Service Line:+86-022-82164980
Address:FL-4, Building A5, International Enterprise Community, Tianjin, China
Email:[email protected]
KMD Bioscience has rich experience in the field of antibody production, with a comprehensive antibody production system and a one-stop antibody development technology platform. It can provide comprehensive services, including bispecific antibody, neutralizing antibody development, antibody humanization, biosimilar antibody development, ADC development, and other diversified types. KMD Bioscience also offers complete upstream and downstream supporting services from immunogen preparation to the development of various biosimilar antibody and monoclonal antibodies. KMD Bioscience's standard production line can provide customers with neutralizing monoclonal antibody development services and neutralizing polyclonal antibody preparation services for viral antigens, including antibody humanization, affinity optimization, ADC design and development, CAR-T subsequent sequence design, etc. Based on strict quality control, high-quality neutralizing antibodies can be obtained. In addition, KMD Bioscience uses various techniques such as single B cell technology, phage display technology, and antibody humanization strategy to provide neutralizing antibody production services.
KMD Bioscience excels in utilizing phage display technology to facilitate the display of fusion proteins on phage surfaces, providing a variety of animal sources (rabbits, mice, sheep, chickens, etc.) based on specific customer needs. Based on flow cytometry sorting technology, KMD Bioscience can amplify the required antibody genes from single B cells. With the help of single B cell technology, positive B cells can be directly isolated from the peripheral blood of immunized animals and their antibody genes can be cloned. KMD Bioscience builds antibody libraries based on multiple phage display technology platforms, with a storage capacity of up to 10^8-10^9. It can quickly obtain neutralizing antibodies that customers need, and uses EC50 validation, BLI/SPR validation, antibody validation, and other methods to ensure reliable results, saving customers time and reducing the cost of neutralizing antibody development experiments.
Neutralization Monoclonal Antibody Development Service
When pathogens such as viruses invade the body, B lymphocytes produce neutralizing antibodies that can specifically recognize and bind to viral surface antigens, effectively preventing the virus from binding to host cell receptors and thus blocking virus replication. Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies have high specificity and targeting. Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies can specifically bind to specific antigens on the surface of viruses or cells. This specific binding enables the antibody to accurately recognize the target antigen, reducing the probability of damage to non target cells or tissues caused by the antibody. Based on the high targeting ability of neutralizing monoclonal antibodies, it can directly target pathogens or diseased cells, reducing side effects. Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies directly neutralize viral particles, preventing the virus from entering cells and replicating, effectively inhibiting the spread and infection of the virus, and possessing high efficiency and efficacy. At present, the production technology of neutralizing monoclonal antibodies is relatively mature, which can achieve large-scale production and purification. Neutralizing antibody test is an experimental method used to detect antibody function, aimed at evaluating whether antibodies can prevent pathogens from infecting cells. The neutralizing antibody test is based on the principle of antibody neutralization, which refers to the ability of antibodies to bind to pathogens and prevent them from infecting cells. In neutralizing antibody test, the antibody is mixed with the pathogen to bind to the antigen on the surface of the pathogen. Then, the mixture is co cultured with host cells to observe whether the pathogen undergoes antibody neutralization, in order to evaluate the ability of antibody neutralization. In viral infectious diseases, neutralizing monoclonal antibodies can specifically neutralize the virus and prevent it from entering cells for proliferation. Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies can also be used as a short-term preventive measure for high-risk populations, by injecting antibodies to rapidly increase antibody levels in the body, thereby enhancing resistance to viruses. For example, the subcutaneous injection of REGN-COV was studied to prevent COVID-19 infection, and the results showed that it could significantly reduce the risk of symptomatic infection. In clinical diagnosis, monoclonal antibodies are also used for virus detection, disease diagnosis, and other aspects to improve the accuracy and sensitivity of diagnosis. In scientific research, neutralizing monoclonal antibodies are commonly used for studying viral epitopes and the interaction between viruses and host cells, providing a theoretical basis for virus prevention, control, and treatment. Through large-scale production, the production cost of antibodies can be reduced. The neutralizing monoclonal antibodies prepared by KMD Bioscience have strong specificity and almost no cross reactions. By optimizing the antibody production process, KMD Bioscience can quickly deliver high-quality neutralizing monoclonal antibodies and use phage display technology to construct phage antibody display libraries of different species for customers. The process of preparing neutralizing monoclonal antibodies by KMD Bioscience is shown in Figure 1.
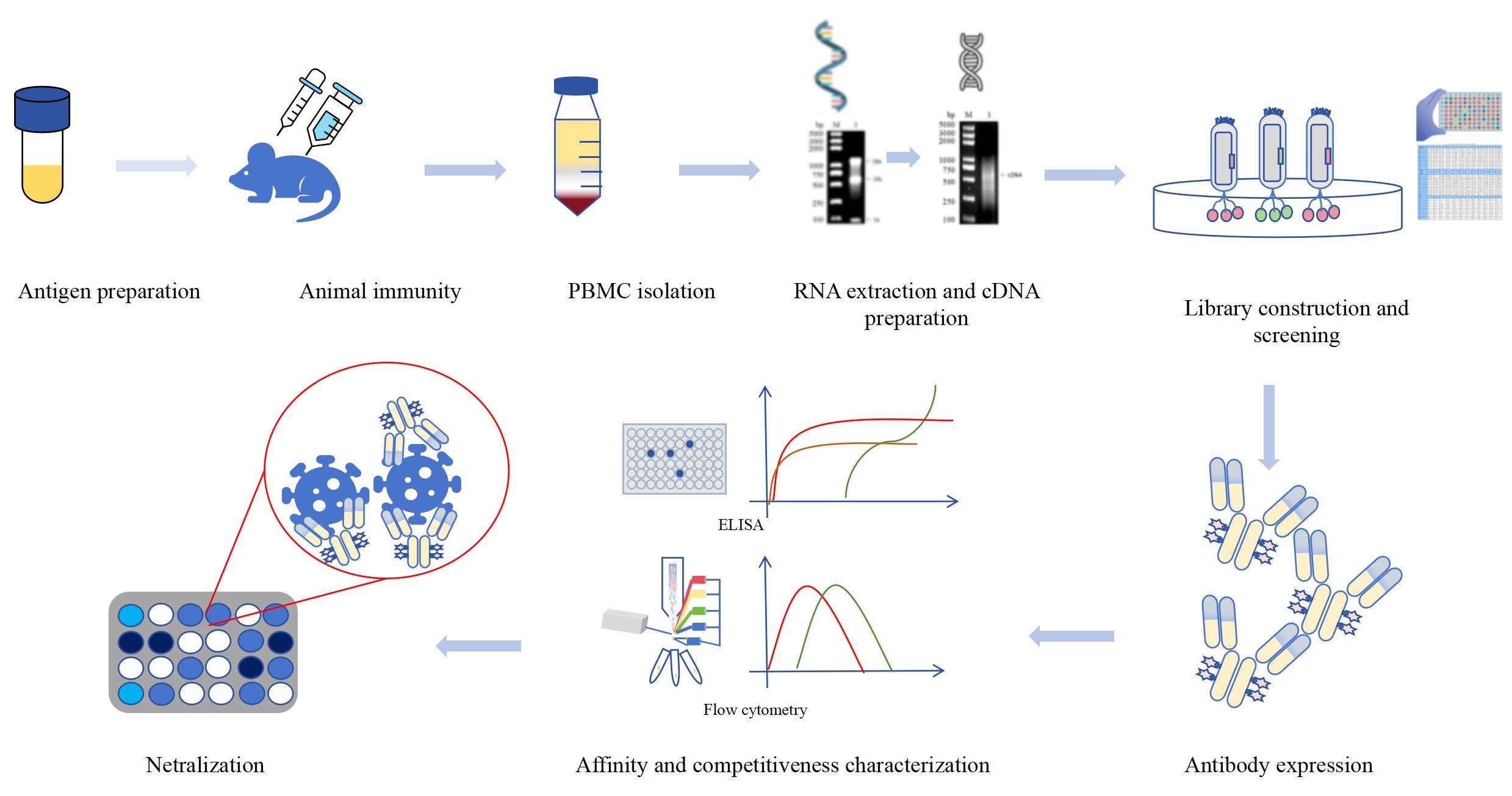
Figure 1 Development process of neutralizing monoclonal antibodies based on phage display technology
Neutralization Monoclonal Antibody Development Service Workflow
|
Step |
Service Content |
Timeline |
|
Step 1: Animal immunity |
(1) The animal was immunized 4 times, with one booster shot, for a total of 5 doses. (2) Negative serum before immunization was collected, and ELISA was performed on the fourth dose to detect serum titer. (3) If the fourth dose of serum antibody titer meets the requirements, booster immunization will be administered again 7 days before blood collection. If it does not meet the requirements, routine immunization will continue. (4) Qualified potency, blood collection and separation of monocytes. |
10 weeks |
|
Step 2: cDNA preparation |
(1) PBMC Total RNA Extraction (RNA Extraction Kit). (2) High fidelity RT-PCR preparation of cDNA (reverse transcription kit). |
1 day |
|
Step 3: Construction of neutralizing monoclonal antibody library |
Based on phage display technology: (1) Using cDNA as a template, amplify antibody genes using two rounds of PCR. (2) Phage construction and transformation: gene splicing phagemid vector, electroporation transformation of TG1 host bacteria, construction of antibody library. (3) Identification: 24 clones were randomly selected, and PCR identification showed a positive rate and insertion rate. (4) Assisted phage preparation: phage amplification+purification (5) Antibody display library rescue. |
3-4 weeks |
|
Step 4: Antibody library screening (3 rounds) |
Based on phage display technology: (1) Three rounds of screening are performed by default (solid-phase screening): pressure screening to remove non-specific antibodies to the maximum extent possible. (2) Single clone selected for phage amplification, IPTG induced expression, and ELISA detection of positive clones. (3) All positive clones were selected for gene sequencing. |
4-5 weeks |
| Step 5: Antibody validation |
ELISA to verify antibody binding to antigen (delivery of EC50 data).
Function verification: flow cytometry verification |
2-3 days |
| Step 6: Antibody neutralization | Delivery of neutralizing antibodies | 2-3 weeks |
Advantages of Neutralization Monoclonal Antibody Development Service
FAQ-Neutralization Monoclonal Antibody Development
1. What are the neutralizing antibodies?
A: When the foreign body enters the organism, the immune system will work quickly, produce corresponding antibodies, and the foreign body combined to protect the body from the interference of the foreign body. The neutralizing antibody is the antigen produced when the foreign body invades the surface of the foreign body and prevents the receptor of the foreign virus from recognizing the body, thus blocking the way for the virus to enter the cells. Some scientists call the antibodies that can bind to a particular protein and interfere with its function as neutralizing antibodies. When the pathogen invades the body, it needs to be identified by the specific structure of the pathogen itself and the ligand on the body, so the pathogen can infect the body and cause body disease. Neutralizing antibodies are water-soluble proteins produced by their cells as the body adapts to the occurrence of immunity. When the pathogenic pathogen invades the body, the immune cells of the body are stimulated, the neutralizing protein is secreted, and then the neutralizing antibody is transported to all parts of the body through blood transport, so that it combines with the pathogen, preventing the combination of the virus and the body, and neutralization the virus.
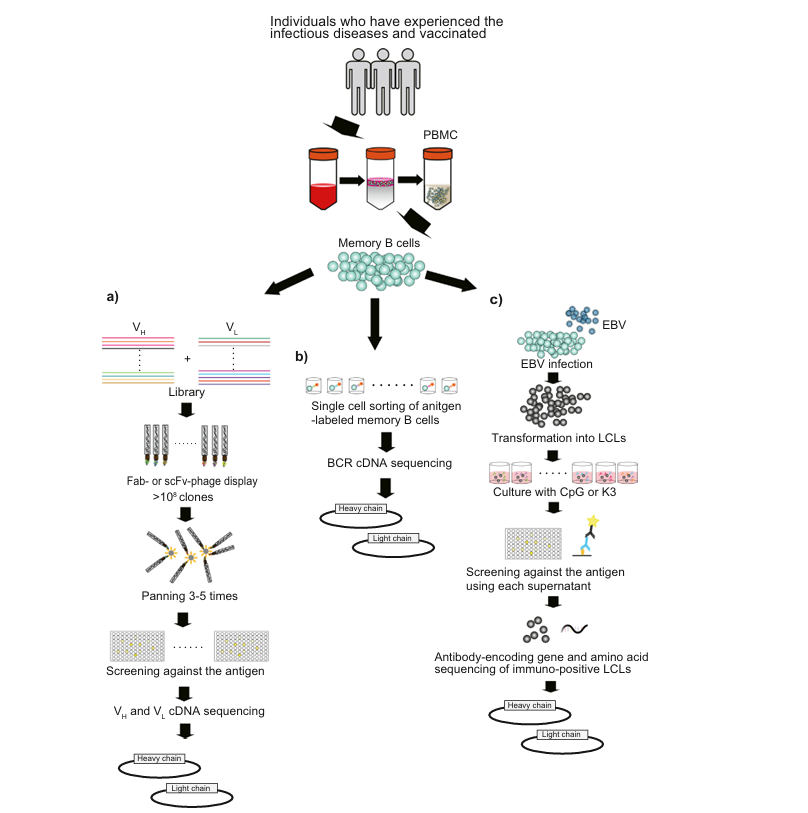
Figure 2: Production of neutralizing monoclonal antibodies. (Reference documentation: Otsubo R, Yasui T. Monoclonal antibody therapeutics for infectious diseases: Beyond normal human immunoglobulin. Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Dec;240:108233. )
2. In the neutralizing monoclonal antibody development service, we may have no or low potential after immunization animals. How can we solve it?
A: In neutralizing monoclonal antibody development services, select not carry pathogens, healthy animals as immunogens, but we may choose antigen molecular weight size is not suitable or antigen immunogenicity is inappropriate, resulting in animal immunization Elisa detection no titer or titer reach the desired target, at the same time the choice of immune adjuvant, different immunization procedures, immunization dose and immunogen is oral or intramuscular or subcutaneous injection of injection will also affect our serum neutralizing antibody titer. If we encounter a similar situation mentioned above, we can first optimize our antigens. If the antigen is a small molecule, we can couple it and the macromolecule to increase the immunogenicity of our antigen and ensure that the molecular weight of our antigen is not less than 25 kDa. At the same time, we can also change different immune adjuvants. In addition to the frequent Freund's complete and incomplete adjuvants, we can also use other new adjuvants to try to increase immunogenicity. At the same time, our immunization program should be redesigned according to the different immunogens and adjuvants, and should not be uniform. If the titer has not reached the expected target after three immunizations, we can strengthen the immunization to improve the titer. At the same time, we can take multi-point back injections, peritoneal injections, intramuscular injections, and other site immunizations to improve the antibody titer. We can prepare neutralizing antibodies with high potency, strong specificity, and stability.
3. What makes neutralizing antibodies work?
A: Neutralizing antibodies are methods that prevent receptors on the surface of pathogens from recognizing and then entering the cells to prevent pathogens from invading the body. When the virus is coated, the neutralizing antibodies can prevent the virus from attaching to the cells and entering the cells. When the virus is uncoated, neutralizing antibodies can bind to the viral capsid protein, which is the protein shell of the virus and can protect the genetic material of the virus. Neutralizing antibodies can also change the structure and shape of the pathogen, and then prevent the virus from entering the cells to replicate and infect the body. In microbial infections, neutralizing antibodies can quickly eliminate the effects of toxin production. Once the virus and neutralizing antibodies combine, the pathogen is engulfed by leukocytes, and the spleen of the body can automatically filter the pathogen, making the pathogen's metabolites excreted through the urinary system. Neutralizing antibodies are generally through passive immunity to complete the body's disease treatment.
4. In the neutralizing monoclonal antibody development service, how do we solve the situation that no hybridoma cells and cells do not grow after cell fusion?
A: The most important step in the preparation service of neutralizing monoclonal antibodies is to complete the fusion of SP20 cells and spleen cells, which produce hybridoma cells that consistently produce neutralizing antibodies. After the fusion of SP20 cells and spleen cells, we may encounter after fusion hybridoma cells that do not grow or are long, the reason may be that the medium and serum we used when growing the hybridoma cells are not suitable for growth, or we used the fusion reagent PEG fusion quality is not good or the concentration is not enough, resulting in the cells without successful fusion. The choice of the simultaneous preparation of monoclonal antibody mouse strains is also one of the key factors, and our added inappropriate timing and concentration of HAT and HT in hybridoma cell growth also leads to fusion failure. For the above reasons, how can we solve the fusion after hybridoma cells do not grow or very few, KMD Bioscience chooses suitable medium and serum, chooses quality assurance PEG and neutralization antibodies has rich experience, and can help customers better complete the preparation of neutralizing antibody, KMD Bioscience choose pure strains of balb/c mice as immune animals, choose the appropriate HAT and HT concentration, promote the growth of hybridoma cells. At the same time, KMD Bioscience has its biological cells.
5. In the neutralizing monoclonal antibody development service, how to screen and identify the antibodies, and how to make the antibodies purified simultaneously?
A: In neutralizing monoclonal antibody development services, cell fusion grows to the bottom of the hole, we detect the fusion hybridoma cell supernatant Elisa, then select a positive clone hole to continue to subclone but may appear after fusion detection, not positive clones or are positive clones. At this time, we can first think about whether there is any error in our Elisa steps, set the PBS, negative control, and positive control group to determine that there is no error in our experimental operation, and then we can add a blank medium to test whether the serum affects our experimental results. Finally, if the hybridoma cells are too small and insufficient antibodies may lead to insufficient potency, we can wait for the fusion cells to grow again for some time. Depending on the origin and the mAb preparation methods, the mAb samples were classified into different types, such as ascites, hybridoma supernatant, etc. Samples obtained by injection of hybridoma cells into the abdominal cavity of animals are called ascites samples, and the concentration of monoclonal antibodies accumulated in ascites is usually high and is suitable for large-scale antibody production and purification. The methods of antibody purification included Protein A / G purification, ion exchange chromatography, gel filtration, precipitation, and hydrophobic cation chromatography.
How to Order?
If you have any questions regarding our services or products, please feel free to contact us by E-mail: [email protected] or Tel: +86-400-621-6806