Service Line:+86-022-82164980
Address:FL-4, Building A5, International Enterprise Community, Tianjin, China
Email:[email protected]
KMD Bioscience, with years of research experience in antibody discovery, focuses on providing customers with efficient, highly specific, and affinity nucleic acid aptamer in vitro screening services. Based on customers' specific screening targets, we tailor aptamer selex screening solutions and quickly and accurately screen aptamers for the target. KMD Bioscience can provide aptamer selex screening services based on multiple sample types (including proteins, peptides, amino acids, small molecule substances, cells and bacteria, metal ions, etc.), and the services provided to customers cover the upstream and downstream of aptamer selex screening, from gene analysis and synthesis, nucleic acid aptamer sequence design, aptamer in vitro screening, aptamer synthesis, to affinity determination. KMD Bioscience can arrange experiments at every stage according to customer needs. For some metal ions with simple structures and single binding sites, KMD Bioscience uses affinity chromatography SELEX and graphene oxide SELEX screening techniques, carefully planned by a team of scientists to meet the diverse needs of customers.
The nucleic acid aptamer services provided by KMD Bioscience for various types of samples are based on the SELEX screening technology of the SELEX library to screen and obtain corresponding DNA or RNA sequences. Multiple screening methods (including but not limited to cell-SELEX, magnetic bead SELEX, affinity chromatography SELEX, capture SELEX, etc.) are used to meet the screening requirements of different samples. At the same time, KMD Bioscience's selex library has a capacity of up to 10^13-10^14. After 6-10 rounds of screening and enrichment, it can ensure the acquisition of aptamers targeting the target substance (with binding affinity at the nM pM level), which has greater advantages compared to conventional aptamer screening. The research team of KMD Bioscience lays a solid foundation for the subsequent functional validation of aptamers for customers, including but not limited to affinity validation, competitive ELISA validation, in vitro targeted cell functional validation (such as in vitro recognition and inhibition of nucleic acid aptamers, in vitro flow cytometry blocking function, etc.), and in vivo functional validation (such as in vivo targeted inhibition function validation of aptamers, signal pathway blocking function validation, etc.), providing support for customers' subsequent research work on targeted molecular drug development.
Metal Ion Nucleic Acid Aptamer Screening Service
Due to its high specificity, strong affinity, excellent stability, and ease of preparation and labeling, the screening techniques for aptamers in fields such as cells, fungi, proteins, and small molecules have become increasingly sophisticated. Due to the small molecular weight and single binding site of metal ions, screening methods need to be specially designed. Current research mainly focuses on heavy metal ion aptamers, such as Pb2+, Cd2+, and Hg+. KMD Bioscience provides metal ion nucleic acid aptamer screening services through affinity chromatography SELEX and graphene oxide SELEX, based on the selenium library screening technology.
When conducting metal ion adaptation screening, there are certain requirements for the sample, and the metal ion sample should have high purity to reduce the interference of impurities in the screening process. The concentration of metal ions should be moderate, neither too high nor too low, to ensure effective binding during the screening process. Metal ion samples should be kept stable to avoid chemical changes or degradation during the screening process. Relatively speaking, selex library should have sufficient sequence diversity to cover possible adapter sequences. The length of oligonucleotide sequences should be moderate to form stable structures and effectively bind with metal ions. The metal ion sample and oligonucleotide library are mixed together and incubated in a specific buffer system and suitable temperature to allow the metal ions to fully bind to the random nucleotides in the library. During the screening process, temperature, pH value, ion strength, and other conditions should be strictly controlled to ensure the accuracy and reproducibility of the screening. After multiple rounds of screening, the final enriched oligonucleotide library needs to undergo high-throughput sequencing analysis to determine the optimal adapter sequence through bioinformatics analysis, and further optimization and validation. Therefore, the sample requirements for screening metal ion nucleic acid aptamers involve the purity, concentration, and stability of metal ion samples, and strict control of screening conditions is necessary to optimize the final results.
SELEX screening technology covers four key steps: binding, separation, amplification, and purification. By repeatedly executing these steps, oligonucleotides with high specificity for the target are accurately identified from the library and sequenced to obtain sequence information. The different designs of nucleic acid aptamer sequences can shape different three-dimensional structures and exhibit affinity for specific metal ions. The chemical properties of metal ions, such as hardness and coordination structure, may affect screening, but their single binding site and similar structures among different metal ions can interfere with the specific recognition of metal ions in the same group by aptamers. Conventional SELEX methods may be difficult to separate highly specific aptamers. KMD Bioscience uses affinity chromatography to immobilize the aptamer library on a solid substrate, enabling the screening of aptamers targeting metal ions. Agar or resin is filled into the chromatography column as a solid matrix, and the library is fixed on the solid matrix under the action of streptavidin biotin. Injecting heavy metal ions into affinity chromatography columns for incubation, some specific nucleic acid sequences have high attraction to the target. Through multiple rounds of screening, high affinity aptamers are obtained. Affinity chromatography SELEX is also widely used for aptamer screening against various heavy metal ions. The process of KMD Bioscience is shown in Figure 1.
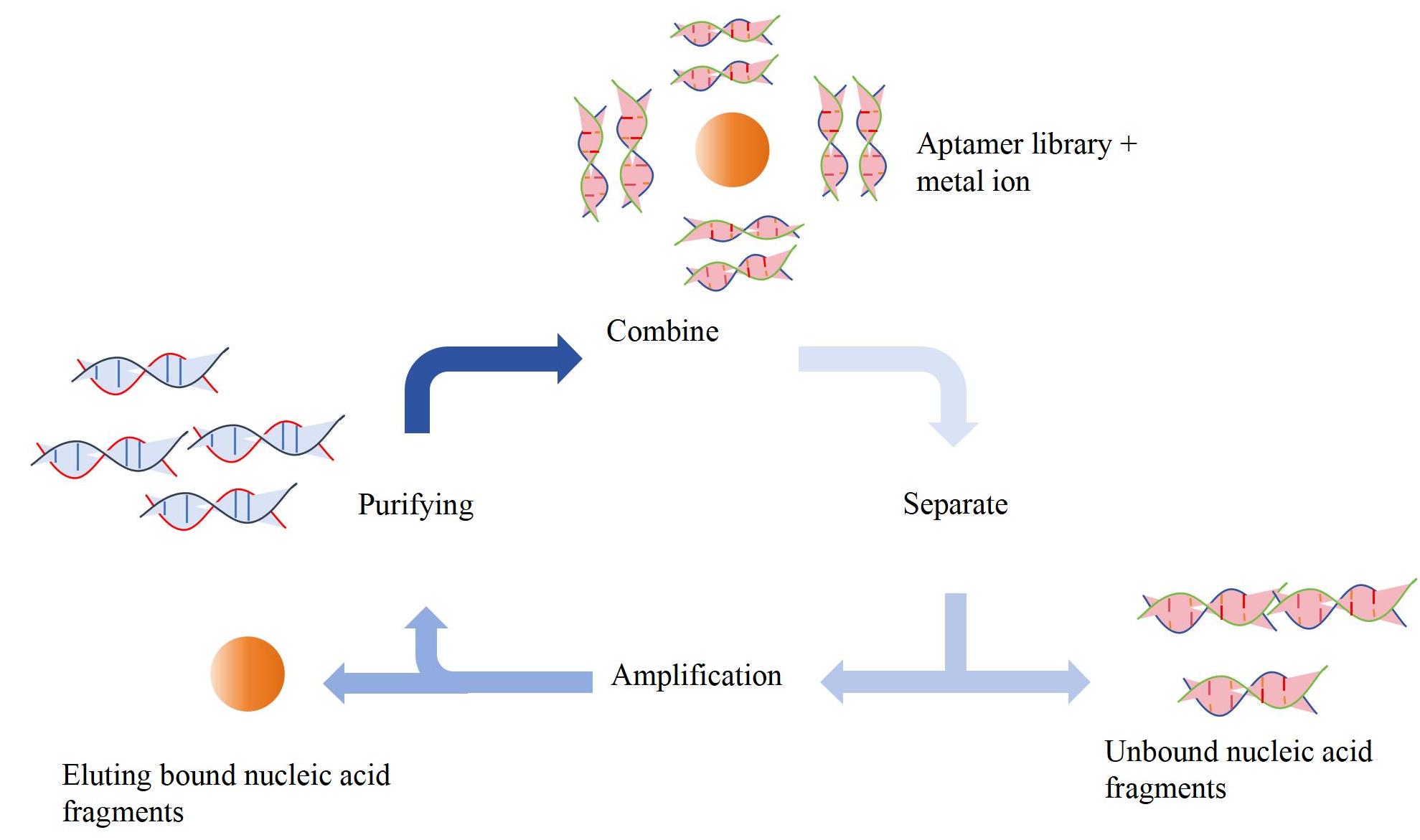
Figure 1 Service process for screening metal ion nucleic acid aptamers
Metal Ion Nucleic Acid Aptamer Screening Service Workflow
|
Step |
Service Content |
Timeline |
|
Step 1: Screening of nucleic acid aptamers |
(1) Customer provides screening targets. (2) The adapter library is fixed on an affinity chromatography column and incubated with metal ions injected into the column. (3) Adaptation library screening and enrichment: PCR amplification enrichment+transcription+gel running recovery, usually 6-10 rounds. (4) Screening products for NGS sequencing. (5) Delivery: 5-15 adapter sequences, experimental report, raw data (including NGS sequencing raw data and gel electrophoresis) |
10-15 weeks |
|
Step2:Synthesis of aptamers and determination of affinity (optional) |
(1) Synthesize aptamers based on sequences. (2) Affinity determination of adapter and target protein, KD determination by BLI or SPR. (3) Delivery: Experimental report, raw data |
4-5 weeks |
Advantages of Metal Ion Nucleic Acid Aptamer Screening Service
FAQ-Metal Ion Nucleic Acid Aptamer
1. What is metal ion aptamer screening?
A: The aptamer is a small nucleic acid folded in a three-dimensional conformation to make the aptamer a specific binding target. The target has a variety of species, either proteins small molecules, or metal ions. In contrast to antibodies, aptamers enable in vitro selection with low immunogenicity. Among them, heavy metal, as the most toxic metal pollutant, can pollute the natural environment, and detecting heavy metal pollution has become an important task. At the same time, heavy metals are also classified as trace elements because of their low content. Therefore, developing an accurate and sensitive heavy metal detection method is very important to ensure human and environmental safety. Aptamers as biological probes show high binding affinity that can be directly converted to high detection sensitivity. On the other hand, high selectivity and stability enable it to detect various targets, especially metal ions. Since identifying aptamers for metal ions, aptamer-based sensors and detection methods have become possible and provide new methods for detecting metal ions, including electrochemical, colorimetric, and fluorometry. KMD Bioscience has been studying in the field of nucleic aptamers for a long time, which can provide customers with metal ion aptamers with excellent performance to help customers better research follow-up projects.
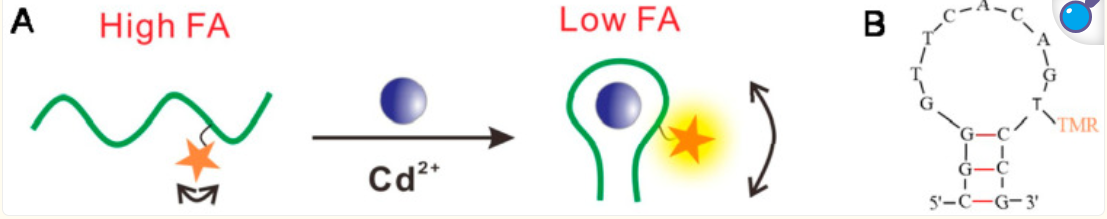
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of fluorescence anisotropy sensor for Cd2+ using TMR-labeled aptamers. (Reference documentation: Yu H, Zhao Q. A Sensitive Aptamer Fluorescence Anisotropy Sensor for Cd2+ Using Affinity-Enhanced Aptamers with Phosphorothioate Modification. Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Oct 17;12(10):887. )
2. What are the applications of metal ion aptamers? What are its advantages?
A: Long-term exposure to toxic heavy metals may also cause cancer in both humans and animals. Therefore, the monitoring of toxic metal ions is an important issue in environmental protection as well as in disease prevention and treatment. However, the high selectivity and sensitivity detection of trace heavy metals remains a challenging area of research. Capapping of target ions from the complex matrix is a key step in detecting heavy metals. So far, researchers have designed several DNA aptamers to identify and detect heavy metal ions, mainly lead, mercury, silver, and so on. These ions can specifically interact with DNA bases to form strong and stable complexes, and some aptamer-based sensors can be used to monitor the concentration of heavy metal ions in water, providing strong support for the early warning and treatment of environmental pollution. In addition, metal ion aptamers can also be used in analytical chemistry, food science, and other fields. In analytical chemistry, aptamers can be used as efficient isolation and enrichment materials for the extraction and purification of metal ions in complex samples. In food science, aptamers can be used to detect heavy metal ion residues in food, which can ensure food safety. As novel recognition elements in biosensors, aptamers outperformed antibodies in terms of low cost, good thermal stability, simple production, ease of modification with functional groups, and conformational changes induced by binding.
3. What are the common methods used in metal ion aptamer screening? What problems do you have? How to solve it?
A: The Capture-SELEX method is often used to screen metal-ion nucleic aptamers. The Capture-SELEX method uses the strong binding force between biotin and avidin, labels the DNA chain in the library using biotin, and then uses the library with avidin, where the ssDNA library is fixed on the magnetic beads. Then, using the fixed library bound to the target, we eluted the magnetic bead library bound to the target and performed PCR amplification to obtain a certain number of secondary libraries. After the whole screening process is completed, we may find that the aptamer affinity does not meet the expected requirements, or the aptamer is not specific enough. In the above situation, we can reduce the non-specificity and improve the affinity by changing the library buffer conditions during the screening process. At the same time, using Capture-SELEX can have higher affinity than using other methods to cure the target, and ePCR can be amplified to avoid the lack of library diversity. KMD Bioscience can improve the efficiency of aptamer screening through the above techniques, but also by optimizing the experimental conditions, to better obtain aptamers. In addition to providing cell nucleic aptamer screening services, it can also provide protein customization and phage display services.
4. What are the common metal aptamers? What is the solution?
A: In the synthesis of metal ion aptamers, we will encounter errors in library design and synthesis or insufficient library diversity. The nucleic aptamer library is up to 10^10-10^14, and the number of random sequences in the library is enough to cover all possible aptamer sequences. Meanwhile, strict quality control, including sequencing verification, was performed to ensure the accuracy of the library. Too low target concentration may lead to the screening of high-affinity aptamers, while too high concentrations may increase non-specific binding. At the same time, KMD Bioscience also optimized the experiment according to the properties of the target to determine the appropriate target concentration, pH value of buffer, and ionic strength and these parameters will affect the binding of the aptamer and the target. The researchers determined the appropriate screening temperature based on the thermal stability of the target and the melting temperature of the aptamer. Negative screening through blank magnetic beads, removal, and nonspecific binding of magnetic beads. Primer dimers and non-specific amplification may occur during PCR amplification. We optimized the PCR amplification conditions, adjusted the primer concentration, and annealing temperature, and used high-quality primers and enzymes for amplification. Finally, KMD Bioscience can provide professional technicians to molecularly perform the sequencing data to ensure the accuracy of the final results.
5. What is the mechanism of the binding of the various metal ions and the aptamers?
A: The recognition of copper ions and aptamers is a process that requires highly regulated aspects, and this recognition process requires the ability of DNA to assist. There are now two possible accounts for the mechanism by which copper ions bind to aptamers, a sandwich where copper ions and 2 adjacent G form a sandwich structure and G and T binding on copper ions and different nucleotide chains. Some researchers have also found that platinum can bind to nucleotides on G and T, which can improve the stability of nucleotide DNA and prevent DNA from continuing replication, transcription, and cell division. Regarding mercury and silver ions, researchers have proposed that they interact with aptamers and lead to structural degeneration. However, the mechanism of metal ions potassium, sodium, and aptamer is related to the four-chain structure. The G-teplex is stable in the presence of monovalent cations (K +, Na +, NH4 +, etc.) because these positive ions coordinate with the negative oxygen atoms in the base to stabilize the G-teplex (G-quadraplex). The binding mechanism of metal ions to aptamers is a complex process involving a variety of interacting forces and factors. This combination has broad applications in biomedicine, materials science, and other fields.
How to Order?
If you have any questions regarding our services or products, please feel free to contact us by E-mail: [email protected] or Tel: +86-400-621-6806