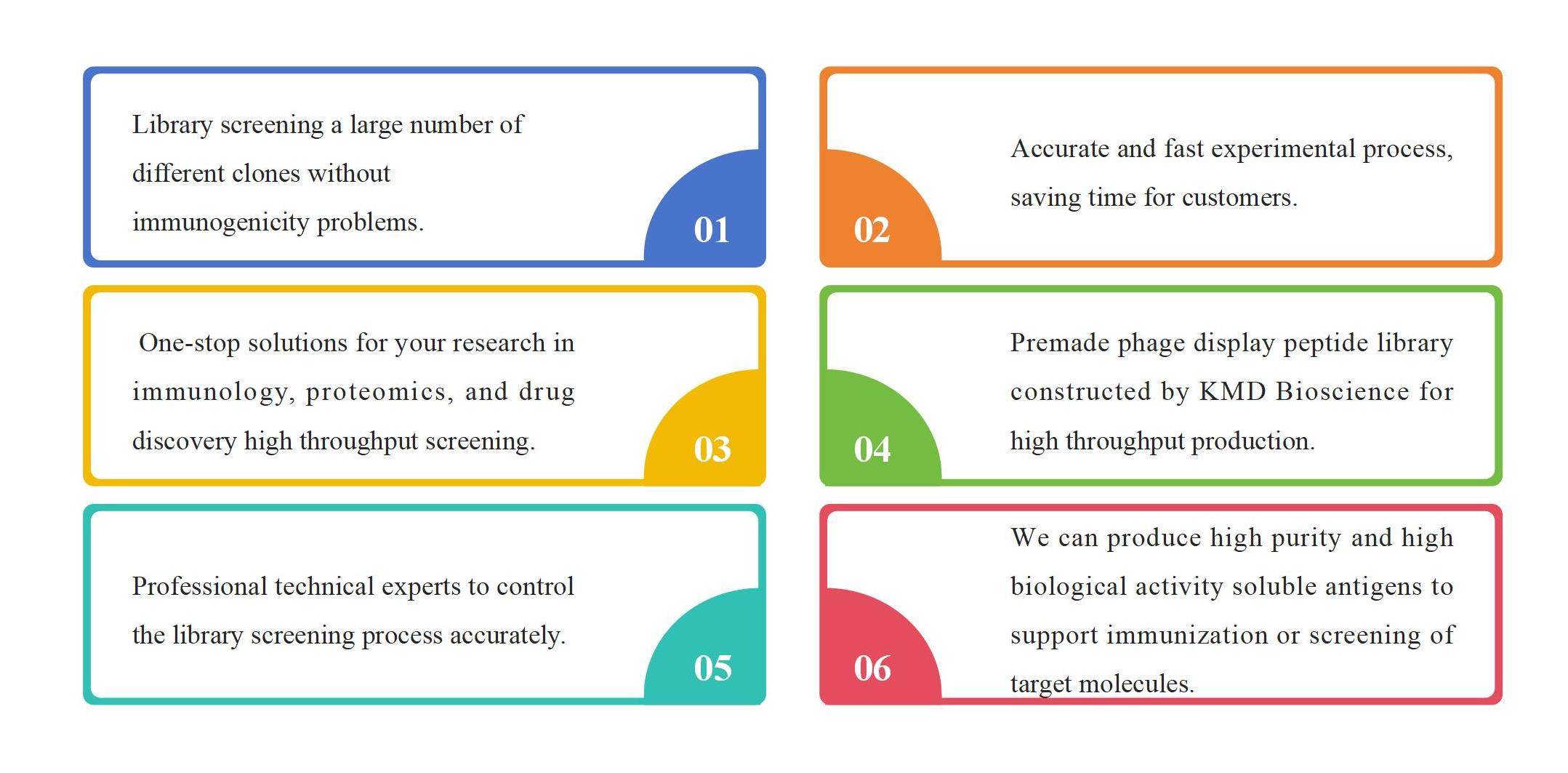
Advantages of Phage Peptide Library Screening Service
How to Order?
If you have any questions regarding our services or products, please feel free to contact us by E-mail: [email protected] or Tel: +86-400-621-6806;