Service Line:+86-022-82164980
Address:FL-4, Building A5, International Enterprise Community, Tianjin, China
Email:[email protected]
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a common respiratory virus, also known as fusion virus, belonging to the genus Pneumovirus in the family Paramyxoviridae. The size of virus particles is about 150nm, slightly smaller than parainfluenza virus, sensitive to ether, no hemagglutination, in human epithelial tissue culture to form a unique syncytium (syncytium), the virus in the cytoplasm of the proliferation of intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies can be seen. There is only one serotype of syncytial virus, and two subtypes have recently been demonstrated by molecular biology methods.RSV infection is the primary cause of viral respiratory infections in infants and young children, posing a serious health risk to children and most likely to involve the respiratory system, with the main mechanisms being airway obstruction, bronchial smooth muscle spasm, and subsequent airway hyperreactivity.The predominant viral strains of RSV mutate annually, making it easy to be infected again and again; it is highly contagious, mainly through the nasopharynx or the eye. Transmission occurs mainly through contact with virus-containing secretions or contaminants in the nasopharyngeal or ocular mucosa. Direct contact is the most common mode of transmission, but droplets and aerosols can also cause transmission, and it is not vaccine-preventable.
KMD Bioscience is a company dedicated to providing high-quality biologically active raw materials such as antigens, antibodies, enzymes and substrates, as well as related technical services. KMD Bioscience has a series of technical platforms for protein recombination, antibody production, purification and diagnostic reagent R&D and production (including immunochromatography, enzyme immunoassay and chemiluminescence); and a group of highly qualified in vitro diagnostic upstream and downstream technicians with rich experience, which provides a guarantee for the company's research and development, and production of high-quality raw materials for in vitro diagnostic reagents and related technologies.
The inventory of reagents associated with Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) that KMD Bioscience can offer:
|
CAT# |
Product Name |
Species |
Host |
Application |
Size |
Inquiry |
|
VAG362 |
Virus |
Vero cell |
ELISA |
1ml |
Inquiry |
|
|
VAG353 |
RSV |
Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
|
20ug, 100ug |
Inquiry |
|
|
VAG354 |
RSV |
Baculovirus-Insect cells |
|
20ug, 100ug |
Inquiry |
|
|
VAG355 |
RSV |
HEK293 Cells |
|
20ug, 100ug |
Inquiry |
|
|
VAG361 |
RSV |
HEK293 Cells |
|
20ug, 100ug |
Inquiry |
|
|
VAG356 |
RSV |
HEK293 Cells |
|
10ug, 20ug |
Inquiry |
|
|
VAG359 |
RSV |
Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
|
20ug, 100ug |
Inquiry |
|
|
VAG343 |
HRSV |
HEK293 Cells |
|
|
Inquiry |
Structure of RSV Virus
RSV is a single negative-stranded RNA virus of the genus Pneumovirus in the family Paramyxoviridae. The genome is 15.2 kb in length and encodes 11 proteins. The RSV genome is 15-16 kb in size and encodes 11 proteins, including 8 structural proteins and 3 nonstructural proteins (NS1, NS2, and M2-2). The structural proteins include 3 transmembrane surface proteins (G, F, and SH), 2 matrix proteins (M and M2-1), and 3 nucleosome proteins (L, N, and P). [G proteins mediate the binding of viruses to host cells, and F proteins mediate the fusion of viral and host cell membranes to allow viral entry into the cell, both of which are essential for viral replication, and both of which contain B-cell and T-cell epitopes, and are the most important viral antigenic proteins for stimulating the body to generate humoral and cellular immunity.The G proteins are highly variable, and their corresponding cellular receptors are not well defined, and are closely related to the cluster of antigenic epitope determinants and the diversity of viral genes. The G protein is highly variable and its corresponding cellular receptor is not well defined, and it is closely related to the antigenic epitope determinants and viral genetic diversity.
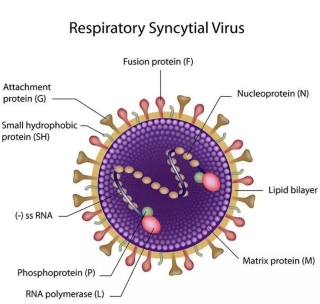
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of the molecular structure of RSV
Mechanism of RSV infection
RSV is an enveloped virus that infects the human airway. The pathogenesis is complex and involves host immune response, pathogens, and environmental factors, and it is most likely to affect the respiratory system, with the main mechanisms being airway obstruction, bronchial smooth muscle spasm, and subsequent airway hyperresponsiveness. It primarily targets ciliated bronchial epithelial cells. An intracellular receptor called nucleolin (NCL) plays a role in facilitating the entry of RSV into the cell.RSV binds itself to the receptor and enters the cell.RSV does this by binding to insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1R) and protein kinase C zeta (PKCζ), using both to generate a signal, or "doorbell", to bring nucleolin into the cell.RSV is also known to bind to insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1R) and protein kinase C zeta (PKCζ), using both to generate a signal, or "doorbell", to bring nucleolin into the cell. " that calls the nucleolin to the surface of the cell where the virus is located. Once the riboprobes reach the "designated" location (the doorway), RSV binds to them, enters and infects the cell.
KMD Bioscience's current portfolio of diagnostically active ingredients covers infectious diseases, oncology, inflammation, metabolism, hormones and more. KMD Bioscience can provide a wide range of bioactive materials and technical services for IVDs, and has served a wide range of domestic and foreign manufacturers of related reagents. These include, but are not limited to, customized development of antigens and antibodies, antigen-antibody labeling and coupling, antibody pair screening and purification, immunochromatography, enzyme immunoassay and chemiluminescence system optimization and process debugging, and many other technologies.