Service Line:+86-022-82164980
Address:FL-4, Building A5, International Enterprise Community, Tianjin, China
Email:[email protected]
KMD Bioscience has been working on the Yeast Hybridization system for over 10 years. Yeast hybridization system of KMD Bioscience consists of yeast display library construction that based on the SMART method, yeast strains, rigorous reporter genes, and highly expressed vectors. The technique can be used to: the study of protein interactions, confirmation of protein interactions, and the definition of the interaction domain of the protein.
The yeast hybridization system is a novel genetic technique used in vivo to identify proteins that encode and interact with target proteins. This system provides multiple innovations for the identification of interacting proteins, and yeast two hybrid assay (Y2H) is the first genetic and molecular method for detecting interacting proteins. In order to study the interactions of a large number of proteins, scientists have developed several Y2H based systems to adapt to the different subcellular localization and biochemical characteristics of different proteins. The yeast two hybrid assay method is performed in vivo, allowing for the detection of interacting proteins in natural structures. The two hybrid system has high sensitivity in detecting weak and transient protein interactions. In addition, the two hybrid system can obtain gene sequences encoding interacting proteins in a concise manner, which only requires the construction of plasmids without the preparation of antibodies or purification of proteins, and without the tedious protein extraction and purification steps required for other in vitro methods for detecting protein interactions.
Traditional yeast two hybrid assay utilizes reporter genes, which are activated by specific transcription factors. Specifically, proteins X and Y to be tested are fused to the DNA binding domain (BD) and the activation domain (AD) of a transcription factor, respectively. BD-X fusion proteins bind to the upstream activator sequence (UAS) of the reporter promoter. AD is recruited to promoters and functional transcription factors are reconstructed during the interaction between X and Y, leading to the subsequent transcription of the reporter gene.
As a gene technology, yeast two hybrid screening provides a sensitive and economical method to test for direct interactions between two target proteins or to use proteins as bait to screen libraries of protein fragments prepared from a desired cell type, tissue, or whole organism. Interactions are determined by sequencing the corresponding plasmids in selected yeast colonies.
(1) Create BD-X bait; (2) Self-activation by BD-X bait test; (3) Perform yeast two hybrid screening and recognition of prey.
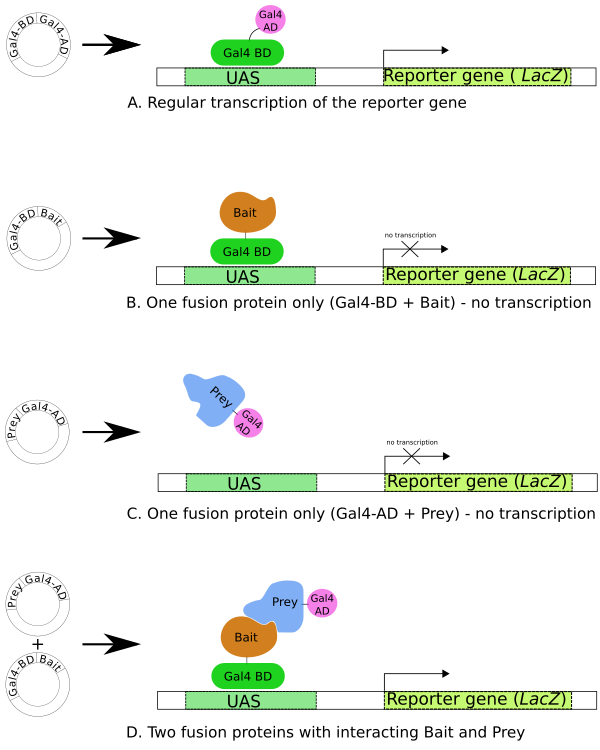
Figure 1 Overview of Yeast two hybrid (Y2H) Screening (Figure source: Wikipedia)
In order to study the interaction of a large number of proteins, scientists have developed several systems based on the Y2H system to adapt to different subcellular localization and biochemical characteristics of different proteins. KMD Bioscience provides clients with a wide variety of systems to meet the specific requirements of various projects. Specifically, proteins X and Y to be tested are fused to the DNA binding domain (BD) and the activation domain (AD) of a transcription factor, respectively.
(1)Yeast one hybrid system: study of protein-DNA interactions.
Yeast one hybrid: The main focus of yeast one hybrid technology is on protein DNA interactions, using a single fusion protein where AD is directly linked to the binding domain.
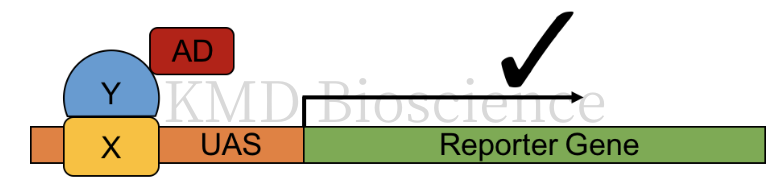
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of Y1H principle
Yeast two hybrid: Discovering protein-protein interactions (PPI) and protein-DNA interactions by testing the physical interactions (such as binding) between two proteins or a single protein and DNA molecule.
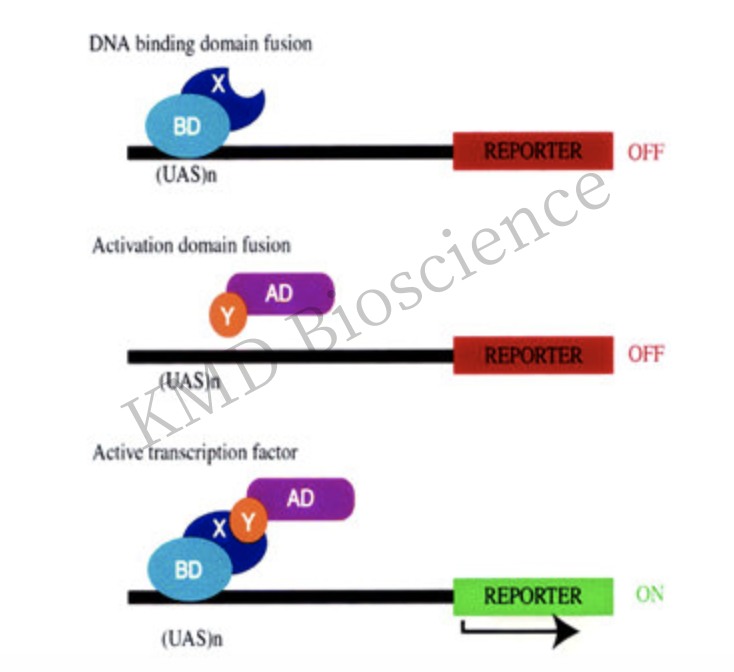
Figure 3 Schematic diagram of the basic principle of Y2H
Yeast three hybrid: mainly used to study RNA protein interactions, hybrid RNA molecules are used to connect two protein fusion domains - these two domains are not intended to interact, but rather interact with intermediate RNA molecules (through their RNA binding domains).
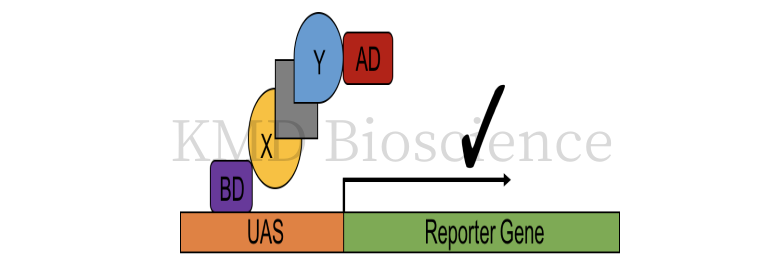
Figure 4 Schematic diagram of Y3H principle
Split ubiquitin yeast two hybrid: One limitation of classical yeast two hybrid screening is that they are limited to soluble proteins, and the split ubiquitin yeast two hybrid system provides a solution for studying protein-protein interactions between insoluble integrated membrane proteins.
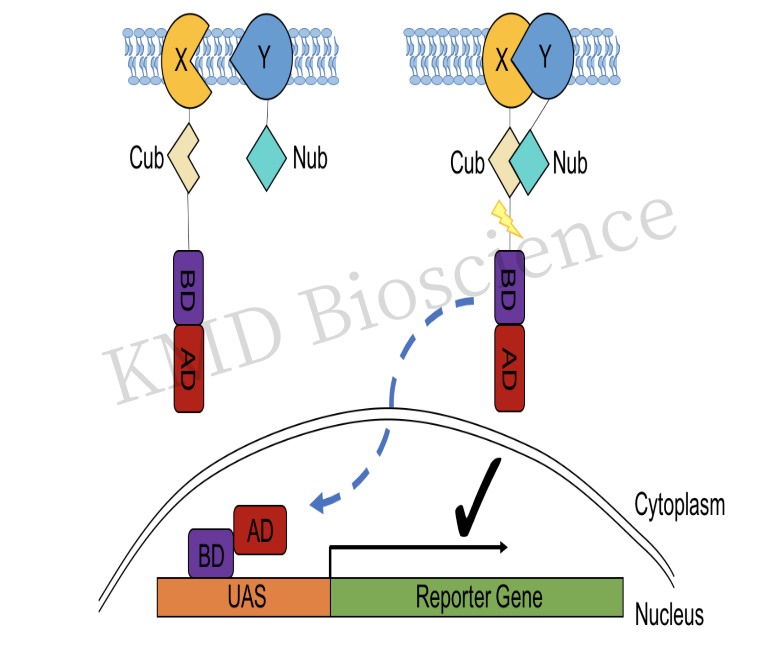
Figure 5 Schematic diagram of the principle of split ubiquitin Y2H
--One-stop service: from yeast display library construction to screening of positive clones, which improves efficiency, avoids errors, and results in objective cost savings for our clients.
Service Content:
--The decoy target gene was inserted into the Y2H vector and then sequenced; it can be either a segmented gene (digested) or a full-length gene
--Test the autoactive capacity and toxicity of decoy genes
--Screening and cross-validation of library materials
--Isolated and extracted positive clones and sequenced DNA
--It is recommended to have at least 2 g of plasmid (with a decoy target gene)
--The gene's DNA sequence so we can design a synthetic protocol to synthesize it (charges apply)
--Several positive clones and DNA sequencing results
--Not less than 2 μg of plasmid per positive clone
--Experimental period: about 6-8 weeks
--Technical experts offer direct service to meet the needs of different testing needs
--Accurate and reliable results can be achieved through the use of highly accurate analytical instruments, experienced operators, and strict quality control
--Highly effective detection and real-time monitoring of the detection process
--Increased detection sensitivity and decreased sample consumption
--Customers' waiting time can be reduced by a shorter experimental cycle
--A real one-stop shop: from building the library to screening positive clones, which improves efficiency, prevents errors and saves customers money
How to Order?
If you have any questions regarding our services or products, please feel free to contact us by E-mail: [email protected] or Tel: +86-022-8216-4980;